Chapter: Mechanical : Metrology and Measurements : Measurement of Power, Flow and Temperature Related Properties
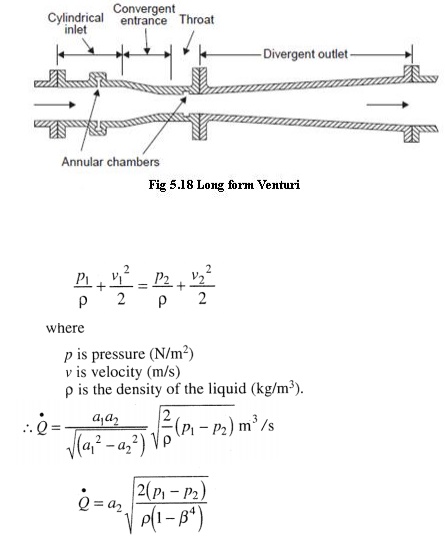
Venturi Meter
Venturi Meter
It consists of a cylindrical inlet section equal to the pipe diameter, a converging conical section in which the cross sectional area decreases causing the velocity to increase with a corresponding increase in the velocity head and a decrease in the pressure head; a cylindrical throat section where the velocity is constant so that the decreased pressure head can be measured and a diverging recovery cone where the velocity decreases and almost all of the original pressure head is recovered. The unrecovered pressure head is commonly called as head loss.
Limitations
This flow meter is limited to use on clean, non- corrosive liquids and gases, because it is impossible to clean out or flush out the pressure taps if they clog up with dirt or debris.
Short Form Venturi Tubes
In an effort to reduce costs and laying length, manufactures developed a second generation, or short-form venturi tubes shown in Figure 5.19.
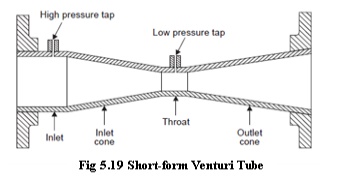
There were two major differences in this design. The internal annular chamber was replaced by a single pressure tap or in some cases an external pressure averaging chamber, and the recovery cone angle was increased from 7 degrees to 21 degrees. The short form venture tubes can be manufactured from cast iron or welded from a variety of materials compatible with the application.
The pressure taps are located one-quarter to one-half pipe diameter upstream of the inlet cone and at the middle of the throat section. A piezometer ring is sometimes used for differential pressure measurement. This consists of several holes in the plane of the tap locations. Each set of holes is connected together in an annular ring to give an average pressure. Venturis with piezometer connections are unsuitable for use with purge systems used for slurries and dirty fluids since the purging fluid tends to short circuit to the nearest tap holes. Piezometer connections are normally used only on very large tubes or where the most accurate average pressure is desired to compensate for variations in the hydraulic profile of the flowing fluid. Therefore, when it is necessary to meter dirty fluids and use piezometer taps, sealed sensors which mount flush with the pipe and throat inside wall should be used. Single pressure tap venturis can be purged in the normal manner when used with dirty fluids. Because the venturi tube has no sudden changes in contour, no sharp corners, and no projections, it is often used to measure slurries and dirty fluids which tend to build up on or clog of the primary devices.
Related Topics