Chapter: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Fundamentals and Applications : Oligonucleotides
Triple Helix-Forming Oligonucleotides
Triple Helix-Forming Oligonucleotides
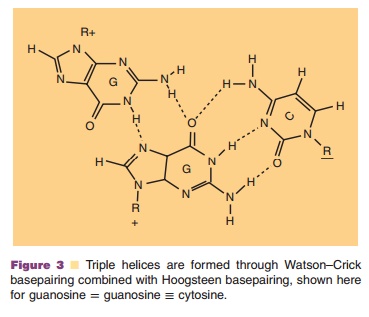
Triple helix-forming oligonucleotides, also known as TFO, act at the
level of transcription of mRNA. Triple helix formation occurs when a polypurine
or poly-pyrimidine DNA or RNA oligonucleotide binds to a
polypurine/polypyrimidine region of genomic DNA. Triple helix-forming ONs can
bind specifically in the major groove of such stretches of DNA to the
polypurine strand, forming (reverse) Hoogsteen hy-drogen bonds (Fig. 3) (Rogers
et al., 2005).
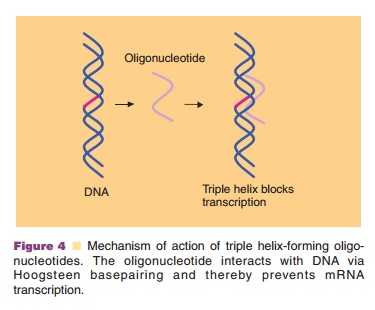
As a result of this binding, triplex-forming ONs can prevent
transcription initiation or elongation by binding promoter, gene or regulatory
DNA regions (Fig. 4). The concept has been validated in vivo,
Triplex-forming ONs have also been used for site-directed mutagenesis
with or without the use of coupled mutagens, as well as
homologous-site-specific recombination using triple-forming ONs alone or in
combination with a donor fragment to correct genetic disorders. This
application will be discussed in the section on gene repair.
Related Topics