Chapter: 9th Science : Living World of Plants - Plant Physiology
What is Photosynthesis?
What is Photosynthesis?
‘Photo’ means ‘light’ and ‘synthesis’ means ‘to
build’ thus photosynthesis literally means “building up with the help
of light”. During this process, the light
energy is converted into chemical energy. Green plants are autotrophic in their
mode of nutrition because they prepare their food materials through a process
called photosynthesis.

The overall equation of photosynthesis can be given
as follows:
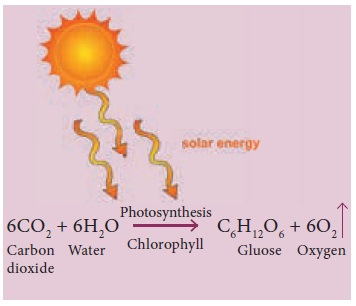
The end product of photosynthesis is glucose which
will be converted into starch and stored. Plants take in carbon dioxide for
photosynthesis; but for its living, plants also need oxygen to carry on
cellular respiration.

1. What else is needed for photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make
their food. A small speck of seed grows and gains weight into a giant tree, due
to photosynthesis. Almost all the other organisms rely on plants for their food
directly or indirectly. Even a carnivore depends ultimately upon plants for its
food, how? Can you highlight? Four important things needed by plants for
photosynthesis:
1. Chlorophyll
- Green pigment present in leaves
2. Water
3. Carbon
dioxide (from air)
4. Light
Let us examine two of these factors
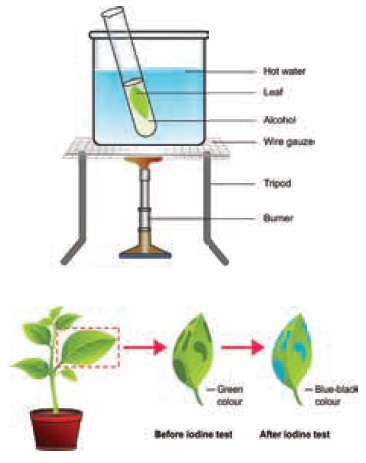
Chlorophyll
Aim: To show
that chlorophyll is essential for
photosynthesis.
We need Coleus (croton)
plant with variegated leaves,
boiling water, alcohol and iodine solution.
Variegated leaf is plucked from Coleus plant kept in sunlight after
de-starching by keeping it in dark room for 24 hours. The picture of the leaf
is drawn and the patches of cholorphyll on the leaf are marked. After immersing
the leaf in boiling water then in alcohol it is tested for starch with iodine
solution.
What do
you observe? The patches of the leaf with chlorophyll turn blue-black. The other portions remain colourless.
What you
conclude? The chlorophyll is essential
for photosynthesis.
Plants take up water through their roots and air
through stomata of their leaves. Chlorophyll is present in the leaf. What else
is needed for photosynthesis? The question that remains to be answered is
whether the process of forming starch by combining carbon dioxide and water
also requires light. Let us do an experiment.
Light
Aim: To show
that sunlight is necessary for
photosynthesis.
What do
you need? potted plant, black paper,
boiling water, alcohol and iodine solution.
How to do?
A potted plant is placed in a dark room for about 2
days to de-starch its leaves. One of its leaves is covered with the thin strip
of black paper as shown in the picture. make sure that the leaf is covered on
both sides.

The potted plant is kept in bright sunlight for 4
to 6 hours. The selected covered leaf is plucked and the black paper is
removed. The leaf is immersed in boiling water for a few minutes and then in
alcohol to remove chlorophyll. The leaf is now tested with iodine solution for
the presence of starch. The covered part of the leaf does not turn blue-black
whereas the uncovered part of the leaf turns blue-black colour. The covered
part of the leaf which did not receive the sunlight was unable to synthesize
starch. Hence it does not turn blue-black colour. But the uncovered part of the
leaf which received sunlight was able to synthesise starch and so it turns
blue-black in colour.
All these four things must be in the leaf, the site
where plants make their food. That raises an interesting question. Of the four,
chlorophyll is present in the leaf. Sunlight falls on the leaf. But how do
plants take air and water to its leaf? How does the water reach the leaves from
the roots? What path does it follow? How does air enter the leaf?
2. Exchange of gas
Roots of the plant take the water from the soil and
transport it to leaves. How water and other nutrients reach the leaf from the
roots? Is the only question that we need to find out? We will see this later.
This leaves us with only one question? How does the plant get air? The leaves
have tiny holes, called stomata,
through which the exchange of air takes place. These holes are so minute that
we need a microscope to see them. The air exchange takes place continuously
through the stomata. Plants inhale and exhale continuously through these
stomata.
3. Transpiration
The loss of water in the form of water vapour from
the aerial parts of the plant body is called as transpiration. There are three
types of transpiration:
1. Stomatal
transpiration - This is the most dominant form of transpiration being
responsible for most of the water loss in plants. It accounts for 90-95% of the
water transpired from leaves.
2. Cuticular
Transpiration – This type of transpiration is responsible for the loss of water
in plants via the cuticle.
3. Lenticular
Transpiration – This type of transpiration is the loss of water from plants as
vapor through the lenticels. The lenticels are tiny openings that protrude from
the barks in woody stems and twigs as well as in other plant organs.
Experiment 1
If you tie a plastic bag over a leaf and place the
plant in light, you will be able to see water condensing inside the plastic
bag. The water is let out by the leaves.

The leaves have tiny, microscopic holes called
stomata. Water evaporates through these stomata. Each stomata is surrounded by
guard cells. These guard cells help in regulating the rate of transpiration by
opening and closing of stomata.
Typically, only 0.1 percent of water taken up by
the plant is used by the plant for producing carbohydrates. That is, if a plant
absorbs one litre of water, only one millilitre will be used to produce
carbohydrate. The remaining 999 millilitres evaporates from the leaf. You will
be able to see how much water a plant releases in the air.


Suppose the weather is hot and the stomata close;
what would be the effect of such a situation in the absorption of carbon
dioxide? Will the rate of photosynthesis be the same? If the plant does not get
water at this time, what effect would this have on its growth? Relate your
answer to the problem of drought affecting agricultural growth. Global warming
implies increased level of average temperature. Can you reason what all the
effect it can have on photosynthesis?
4. Macronutrients and micronutrients
for plants
Nutrients such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
nitrogen, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur and phosphorus, are required
in substantial quantity and are called macronutrient.
Plants also require many other nutrients like iron, manganese, copper, boron,
molybdenum, chlorine, silicon, cobalt, and zinc, but only in minute quantities,
hence, they are called micronutrients.
The water transportation systems of
the plants take these nutrients from the soil and circulate it in the plant.

Related Topics