Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - cancer | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
cancer
CANCER
1. Oral cancer
2. Breast Cancer
The goals of cancer
management are cure, control and palliative care.
Cancer is a disease in
which certain body cells multiply without apparent control, destroying healthy
tissue and organs and endangering life.
There are three main
classifications of cancer- 1. Carcinoma 2. Sarcoma 3. Lymphoma.
Carcinoma: which is cancer of the
epithelial tissue that forms the skin and the linings of the internal
organs.
Sarcoma: which is cancer of
connective tissue such as cartilage, muscle or bone.
Lymphoma: which affects the
blood stream and the lymph system.
1. Oral Cancer
There are two types of
oral cancer, oral cavity cancer which starts in the mouth and the oropharyngeal
cancer which develops in the part of the throat just behind the mouth of the
oropharynx.
Investigation:
·
History and physical examination
·
Biopsy
·
Oral exfoliative cytology
·
Toluidine blue test
·
CT scan
·
MRI scan
·
PET scan
Types of oral cancer
·
Lip cancer
·
Tongue cancer
·
Oral cavity cancer
Lip cancer
Predisposing Factors
Constant over exposure
to sun radiation and fair complexion, recurrent herpetic lesions, irritation
from pipe stem, syphilis and immune suppression.
Clinical Manifestations
Indurated painless ulcer
Management
·
Surgical excision and radiation
Tongue cancer
Predisposing Factors
·
Tobacco, alcohol, chronic irritation, syphilis
Clinical Manifestations
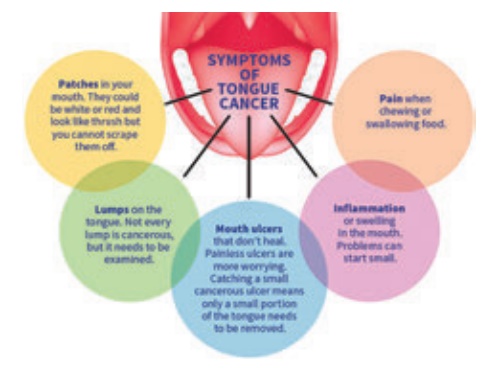
Management
·
Surgery (hemiglossectomy or glossectomy, radiation)
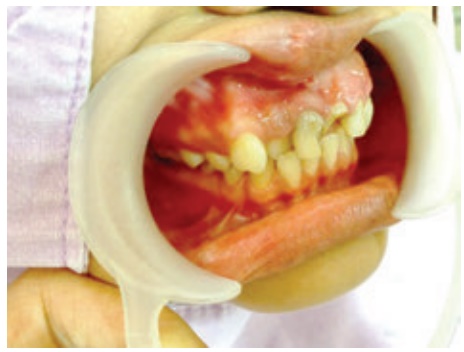
Predisposing Factors
·
Poor oral hygiene, tobacco usage (pipe and ciger smoking, snuff,
chewing tobacco) chronic alcohol intake, chronic irritation (jagged tooth,
ill-fitting prosthesis, chemical or mechanical irritants) human papillomavirus
(HPV)
Clinical Manifestations
·
Leukoplakia, erythro plakia ulceration, sore spot, rough area, pain,
dysphagia, lump or thickening in the cheek. A sore throat or a feeling that
something is stuck difficulty in chewing and speaking (lateral signs)
Management
·
Surgery mandibulectomy radical neck dissection resection of
buccal muscosa internal and external radiation.
2. Breast Cancer
Definition:- cancer is a
disease process whereby cells proliferate abnormally, ignoring growth
regulating signals in the environment surrounding the cell.
Causes
·
No definite cause
·
Hormones and genetics play some role in causing breast cancer
Risk Factors
·
Breast cancer may be seen after the age of 50
·
Personal or family history of breast cancer may lead to a main cause
·
Persons with early menarche may have more chances of getting
breast cancer
·
Females who are not having children are more prone to breast
cancer
·
Late maternal age at first birth
·
Late menopause also one of the cause Exposure to ionizing radiation
·
Obesity also rarely cause breast cancer
Signs and Symptoms
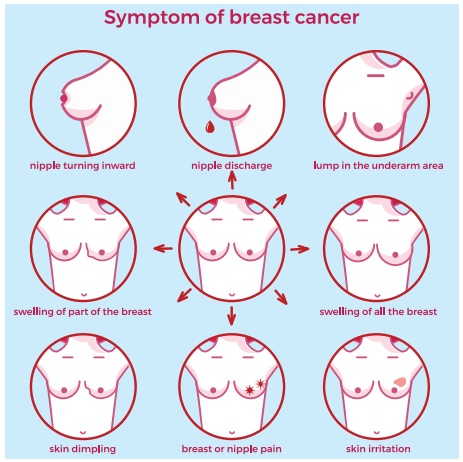
·
Non tender, fixed, hard mass with irregular border in the breast
·
Peau d’ orange (orange peel) appearance of the skin seen on the
breast
·
Nipple retraction in advanced cancer
·
Ulcerating and fungating lesions
Investigation
·
Self breast examination
·
Fine needle biopsy
·
Open biopsy
·
Incisional biopsy
·
Core biopsy
·
Histologic examination
Management
Surgical Management:
·
Mastectomy – removal of the affected breast Modified radical mastectomy
·
Breast conservation surgery Lumpectomy
·
Partial mastectomy
·
Segmental mastectomy
·
Quadrantectomy. (Axillary lymph node dissection)
·
Radiotherapy
·
Chemotherapy
·
Hormonal therapy
·
Bone marrow transplantation
Nursing Management
·
Family support
·
Exercise
·
Psychological exercise or emotional support to patient and family
members
·
Dressing
·
Relieving pain and comfort
·
Maintain skin integrity
·
Educate post operative exercise
Family Support:
Family and members
should be supported with proper counselling. Explain them about the management
modalities available now. Family members are advised to support the patient who
is suffering with cancer.
Post Operative
Exercises:
·
Wall climbing exercise: Advise to stand near the wall and face the
wall, advise to put the affected side on the wall, and slowly move the hand on
the wall with finger walk.
·
Rope pulling exercise: Advise to hang the rope on a rod and hold
the two ends of the rope with two hand and lift the hand one by one in opposite
direction.
·
Rope turning exercise: Tie a rope on the door and the turn the
rope with hand of affected side.
Dressing:
·
Breast binder may be applied if necessary
Related Topics