Chapter: XML and Web Services : Implementing XML In E–Business
Implementing XML In E–Business
B2B:
One of the main sources of customers for
business is other businesses. This is comparably a large market than selling
directly to end users.ƒ This may involve negotiating prices, sales terms,
credit, delivery and product specifications.
B2C
Applications:
Many of the early developments on the Internet
were focused on helping businesses directly sell goods to their customers. This
is Business to Consumer ( B2C ). The Promise of B2C is avoidance of any
middleman Other than increased complexity and potential cost in dealing with
customers on a direct basis using B2C, a company implementation of B2C
techniques faces danger of channel conflict or disintermediation.
Different
types of B2B interaction:
Roles that the parties play in B2B E-Commerce
(4 main types )
ƒ
Buyers
ƒ
Suppliers
ƒ
Market
Places [ third party organization ]
ƒ
Service
Providers [ third party organization ]
ƒ
Forms of
Supply Chain Relationship
ƒ
Direct
Partnership
ƒ
Multi-party
Procurement
ƒ
Agents
and Distributors
ƒ
Exchanges
, Auctions and Digital Transaction Hubs
Components
of e-business XML systems:
E-Business systems are not monolithic
structures Components are as below Enterprise and back-end integration Various
network and foundational layers Messaging in a transport, routing and packaging
context Registries and / or repositories, Data Dictionaries, Process and
workflow,Trading partner Agreements, Business Vocabularies.
EbXML:
EbXML means Electronic Business XML. Global
Standard for electronic business ebXML enables anyone, anywhere to do business
with anyone else over the Internet Specifically designed to support SMEƒ
Complementary to existing B2B initiatives
(UDDI, RosettaNet, TradeXchange, etc.)
