Chapter:
Superconductors

- The resistivity of most
metals increases with increase in temperature and vice-versa. There
are some metals and chemical compounds whose resistivity becomes zero when
their temperature is brought near 00Kelvin (-2730C). At
this stage such metals or compounds are said to have attained
superconductivity. Example - mercury becomes superconducting at approximately
4.5 Kelvin (-268.50C). Superconductivity was discovered by Heike
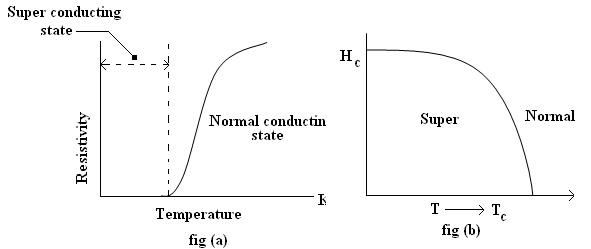
Kamerlingh Onnes. The transition from normal conductivity to superconductivity
takes place almost suddenly; it occurs over a very narrow range of temperature
about 0.050K. The temperature at which the transition takes place
from the state of normal conductivity to that of superconductivity is called
transition temperature. Superconductors are used for producing very magnetic
fields of about 50 Tesla. Magnetic energy can be stored in large
superconductors and drawn as required to counter the voltage fluctuations
during peak loading. Superconductors can be used to perform logic and storage
functions in computers. As there is no, I2R losses in a
superconductor, so power can be transmitted through the superconducting cables
without any losses. Superconducting property can be destroyed by applying
external magnetic field as in fig (b). In fig (b) HC is the
critical magnetic field and TC critical temperature.
Conductors: Substances like
copper, aluminium, silver which allow the passage of current through
them are conductors. The valence band of these substances overlaps the
conduction band as shown in fig (b). Due to this overlapping, a large number of
free electrons are available for conduction. This is the reason, why a slight
potential difference applied across them causes a heavy flow of current through
them.
Related Topics