Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 4 : Hydrogen
Answer the following questions: Hydrogen (Chemistry)
Hydrogen (Chemistry)
Answer the following questions
22. Explain why hydrogen is not placed with the halogen in the periodic table.
●
The hydrogen has the electronic configuration of 1s1 which resembles
with ns1 general valence shell configuration of alkali metals.
●
Like the formation of halides (X−) from halogens, hydrogen also has
a tendency to gain one electron to form hydride ion (H−) whose
electronic configuration is similar to the noble gas, helium.
●
However, the electron affinity of hydrogen is much less than that of halogen
atoms.
●
Hence, the tendency of hydrogen to form hydride ion is low compared to that of
halogens to form the halide ions.
1/2
H2 + e− → H− ΔH = +36
kcalmol−1
1/2
Br2 + e− → Br− ΔH =
-55 kcalmol−1
●
Since, hydrogen has similarities with alkali metals as well as the halogens; it
is difficult to find the right position in the periodic table.
●
However, in most of its compounds hydrogen exists in + 1 oxidation state.
Therefore, it is reasonable to place the hydrogen in group 1 along with alkali
metals.
Q. An the cube at 0° C is placed in some liquid water at 0° C, the ice cube sinks - Why ?
23. Discuss the three types of Covalent hydrides.
1.
Electron precise (CH4, C2H6, SiH4,
GeH4)
2.
Electron - deficient (B2H6) and
3.
Electron - rich hydrides (NH3, H2O)
24. Predict which of the following hydrides is a gas on a solid (a) HCl (b) NaH. Give your reason.
HCl. This is a covalent hydride in which
hydrogen is attached to another element by sharing of electrons. Since HCl consist of discrete, small molecules
that have relatively weak intermolecular forces, they are generally gases or
volatile liquids.
25. Write the expected formulas for the hydrides of 4th period elements. What is the trend in the formulas? In what way the first two numbers of the series different from the others ?
●
The expected formula is MH or MH2 (M = Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Zn)
●
Trend in formulas : Most of the hydrides are non - stoichiometric with variable
composition (TiH1.5 – 1.8 and PdH0.6 – 0.8)
●
The first two members of the series form ionic hydrides whereas others form
covalent or metallic hydrides.
26. Write chemical equation for the following reactions.
i. reaction of hydrogen with tungsten (VI) oxide NO3 on heating.
ii. hydrogen gas and chlorine gas.
i)
WO3 + 3H2 → W + 3H2O
ii)
Hydrogen reacts with chlorine to give hydrogen chloride at room temperature
under light H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
27. Complete the following chemical reactions and classify them in to (a) hydrolysis (b) redox (c) hydration reactions.
i. KMnO4 + H2O2 →
ii. CrCl3 + H2O →
iii. CaO + H2O →
i)
2KMnO4 (aq) + 3H2O2 (aq) → 2MnO2
+ 2KOH + 2H2O + 3O2(g) − Redox reaction
ii)
CrCl3 + 6H2O → [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3.-
Hydration reaction
iii)
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 - Hydrolysis reaction
28. Hydrogen peroxide can function as an oxidising agent as well as reducing agent. substantiate this statement with suitable examples.
●
Hydrogen peroxide can act both as an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent.
Oxidation is usually performed in acidic medium while the reduction reactions
are performed in basic medium
In
acidic conditions :
H2O2
+ 2H+ + 2e− → 2H2O (E0 = + 1.77V)
For
example,
2FeSO4
+ H2SO4 + H2O2 → Fe2(SO4)3
+ 2H2O
In
basic conditions :
H2O2−
+ OH− → O2+ H2O + 2e− (E° = + 0.08V)
For
example, 2KMnO4 (aq) + 3H2O2 (aq)
→ 2MnO2 + 2KOH + 2H2O + 3O2 (g)
29. Do you think that heavy water can be used for drinking purposes ?
Heavy
water is not used for drinking, because it reduces the activity of plants,
animals and human beings. It is not the basic for life as ordinary water.
