Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Types Of Crystals
TYPES OF CRYSTALS
Crystals are classified into the following four types
depending upon the
nature of the units which occupy the lattice points.
1. Molecular Crystals 2. Covalent
Crystals
3. Metallic Crystals 4. Ionic
Crystals
1
Molecular Crystals
The lattice points in molecular crystals consist of
molecules which do not carry any charge. The forces binding the molecules
together are of two types (i)
Dipole-dipole interaction and (ii) Vanderwaal's forces. Dipole-dipole forces occur in solids which consists of polar molecules e.g.,
ice. The Vanderwaal's forces are more
general and occur in all kinds of molecular solids.
2
Covalent Crystals
The lattice in covalent crystals consists of atoms linked
together by a continuous system of covalent
bonds. Diamond is a good example for this type.
3
Metallic Crystals
Metallic crystal consists of an assemblage of positive
ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons. Thus, each electron belongs to a
number of positive ions and each positive
ion belong to a number of electrons. The force that binds a metal ion to a
number of electrons within its sphere of influence is known as metallic bond. This force of attraction is strong and is thus
responsible for a compact solid
structure of metals.
4
Ionic Crystals
In ionic crystals, the units occupying lattice points are
positive and negative ions. Each ion of a given sign is held by coulombic
forces of attraction to all ions of
opposite sign. The forces are very strong. The ionic crystals have the
following
characteristics.
i.
The heats of vapourisation of ionic
crystals are high.
ii.
The vapour pressure of ionic crystals at
ordinary temperature are very low.
iii.
The melting and boiling points of ionic
crystals are very high.
iv.
Ionic crystals are hard and brittle.
v.
Ionic crystals are insulators in the
solid state.
vi.
Ionic crystals are soluble in water and
also in other polar solvents. Ionic solids are good conductors when dissolved
in water.
5 Types of Ionic Crystals
The structure of ionic crystals is determined by the
ratio of the numbers, the ratio of the sizes and the structural units. In general,
ionic crystals are classified into AB and AB2 type.
Substance of the general formula AB mostly crystallise in
one of the following six forms.
AB
AB AB AB AB AB
Lattice
type :
CsCl NaCl FeS ZnO ZnS BN
Coordination
number :8
6 6 4 4 3
Let us discuss the structure of CsCl for AB type. It is
body centered cubic system. The chloride ions are at the corners of a cube
where as Cs+ ion is at the centre of the cube or vice versa. Each Cs+ ion is connected with eight Cl- ion and Cl- is connected with eight Cs+ ions.
Number of chloride ions per unit = Nc/8 = 8/8 =1
Number of cesium ion per unit = Nb/1 = 1/1 =
1
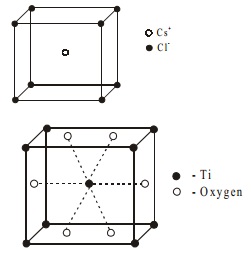
Thus number of CsCl units per unit cell is one.
Compounds having the general formula AB2 generally crystallise in forms based on the following eight typical lattices like CO2, SiO2, TiO2, CaF2, Cu2O, FeS2, CdI2 and MoS2. For example
Rutile (TiO2)
has the following structure.
Related Topics