An
end-to-end B2B XML Framework Components:
·
Registry
and Repository
·
ƒ Core
Components
·
ƒ ebXML
Specification Schema
·
ƒ
Business Process Model
·
ƒ
Information Model
·
ƒ
CPP/CPA
·
ƒ
Message Service
ebXML:
Infrastructure Components
·
ƒ
Collaborative Protocol Profile ( cpp )
·
ƒ Core
Components
·
ƒ
Registry and Repository
·
ƒ
Messaging
·
ƒ
Business Process Modelling
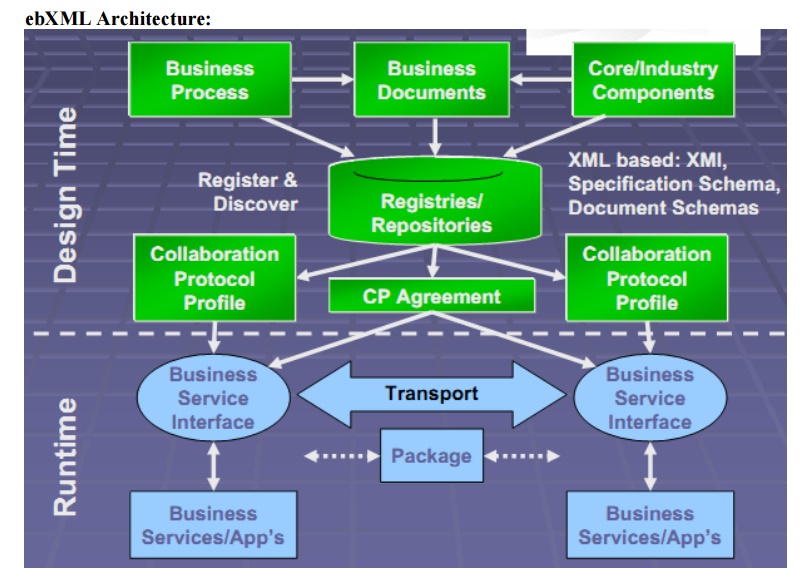
ebXML Process:
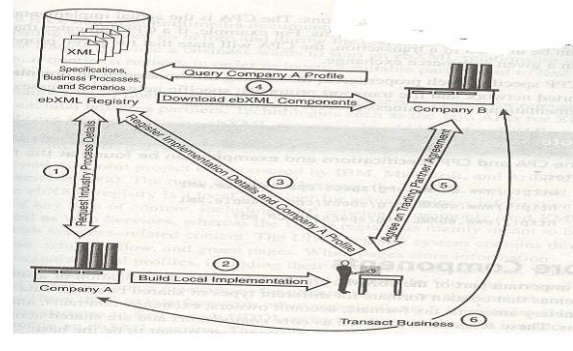
ebXML Architecture:
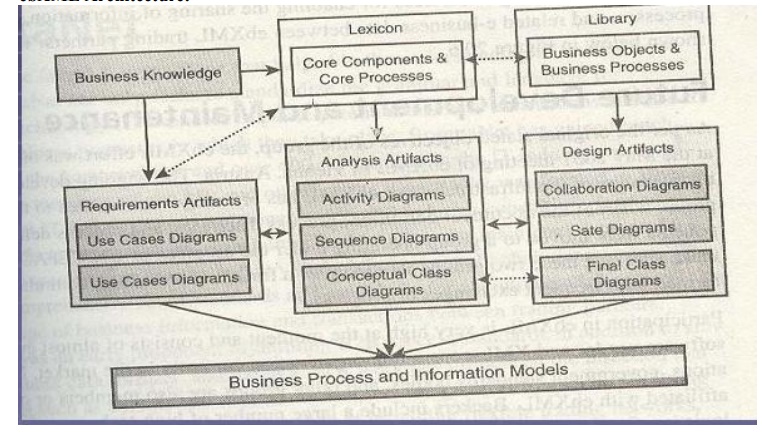
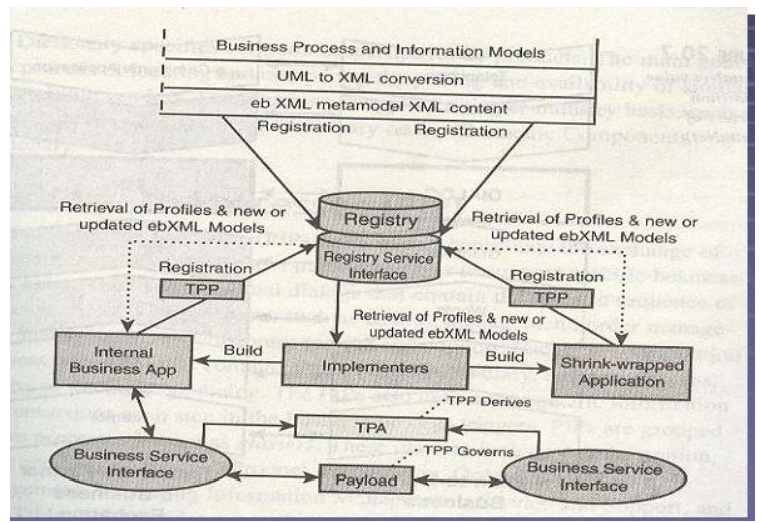
Functional Service View of ebXML:
ebXML
Vision:
A global electronic market place where
enterprises of any size, anywhere can find each other electronically conduct
business using XML messages. According to standard business process sequences
with clear business semantics according to standard or mutually agreed trading
partner protocol agreements using off the shelf purchased business
applications.
B2B
Collaboration:
B2B collaboration requires more than just an
XML protocol and a service registry. You have to deal with Business semantics,
Negotiating terms and conditions, Interoperability, Security and Privacy
Reliability.ebXML provides concrete specifications to enable dynamic
B2Bcollaborations
B2B Collaboration Process:
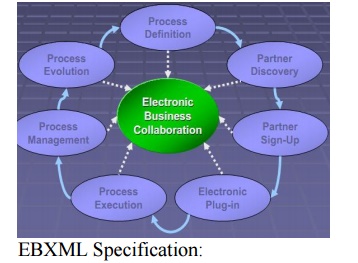
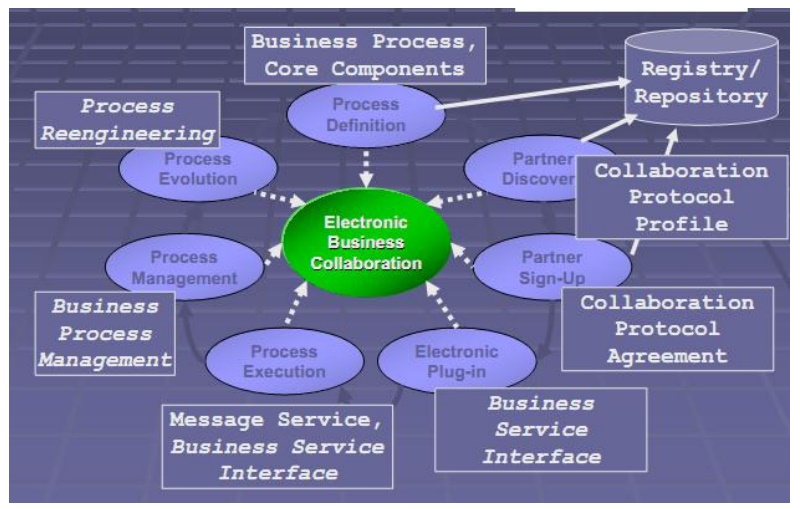
Collaboration
Protocol:
Collaboration Protocol Profile is defined using
ebXML Specification Schema Concrete specification of your ebusiness offerings
Business scenarios you support Service interfaces you implement Document
formats exchanged Technical requirements/options (protocols, security,
reliability) Composed of Business process models Information models Context
rules.
