Home | Electrical properties of insulating materials
Chapter:
Electrical properties of insulating materials

Insulation resistance-is the property, by the virtue of which, a material resists flow of electrical current. It should be high as possible. Insulation resistance is of two types:
Electrical properties
of an insulating material are:
Insulation resistance-is the property, by the virtue of which, a material resists flow of electrical current. It should be high as possible. Insulation resistance is of two types:
(i) Volume resistance; (ii) Surface resistance.
The resistance offered to the current, which flows through the material is called volume resistance. The resistance offered to the current, which flows over the surface of the insulating material is called surface resistance. Factors that affect the insulation resistance are-temperature variations, exposure to moisture, voltage applied, aging.
Dielectric Strength- is therefore the minimum voltage which when applied to an insulating material will result in the destruction of its insulating properties. It can also be defined as the maximum potential gradient that the material can withstand without rupture, or without loosing dielectric properties. This value is expressed in volts or kilovolts per unit thickness of the insulating material. This value is greatly affected by the conditions under which the material is operated. Factors affecting the dielectric strength are temperature and humidity.
Dielectric Constant- Every insulating material has got the basic property of storing charge (Q), when a voltage (V) is applied across it. The charge is proportional to the voltage applied i.e. Q α V, or Q = CV. Where C is called the capacity or capacitance of the material across which the voltage is applied. Every insulating material behaves as a capacitor. Capacitance is different for different insulating material. The property of insulating materials that causes the difference in the value of capacitance, with the physical dimensions remaining the same is called dielectric constant or permittivity (∈) and ∈ = C/Co, where C is capacity in presence of Dielectric and Co is the capacity in air or vacuum or in the absence of dielectric. Dielectric loss and Loss angle: When a perfect insulation is subjected to alternating voltage, it is like applying alternate voltage to a perfect capacitor. In a perfect capacitor the charging current would lead the applied voltage by 900 exactly. This means that there is no power loss in the insulation. In most insulating materials this is not the case. There is a definite amount of dissipation of energy when an insulator is subjected to alternating voltage. This dissipation of energy is called dielectric loss. Factors affecting dielectric loss are - Frequency of applied voltage, humidity, temperature rise and voltage.
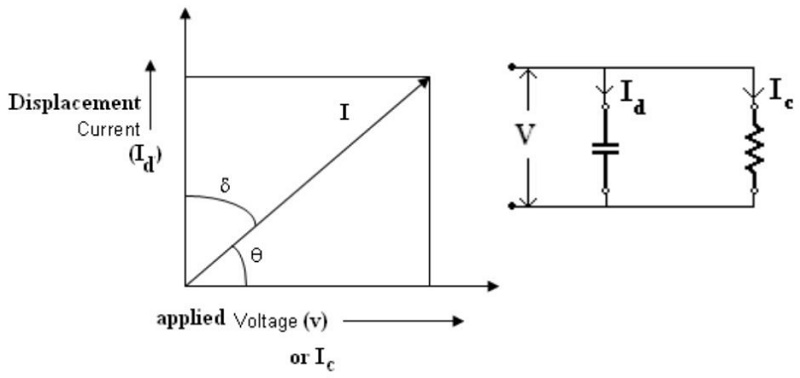
The dielectric phase angle is θ and δ = 900 - θ is the dielectric loss angle as shown in the fig. below.
Insulation resistance-is the property, by the virtue of which, a material resists flow of electrical current. It should be high as possible. Insulation resistance is of two types:
(i) Volume resistance; (ii) Surface resistance.
The resistance offered to the current, which flows through the material is called volume resistance. The resistance offered to the current, which flows over the surface of the insulating material is called surface resistance. Factors that affect the insulation resistance are-temperature variations, exposure to moisture, voltage applied, aging.
Dielectric Strength- is therefore the minimum voltage which when applied to an insulating material will result in the destruction of its insulating properties. It can also be defined as the maximum potential gradient that the material can withstand without rupture, or without loosing dielectric properties. This value is expressed in volts or kilovolts per unit thickness of the insulating material. This value is greatly affected by the conditions under which the material is operated. Factors affecting the dielectric strength are temperature and humidity.
Dielectric Constant- Every insulating material has got the basic property of storing charge (Q), when a voltage (V) is applied across it. The charge is proportional to the voltage applied i.e. Q α V, or Q = CV. Where C is called the capacity or capacitance of the material across which the voltage is applied. Every insulating material behaves as a capacitor. Capacitance is different for different insulating material. The property of insulating materials that causes the difference in the value of capacitance, with the physical dimensions remaining the same is called dielectric constant or permittivity (∈) and ∈ = C/Co, where C is capacity in presence of Dielectric and Co is the capacity in air or vacuum or in the absence of dielectric. Dielectric loss and Loss angle: When a perfect insulation is subjected to alternating voltage, it is like applying alternate voltage to a perfect capacitor. In a perfect capacitor the charging current would lead the applied voltage by 900 exactly. This means that there is no power loss in the insulation. In most insulating materials this is not the case. There is a definite amount of dissipation of energy when an insulator is subjected to alternating voltage. This dissipation of energy is called dielectric loss. Factors affecting dielectric loss are - Frequency of applied voltage, humidity, temperature rise and voltage.
The dielectric phase angle is θ and δ = 900 - θ is the dielectric loss angle as shown in the fig. below.

Also
I is the phasor sum of Id and Ic ,
where Ic is the conduction current which is in phase with the applied voltage
and Id is the displacement current which is in quadrature phase with applied
voltage.
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
: Electrical properties of insulating materials |
Related Topics