Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Peripheral Lymphoid Organs : Lymph nodes, Spleen
Structure and Functions of the Immune System
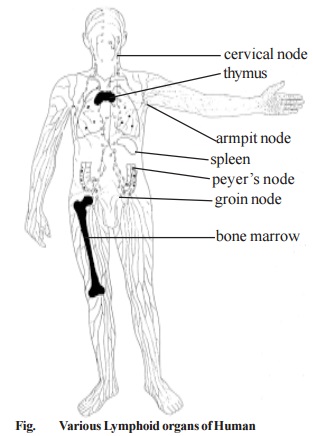
The lymphoid system consists of the lymphoid cells (lymphocytes and plasma cells) and lymphoid organs. Based on different roles they perform, lymphoid organs can be classified into central (primary) and peripheral (secondary) lymphoid organs. The central lymphoid organs are lymphoepithelial structures in which the precursor lymphocytes proliferate, develop and acquire immunological capability. In mammals, the bone marrow, the thymus and the bursa of fabricius in birds represent primary lymphoid organs. After acquiring immunocompetence, the lymphocytes migrate along blood and lymph streams, accumulate in the peripheral lymphoid organs and, following antigenic stimulus, effect the appropriate immune response. The spleen, lymph nodes and mucosa - associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) constitute the major peripheral or secondary lymphoid organs. Lymphoidal tissues in the gut ( peyer's patches), appendix, tonsils, salivary glands, tear glands and also the secretion (colostrums) of the lactating breast of the mother also are included in the immune sysytem.
Peripheral Lymphoid Organs
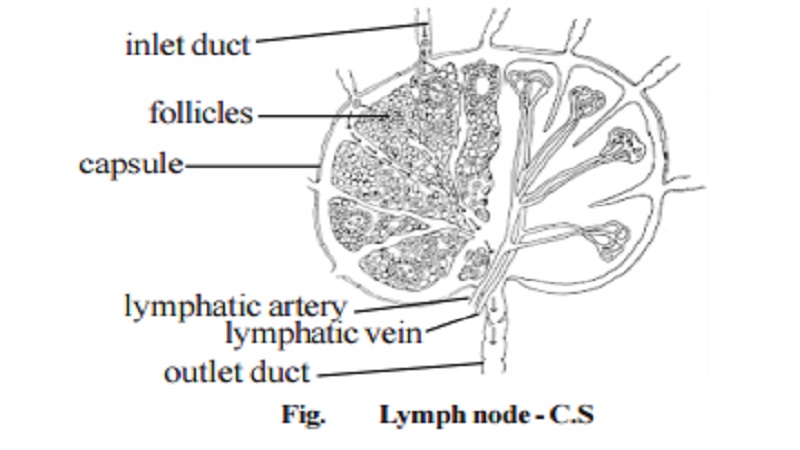
A. Lymph nodes :
The lymph nodes are small, round or ovoid bodies placed along the course of lymphatic vessels. They are surrounded by a fibrous capsule from which trabeculae penetrate into the nodes. The node can be differentiated into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. In the cortex are accumulations of lymphocytes (primary follicles) within which germinal centers (secondary follicles) develop during antigenic stimulation. The follicles contain, besides proliferating lymphocytes, dendritic macrophages which capture and pro-cess the antigen. In the medulla, the lymphocytes are arranged as elongated branching bands (medullary cords). The cortical follicles and medullary cords contain B lymphocytes and constitute the bursa or bone marrow dependent areas. Between the cortical follicles and medullary cords, there is a broad, intermediate zone called paracortical area which contains T lymphocytes and constitutes the thymus dependent area.
Lymph nodes act as a filter for the lymph. Each group of nodes drain a specific part of the body. They phagocytose foreign materials including microorganisms. They help the proliferation and circulation of T and B cells. They enlarge following local antigenic stimulation. In the human body, totally about 600 lymph nodes are distributed.
B. Spleen :
It is the largest lymphoid organ. It contains red and white pulp re-gions that serve as filters. The macrophages within the spleen help to remove and destroy pathogens.
Functions of Spleen :
1. The spleen serves as the graveyard for effete(aged) red blood cells, 2. It acts as a reserve tank and setting bed for blood and 3. It acts as a systemic filter for trapping circulating blood borne foreign particles. (The immunological function of the spleen is primarily directed against blood borne antigens).
Related Topics