Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Spine Surgery
What are somatosensory and motor evoked potentials?
What are somatosensory and motor evoked potentials?
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is the
measurement of the spontaneous activity of the brain. Evoked potentials are a
measurement of the electrical responses “evoked” by a stimulus to the nervous
system. Evoked potential moni-toring is utilized in patients felt to be at high
risk for spinal cord injury from surgical trauma, operative position, or
impairment of blood supply.
The most commonly utilized evoked potentials
are those produced by stimulation of the sensory system: somatosen-sory evoked
potentials (SSEPs). In this technique a peripheral nerve (e.g., posterior
tibial or median) is stimulated and the neural response measured. A
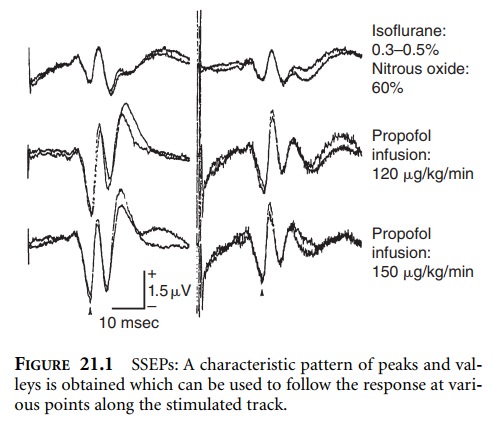
characteristic pattern of peaks and valleys is obtained which can be used to
follow the response at various points along the stimulated tract (Figure 21.1).
This technology intermittently determines the integrity of the posterior spinal
sensory pathways and large peripheral nerves. Significant changes in the SSEPs
may consist of alterations in amplitude, latency, and/or morphology compared
with baseline waveforms. Changes in SSEP waves that indicate possible
disruption of the sensory pathway include a decrease in the amplitude of the
waveform and an increase in the latency of those waves.
Motor evoked potentials (MEPs) are electrical
impulses measured in the peripheral nerves and muscles in response to
stimulation of the cortex or spinal cord. MEPs may be used in conjunction with
SSEPs when there is a possibility of injury to the motor pathways in the
anterior spinal cord. Two basic techniques for stimulating the cerebral motor
cortex are direct transcutaneous electrical stimulation and transcutaneous
magnetic stimulation. Addition of MEPs to SSEP monitoring may increase
detection of potential injury by as much as 10%. MEPs may also be useful in the
detection of spinal cord ischemia during aortic cross-clamping for
thoraco-abdominal aneurysm repair.
Related Topics