Chapter:
Terms: valence band, conduction band, valence electrons, and energy gap
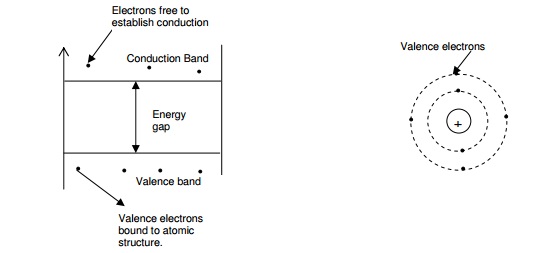
Valence Electrons: The
electrons in the outermost orbit are called valence electrons, since these
electrons are fixed in the outer orbit with the neighbouring atom in a crystal.
These electrons being far away from the nucleus possess the least binding
energy and are easily affected by external influences. A very little energy is
required to free them from their parent atoms. When the valence electrons of an
atom are less than four, the material is usually a metal or a conductor. When
the number of electrons in the outermost orbit is more than four, the material
is usually an insulator. When the number of valence electrons in an atom is
exactly four, the material is a semi-conductor.
Conduction Band: It
represents a larger group of permissible energy levels. The orbits in the conduction
band are very large and an electron in this band experiences almost negligible
nucleus attraction. In fact an electron in the conduction band does not belong
to any particular atom and it moves randomly throughout the solid. So these
electrons in the conduction band are called free electrons. If any material has
empty conduction band, no conduction band is possible.
Valence Band: It represents the range of
energies possessed by the valence electrons, that is the electrons
in the outermost orbit. This band has the electrons having the highest energy
and it can be partially or completely filled. When this band is filled, it
means that the electrons occupy all permissible energy levels in the band and
no electrons can move in a filled band. Thus an electron in a completely filled
band cannot contribute to electric current. The partially filled band can
accommodate more electrons.
Energy
Gap: The minimum amount
of energy that is required to lift an electron from a valence band
to the conduction band is called energy gap, and is represented by the
separation between these two bands, i.e., valence and conduction bands. This
gap is also called forbidden energy gap. It also indicates the bondage of
valence electrons to the atom. This means if the energy gap is more, then the
valence electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus. This energy gap determines
the conductivity of a material.
Related Topics