Chapter: Plant Biology : Spore bearing vascular plants
Water ferns
Water ferns
The aquatic ferns do not resemble typical ferns and are the only heterosporous ferns. Members of one of the two families, the Marsileaceae, have a rhizomesubmerged or in mud and aerial leaves a few centimeters high resembling clover with two or four leaves, or grass. The sporangia derive from one cell, so are leptosporangiate but have no specialized dispersal. They are borne on separate short stems in a hard oblong or spherical body a few millimeters long covered with rough hairs, the ‘pills’ of the pillwort (Pilularia; Fig. 5). They produce sori inside these, each sorus bearing both megasporangia and microsporangia. Only one spore matures in each megasporangium. Spores are released into water.
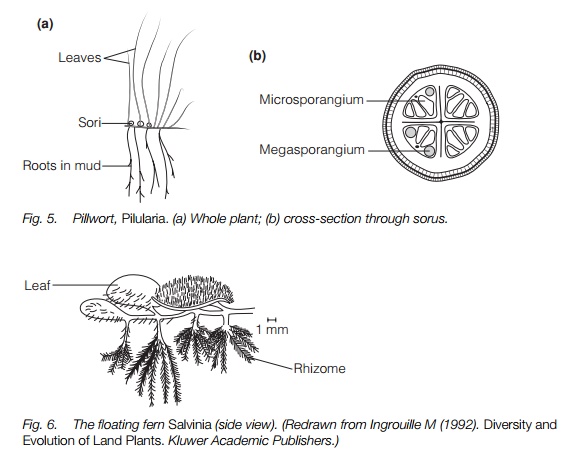
The two genera of floating water ferns are not attached to a substrate and both spread vegetatively in a similar way to other floating flowering plants. Salvinia (Fig. 6) has whorls of three simple leaves 3–10 mm long on each rhizome and no roots. Azolla has a tiny two-lobed leaf, with a cavity in the lower lobe containing a cyanobacterium that fixes nitrogen and roots trailing into the water from the nodes. Megasporangia and microsporangia are produced separately on the undersides of the leaves and spores released are into the water. In Azolla there is one megaspore per sporangium, but Salvinia has more than one.
Related Topics