Business
Scenarios:
It is Often defined by Industry Groups as
Standard business scenarios remove the need for prior agreements among trading
partners,
It is a Business Process Model, Interactions
between parties,Sequencing of interactions, Documents exchanged in each
interaction.
It is a Information Model that is Document
definition, Context definition, Context rules Core Components
Core
Components:
Reusable low Reusable low- -level data structures.
·
e.g.,
party, address, phone, date, currency
·
It is
Context –sensitive
o Industry Sector Industry Sector
o Product Product
·
Business
process Business process
o
Geo-
-political region
o
Official
constraints
§
LegislativeStandards
§
Good
practice
§
Contractual
Business Process:
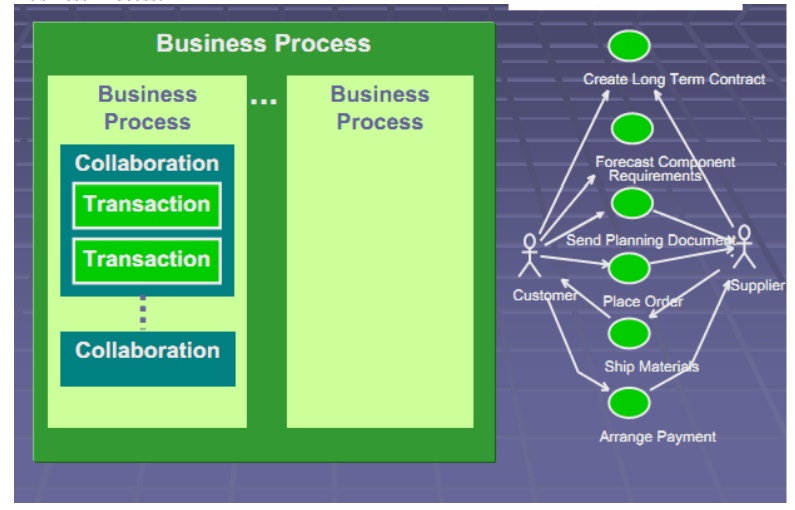
ebXML Specification Schema:
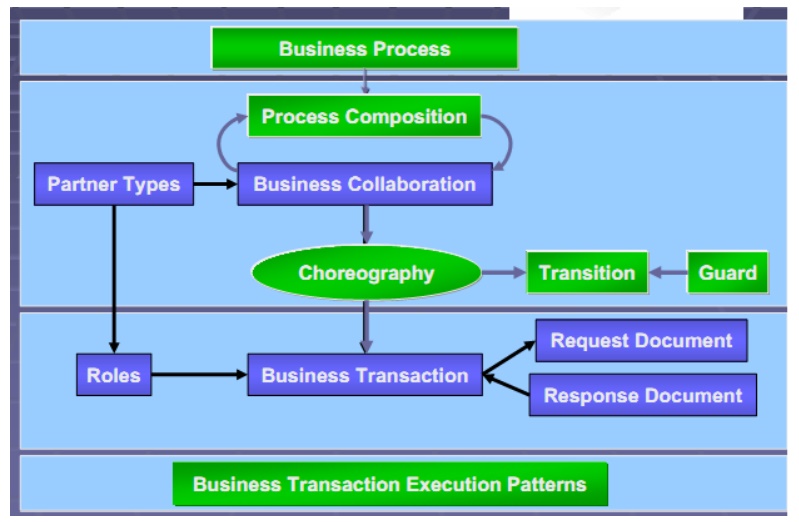
BP and Info Modeling Architecture:
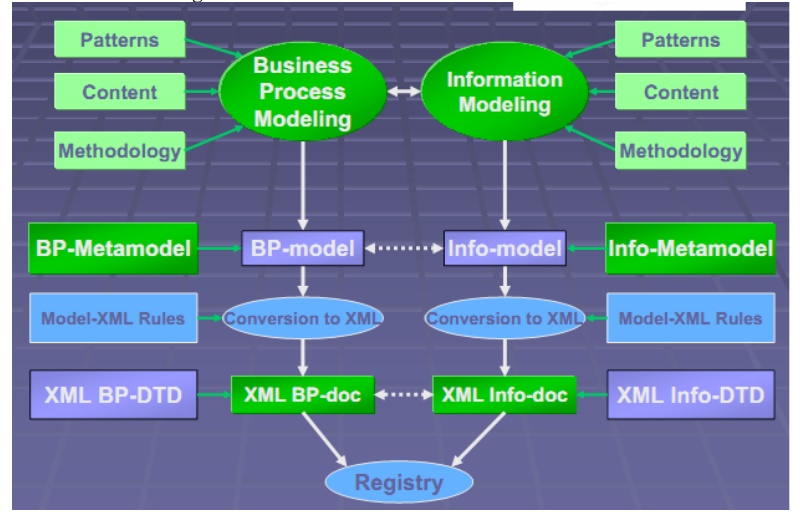
Conversion
of UML Models to XML:
·
Business
process definitions Business process definitions
· XML
Schema and DTD generation XML Schema and DTD generation
Populate classification scheme
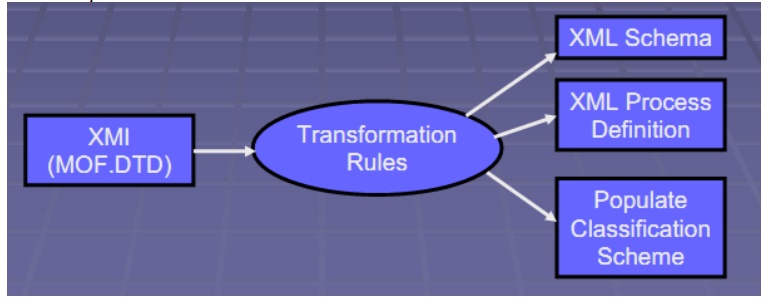
Traditional
Classification Scheme:
