Chapter: Diseases of The Brain and Nervous System(A Health Education Guide): Movement Disorders And Dystonia
Neurons & tracts on Movements of the human body
MOVEMENT DISORDERS AND DYSTONIA
The movements of the human body are mostly voluntary and are dependent on three major groups of neurons & tracts, each of which comprises a different system.
i. Pyramidal system.
ii. Para pyramidal system.
iii. Extra pyramidal system.
The first system is the most important of them all. The hindrance in the normal working of this system leads to paralysis, i.e. defect in the neurons causes the organs to stop functioning, gradually leading to spasticity.
1. Pyramidal system arises from the neurons of theposterior portion of the frontal lobe of the brain and the anterior part of the parietal lobe, which form the corona radiata, and passes through the posterior portion of the internal capsule situated between the basal ganglia. [Please see picture: 2 chapter: 1 ]. It then passes below ‘the cerebral peduncle forming the pyramidal tracts. These tracts decussate in the medulla and pass to the contra lateral halves of the spinal cord, as the crossed lateral corticospinal tracts. These end into the cells of the spinal cord, known as anterior horn cells. It is these lower motor neurons that ultimately control the movement of the limbs. The orders from the brain are sent through these lower motor neurons so that the movement of the body is initiated. This entire process is completed in less than a second. Thus the frontal lobe of the brain is the main part of the entire system. Also -along with this there is another part of the brain known as supplementary motor cortex that generates messages before movements. The contribution of this part is also very high. Any damage to the pyramidal system results in paralysis.
2. The Para pyramidal system mainly consists of rubrospinal, tectospinal, reticulospinal, and vestibulo-spinal tracts. Its main function is to influence the pyramidal system in such a way that voluntary movements are conducted in a particular systematic way. Red nucleus, tectum etc. various parts of the brain are associated with it. Any damage to it results in symptoms like imbalance, tremors etc.
3. The diseases we are going to talk in this chapter are called movement disorders. The nuclei or cluster of cells affected in these disorders are chiefly basal ganglia which are situated in the middle of the brain on either side. This system is called extra pyramidal system. We will discuss the diseases known as movement disorders. The neurons present in the middle part of the brain called basal ganglia perform a very important activity and form the extra pyramidal system.
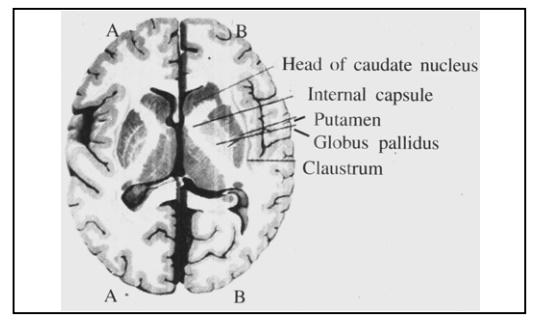
As shown in the picture the system consists of frontal lobe, globuspallidus, putamen, caudate nucleus, claustrum and amygdala etc. This system controls the pyramidal system in its own way. Any fault or cessation of function of this system does not produce paralysis but can create two types of problems which we call as syndromes.
a. Akinetic rigid syndrome (Parkinsonism- which will be discussed in detail in the subsequent chapter) in which there is stiffness of limbs and all functions become slow, there is also trembling in the limbs and all movements becomes slow. This occurs due to the deficiency of a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
b. Hyper kinetic disorders: In short, an excess of dopamine in the brain results in hyper kinetic disorder. Here uncontrolled extra movements like dystonia, chorea, dyskinesia and hemiballismus accompany the voluntary movements.
Related Topics