Chapter: Physics : Photonics and fibre Optics
The Fiber Optic Communication System: Principle, Working, and Advantages
OPTICAL FIBER AS AN OPTICAL WAVEGUIDE
Optical fibers are used as dielectric waveguides for electromagnetic signals of optical frequencies. Figure shows the block diagram of transmission of sound along the optical fiber and conversion again to sound at the other end.
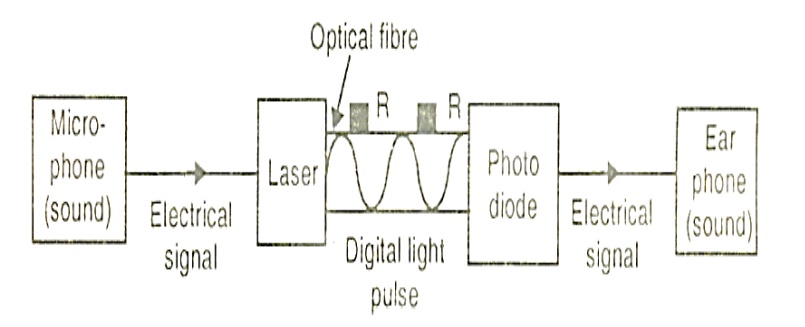
i. Sound is first converted into electrical signal by a microphone.
ii. The electrical signals modulate the intensity of light from laser.
iii. Then the information is carried along the fiber in a digital form.
Boosters or repeaters are placed at a distance of about 50km of cable to make up the signal loses occurring due to scattering and absorption.
iv. At the receiving place, a photodiode converts the digital light pulses into corresponding electrical signals.
v. The electrical signals are then converted into sound by an earphone ( receiver) Time division multiplexing system is used to transmit many thousands of telephone cells through a single optical fiber with the use of digital pulses.
THE FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
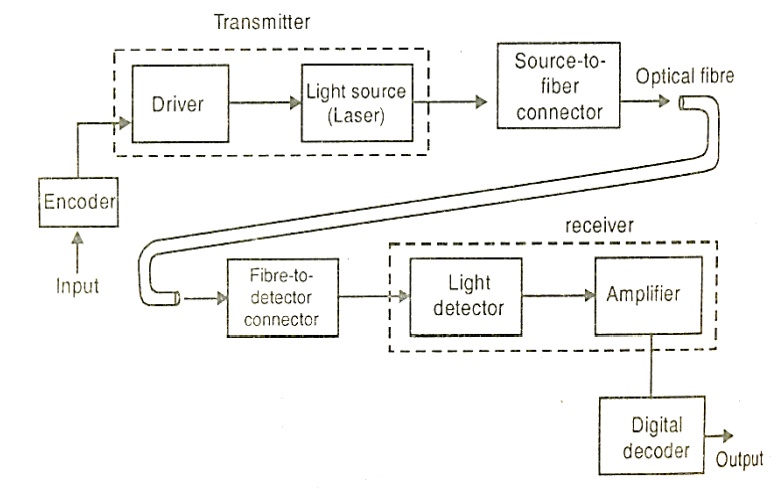
Figure shows the schematic diagram of a fiber optic communication system. The major components of an optical fiber communication system are
i. The optical transmitter
ii. The optical fiber
iii. The optical receiver
PRINCIPLE:
Basically, a fiber optic system converts an electrical signal to an infrared light signal. This signal is transmitted through an optical fiber. At the end of the optical fiber, it is reconverted into an electric signal
Working:
1. Encoder encodes the information in the binary sequence zeros and ones.
a. Encoder is an electric circuit where in the information is encoded into binary sequences of zeros and one. In the light wave transmitter each ‘one’ corresponds to an electrical pulse and ‘zero’ corresponds to an absence of a pulse. These electrical pulses are used to turn a light source on and off very rapidly. The driver converts the incoming electrical signal into a form that will operate with the light source.
2. These electrical pulses are used to turn a light source on and off rapidly.
3. The optical fiber acts as a wave guide and transmits the optical pulses towards the receiver, by the principle of total internal reflection.
4. The light detector receives the optical pulses and converts them into electrical pulses. These signals are amplified by the amplifier.
5. The amplified signals are decoded by the decoder.
ADVANTAGES:
1. Extremely wide bandwidth.
a. Optical frequencies are very large (1015 Hz) as compared to radio frequencies (106Hz) and microwave frequencies (1010 Hz). The rate at which information can be transmitted is directly related to signal frequency. Therefore, a transmission system that operates at the frequency of light can theoretically transmit information at a higher rate than systems that operate at radio frequencies or microwave frequencies.
2. Lack of cross talk between parallel fibers.
a. There is virtually no signal leakage from fibers. Hence, cross-talks between neighboring fibers are almost absent. This is quite frequent in conventional metallic system
3. Immunity to inductive interference
a. Since optical fibers are not metallic, they do not pick up electromagnetic waves. The result is noise free transmission i.e., fiber optic cables are immune to interference caused by lighting or other electromagnetic equipment
4. Smaller diameter and light weight cable
a. Optical fibers, because of their light weight and flexibility, can be handled more easily than copper cables.
5. Signal security
a. The transmitted signal through the fibers does not radiate. Further the signal
cannot be tapped from a fiber in an easy manner. Therefore, optical fiber communication provides a hundred percent signal security hence this system is highly suited to secure communications in defence communication networks.
6. Economical & Low loss per unit length.
Related Topics