30. What is water-gas shift reaction ?
The
carbon monoxide of the water gas can be converted to carbon dioxide by mixing
the gas mixture with more steam at 400°C and passed over a shift converter
containing iron/copper catalyst. This reaction is called as water gas shift
reaction.
CO
+ H2O → CO2 + H2
31. Justify the position of hydrogen in the periodic table ?
●
The hydrogen has the electronic configuration of 1s1 which resembles
ns1 general valence shell configuration of alkali metals.
●
Like the formation of halides (X−) from halogens, hydrogen also has
a tendency to gain one electron to form hydride ion (H−) whose
electronic configuration is similar to the noble gas, helium,
●
However, the electron affinity of hydrogen is much less than that of halogen
atoms.
●
Hence, the tendency of hydrogen to form hydride ion is low compared to that of
halogens to form the halide ions.
1/2
H2 + e− → H− ΔH = +36 kcalmol−l
1/2
Br2 + e− → Br − ΔH = −55 kcalmol−l
●
Since, hydrogen has similarities with alkali metals as well as the halogens, it
is difficult to find the right position in the periodic table.
●
However in most of its compounds hydrogen exists in +1 oxidation state.
● Therefore it is reasonable to place the hydrogen in group 1 along with
alkali metals.
32. What are isotopes? Write the names of isotopes of hydrogen.
Elements
with same atomic number but with different mass number are called isotopes.
Hydrogen
has three naturally occurring isotopes, viz, protium (1H1
or H), deuterium (1H2 or D) and (1H3
or T) tritium.
33. Give the uses of heavy water.
Heavy
water is widely used as moderator in nuclear reactors as it can lower the
energies of fast neutrons.
It
is commonly used as a tracer to study organic reaction mechanisms and
mechanisms of metabolic reactions.
It
is also used as a coolant in nuclear reactors as it absorbs the heat generated.
34. Explain the exchange reactions of deuterium.
CH4
+ 2D2 → CD4 + 2H2
2NH3
+ 3D2 → 2ND3 + 3H2
35. How do you convert parahydrogen into ortho hydrogen ?
1.
The para form can be catalytically transformed into ortho - form using platinum
or iron.
2.
It can also be converted by passing an electric discharge,
3.
Heating above 800°C
4.
Mixing with paramagnetic molecules such as O2, NO, NO2 or
with nascent / atomic
36. Mention the uses of deuterium.
1.
As moderator in nuclear reactor
2.
To find the mechanism of a chemical reaction it is used as tracer element
37. Explain preparation of hydrogen using electrolysis.
High
purity hydrogen (>99.9%) is obtained by the electrolysis of water containing
traces of acid or alkali or the electrolysis of aqueous solution of sodium
hydroxide or potassium hydroxide using a nickel anode and iron cathode.
However, this process is not economical for large - scale production.
At
anode : 2OH− → H2O + 1/2 O2 + 2e−
At
cathode : 2H2O + 2e− → 2OH− + H2
Overall
reaction : H2O → H2 + 1/2 O2
38. A groups metal (A) which is present in common salt reacts with (B) to give compound (C) in which hydrogen is present in –1 oxidation state. (B) on reaction with a gas (C) to give universal solvent (D). The compound (D) on reacts with (A) to give (B), a strong base. Identify A, B, C, D and E. Explain the reactions.
Common
salt is NaCl
The
metal in this salt is Na(A)
2Na
+ H2 (B) → 2NaH (C)
H2
+ O2 (D) → 2H2O (E)
H2O + 2Na → 2NaOH(F) + H2
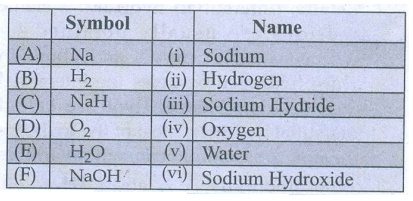
Symbol : Name
(A)
Na : (i) Sodium
(B)
H2 : (ii) Hydrogen
(C)
NaH : (iii) Sodium Hydride
(D)
O2 : (iv) Oxygen
(E)
H2O : (v) Water
(F)
NaOH : (vi) Sodium Hydroxide
39. An isotope of hydrogen (A) reacts with diatomic molecule of element which occupies group number 16 and period number 2 to give compound (B) is used as a modulator in nuclear reaction. (A) adds on to a compound (C), which has the molecular formula C3H6 to give (D). Identify A, B, C and D.