Taxonomies:
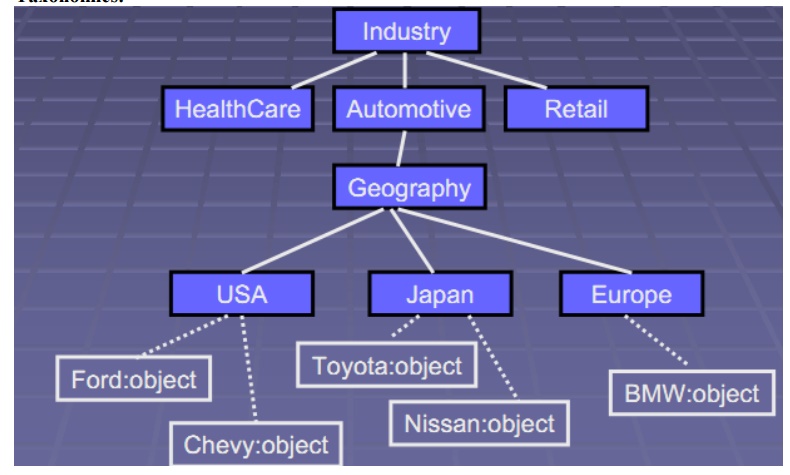
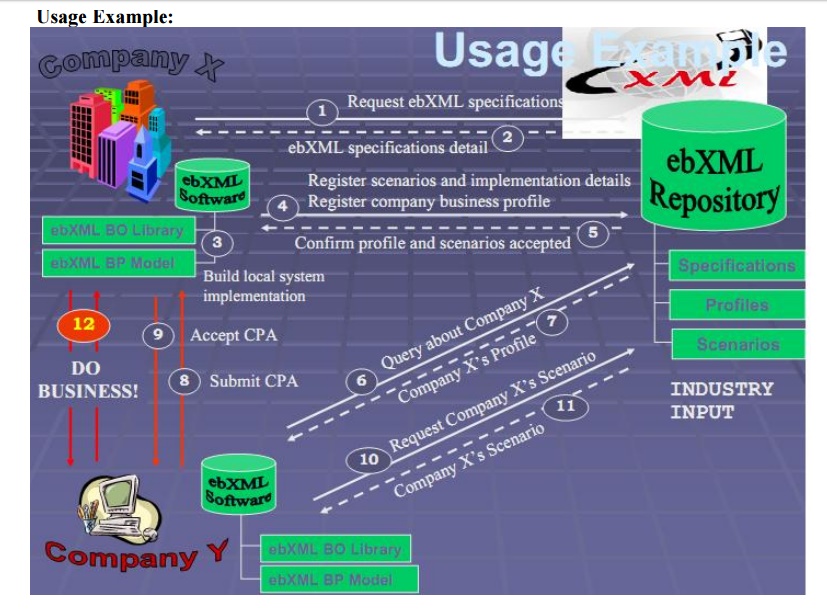
Registering
Your Business:
Register your business in an ebXML Registry
means Index to all information in the repository and Rich query facility.It
Store specifications in an ebXML Repository,
o CPP
o Schemas
Schemas
o Process
models Process models
o Core
components Core components
o
Classification and categorization schemes
Classification and categorization schemes
o Arbitrary
objects and code
ebXML Reg/Rep:
•
ebXML
Registry and Repository
–
Registry = index of things
–
Repository = holder of things
•
Distributed
model
•
Nodes
maintained by
–
Industry groups
–
Market places
–
Exchanges
–
Communities
–
Individual companies
Negotiating
an Agreement:
•
Find registry
and search for partners
•
Examine
CPP
•
Ascertain
compatibility of business process and technical specifications
•
Stipulate
your ―rules of engagement‖
•
Produce
Collaboration Protocol Agreement
–
Conditions under which two partners will conduct business transactions
together
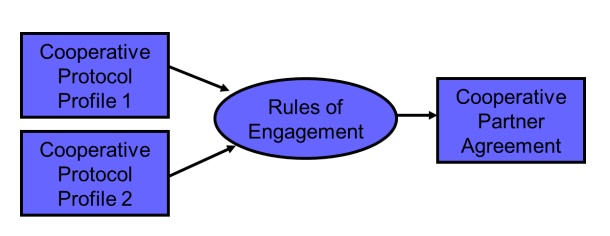
CP
Agreement Formation:
•
Negotiate
two Cooperative Protocol Profiles
•
Party 1
queries and discovers Party 2
