Plant Growth and Development - Vernalization | 11th Botany : Chapter 15 : Plant Growth and Development
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 15 : Plant Growth and Development
Vernalization
Vernalization (Vernal – Spring Like)
Besides
photoperiod certain plants require a low temperature exposure in their earlier
stages for flowering. Many species of biennials and perennials are induced to
flower by low temperature exposure (0oC to 5oC) . This
process is called Vernalization. The
term Vernalization was first used by T.
D. Lysenko (1938).
1. Mechanism of Vernalization:
Two main
theories to explain the mechanism of vernalization are:
i.
Hypothesis of phasic development
ii.
Hypothesis of hormonal involvement
i. Hypothesis
of phasic development
According
to Lysenko, development of an annual seed plant consists of two phases. First
phase is thermostage , which is
vegetative phase requiring low temperature and suitable moisture. Next phase is
photo stage which requires high temperature for synthesis of florigen (flowering hormone).
ii. Hypothesis of hormonal involvement
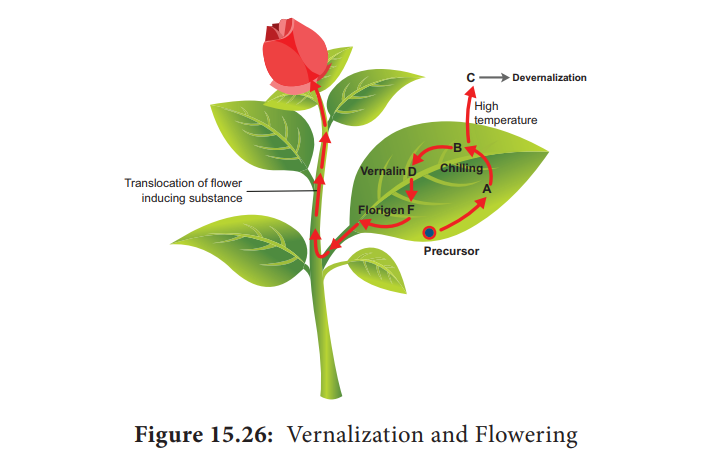
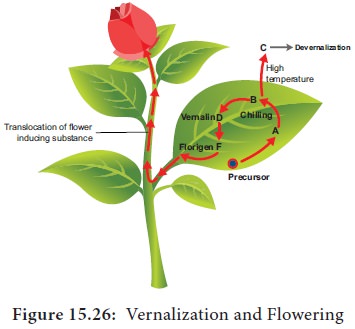
According
to Purvis (1961), formation of a
substance A from its precursor, is converted into B after chilling. The
substance B is unstable. At suitable temperature B is converted into stable
compound D called Vernalin. Vernalin
is converted to F (Florigen). Florigen induces flower formation. At high
temperature B is converted to C and devernalization occurs (Figure 15.26).
2. Technique of Vernalization:
The seeds
are first soaked in water and allowed to germinate at 10o C to 12o
C. Then seeds are transferred to low
temperature (3oC to 5oC) from few days to 30 days.
Germinated seeds after this treatment are allowed to dry and then sown. The
plants will show quick flowering when compared to untreated control plants.
3. Devernalization
Reversal
of the effect of vernalization is called devernalization.
4. Practical applications
1.
Vernalization shortens the vegetative period and
induces the plant to flower earlier.
2.
It increases the cold resistance of the plants.
3.
It increases the resistance of plants to fungal
disease.
4.
Plant breeding can be accelerated.
Related Topics