Diatomic
molecule which occupies Group No.16 and Period number 2 is Oxygen.
2D2
+ O2 → 2D2O (heavy water)

Formula : Name
(A)
D2 : Deuterium
(B)
D2O : Heavy water
(Q
CH3 − CH = CH2 : Propene (or) propylene
(D)
CH3 − CHD = CH2D : Propylene deuteride (or) deuterated
propylene
40. NH3 has exceptionally high melting point and boiling point as compared to those of the hydrides of the remaining element of group 15 - Explain.
NH3
is a covalent hydride which has a lone pair of electron on electro negative
nitrogen atom.
Therefore
it forms inter molecular hydrogen bond with other NH3 molecule. It
forms condensation product of the type (NH3)n. Thus the
boiling point of ammonia is high compared to other elements of group −15.
41. Why interstitial hydrides have a lower density than the parent metal.
Metallic
(interstitial) hydrides: Metallic hydrides are usually obtained by
hydrogenation of metals and alloys in which hydrogen occupies the interstitial
sites (voids). Hence, they are called interstitial hydrides; Most of the
hydrides are non - stochiometric with variable composition (TiH1.5
- 1.8 and PdH0.6 - 0.8). Hence they have lower density
than the parent metal.
42. How do you expect the metallic hydrides to be useful for hydrogen storage ?
●
Metallic hydrides are usually obtained by hydrogen of metals and alloys in
which hydrogen occupies the interstitial sites (voids).
●
Hence, they are called interstitial hydrides. Most of the hydrides are non -
stoichiometric with variable composition (TiH1.5 -
1.8 and PdH 0.6 - 0.8). Some are relatively light, inexpensive
and thermally unstable which make them useful for hydrogen storage
applications.
43. Arrange NH3, H2O and HF in the order of increasing magnitude of hydrogen banding and explain the basis for your arrangement.
● When a hydrogen atom (H) is
covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as flurorine (F) or
oxygen (O) or nitrogen (N), the bond is polarized. Order of electronegativity : F>O>N Ascending
order of hydrogen bond strength:
NH3 < H2O
< HF
44. Compare the structures of H2O and H2O2.
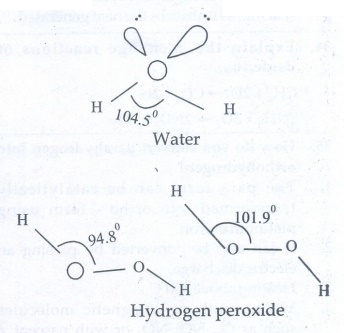
Structure
of H2O:
It
is polar molecule with 2 lone pairs electrons. Oxygen atom in water is sp3
hybridised lp - lp repulsion, is greater than bp − bp repulsion.
The H − O − H bond angle is reduced from 109°28 to 104°. It has a bent shape.
structure
of H2O2:
●
H2O2 has a non - polar structure. The molecular
dimensions in the gas phase and solid phase differ.
●
Structurally H2O2 is represented by the dihydroxyl
formula in which the two OH− groups do not lie in the same plane.
●
One way of explaining the shape of hydrogen peroxide is that the hydrogen atoms
would lie on the pages of a partly opened book, and the oxygen atoms along the
spine.
● In the solid phase of molecule, the dihedral angle reduces to 90.2° due to hydrogen bonding and the O - O-H angle expands from 94.8° to 101.9°
Related Topics