•
Party 1
proposes rules of engagement
•
Sends
CPA to Party 2 for review and acceptance
Collaborative
Protocol Agreement:
•
Agreement
for business interaction between two parties
–
Technical specifications:
•
Message
Service requirements
•
Application
requirements
–
References:
•
CPPs
•
Legal
terms and conditions
Business
Service Interface:
•
Implements
the CPA, supporting dynamic integration
•
Not yet
specified
–
Hand-crafted for the moment
•
Enables
one Party to converse with the other Party using the ebXML Message Service
ebXML
Message Service:
•
Reliable,
secure XML messaging service
–
Enforces the rules of engagement in CPA
•
Transport
independent
•
Extends
SOAP Messages with Attachments (SwA)
–
Reliability framework
–
Security framework
–
Manifest, trace, and delivery options
Delivery Options:
Communications models
–
Synchronous or asynchronous
–
Request/response
– Fire
and forget
–
Multipart message delivery
•
Reliability
options:
– Best
effort
– Once
and only once
Security:
•
Identification
•
Authentication
•
Authorization
•
Privacy
•
Integrity
•
Non-repudiation
•
Logging
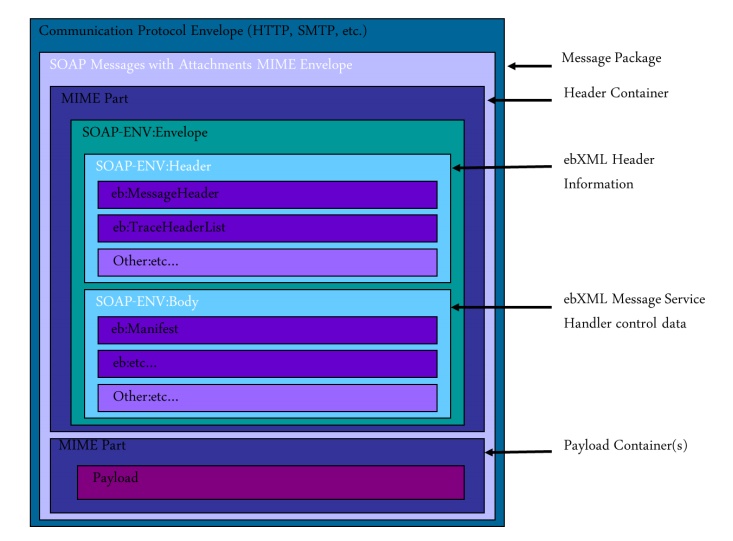
ebXML Message Structure:-
Related Topics