Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Mitral Stenosis
How would you anesthetize this patient?
How would you anesthetize this patient?
Phenylpiperidine opioids (fentanyl, sufentanil,
remifen-tanil and alfentanil), benzodiazepines, and etomidate are all
reasonable choices for anesthetic induction in patients with mitral stenosis
(Table 6.2). Opioids also have the advantage of increasing vagal tone and
slowing the heart rate, usually without associated hypotension. Short-acting barbiturates
produce undesirable venodilation and myo-cardial depression. Ketamine is
contraindicated on the basis of its tachycardic effects. Volatile agents
produce both myocardial depression and vasodilation and should be used
cautiously in low concentrations.
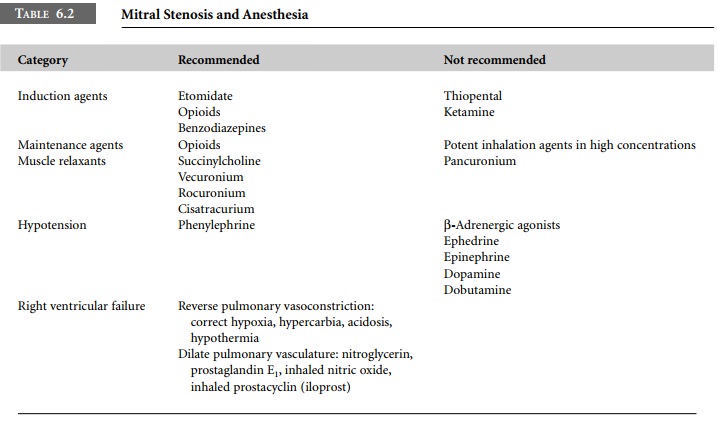
Theoretically, the most suitable neuromuscular blocking agents for
mitral stenosis are succinylcholine, vecuronium, rocuronium and cisatracurium.
For long cardiothoracic procedures continuous intravenous infusions are a good
choice to maintain an adequate level of neuromuscular blockade, which decreases
oxygen consumption during cardiopulmonary bypass. Pancuronium is relatively
contra-indicated since it produces tachycardia.
Related Topics