Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Virology, Virus: Rhabdoviruses
Treatment, Prevention and Control - Rabies Virus Infection
Treatment
No specific antirabies agent is available. Although until recently rabies was considered to be invariably fatal, it has now been demonstrated that complete recovery can occur from established rabies with intensive supportive care and management of complications.
Prevention and Control
Specific prophylaxis in rabies, depending upon whether given before or after exposure can be discussed as pre-exposure pro-phylaxis and postexposure prophylaxis.
◗ Pre-exposure prophylaxis
Pre-exposure prophylaxis is given to persons at high risk, such as dog handlers, other animal handlers, and veterinarians. This is achieved by use of cell culture vaccines, which are more safe. Pre-exposure prophylaxis requires three doses of cell culture vaccines, given on day 0, 7, 21, or on day 0, 28, and 56. A booster dose is recommended after 1 year, and then one dose every year. Animal control and vaccination strategies now have stronger roles than postexposure prophylaxis in preventing the spread of rabies.
◗ Postexposure prophylaxis
Postexposure prophylaxis is started immediately after exposure to infection. After exposure to possibly infected dog or other rabid animals, immediate preventive actions are taken up, which consist of (a) local treatment, (b) confirmation whether or not the animal is rabid, (c) administration of hyperimmune serum, and (d) antirabies vaccine.
Local treatment: This involves prompt cleaning of the wound.Animal bites deposit the virus in the wounds. The wound should be immediately scrubbed with soap and water followed by treatment with quaternary ammonium compounds, such as Cetavlon, tincture, or aqueous solution of iodine or alcohol.
Confirmation whether or not the animal is rabid: Thiscan be made by clinical observation of suspected dog. If dog is still healthy 10 days after biting human, rabies is extremely unlikely. Diagnosis can also be made by demonstration of the Negri bodies in brain tissues at autopsy or viral antigens in the brain tissue or saliva.
Administration of hyperimmune serum: Passive immuni-zation is carried out by administering purified equine rabies immune globulin (ERIG) and human rabies immune globulin (HRIG). Administration of HRIG is promptly made to ensure passive immunization against rabies. The recommended dose of HRIG is 20 IU/kg body weight. Fifty percent of the dose is given into the wound and 50% intramuscularly. It is usually given before or simultaneously with the first dose of the rabies vaccine. It is not given after injection of rabies vaccine. The recommenda-tions for postexposure prophylaxis are presented in Table 64-2.

Antirabies vaccine: Rabies is the only disease where postexpo-sure vaccination is employed extensively and successfully. This is due to long incubation period of the disease. The chances of preventing the rabies are more when vaccination is given to humans as early as possible after exposure.
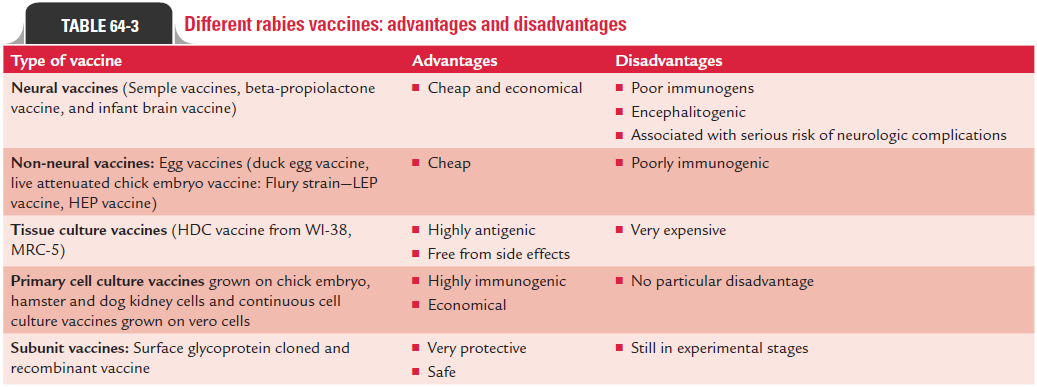
Since the time of Pasteur’s successful use of a rabies vaccine obtained from des-iccated preparation of spinal cord of rabbits in the year 1885, a wide variety of vaccines are being used worldwide to protect humans against rabies even after infection with the virus. Of late, neural-tissue vaccines are gradually being replaced by cell culture vaccines that are grown in human diploid cells and then inactivated with propiolactone. The list of such vaccines with their advantages and disadvantages are summarized in Table 64-3.
Related Topics