Chapter: Mechanical : Robotics : Sensors and Machine Vision
Working principle of Proximity sensors
Working
principle of Proximity sensors
Proximity Sensors:
The output of the
proximity sensors gives an indication of the presence of an object with in the
vicinity job operation.
In robotics these
sensors are used to generate information of object grasping and obstacle
avoidance. This section deals with some of the important proximity sensors used
in robotics.
Proximity sensor is a sensor, which senses the presence or absence of the object without having physical contact between the objects.
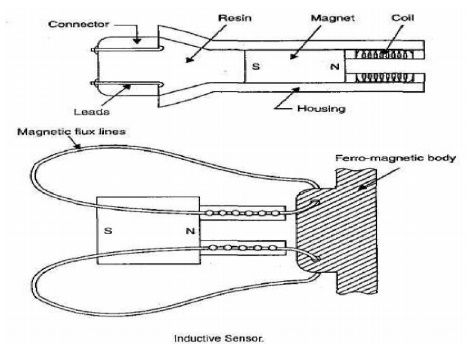
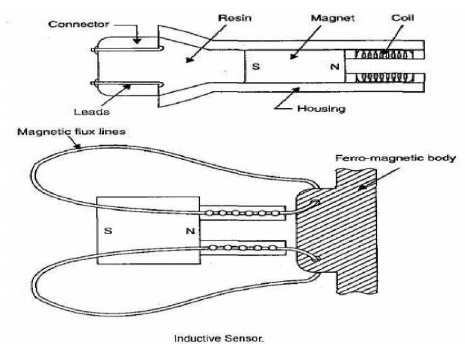
Inductive Proximity Sensors:
The ferromagnetic material brought close to this
type of sensor results in change in position of the flux lines of the permanent
magnet leading to change in inductance of the coil.
The induced current
pulse in the coil with change in amplitude and shape is proportional to rate of
change of flux line in magnet.
Construction:
The proximity inductive
sensor basically consists of a wound coil located in front of a permanent
magnet encased inside a rugged housing. The lead from the coil, embedded in
resin is connected to the display through a connector.
The effect of bringing the sensor in close proximity
to a ferromagnetic material causes a change in the position of the flux lines
of the permanent magnet.
Related Topics