Chapter: Physics : Quantum Physics
Transmission Electron microscope - Principle, Construction, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages
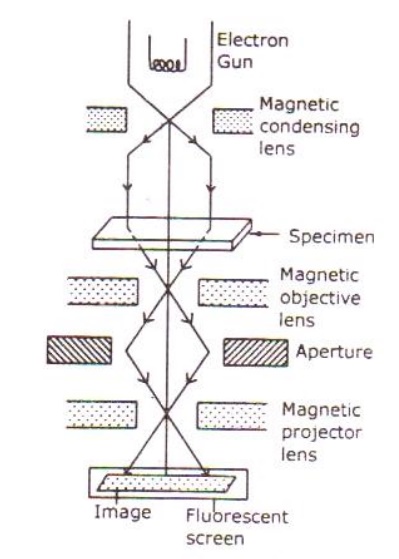
Principle:
Electrons are made to pass through the specimen and the image is formed on the fluorescent screen, either by using the transmitted beam or by using the diffracted beam.
Construction:
It consists of an electron gun to produce electrons. Magnetic condensing lens is used to condense the electrons and is also used to adjust the size of the electron that falls on to the specimen. The specimen is placed in between the condensing lens and the objective lens as shown.
The magnetic objective lens is used to block the high angle diffracted beam and the aperture is sued to eliminate the diffracted beam (if any) and in turn increases the contrast of the image.
The magnetic projector lens is placed above the fluorescent screen in order to achieve higher magnification,. The image can be recorded by using a fluorescent (Phosphor) screen or (CCD – Charged Coupled device) also.
Working:
Stream of electrons are produced by the electron gun and is made to fall over the specimen using the magnetic condensing lens.
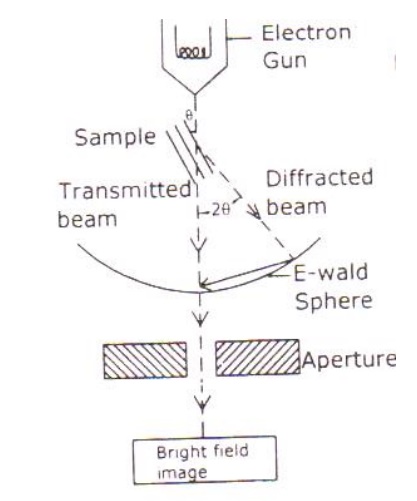
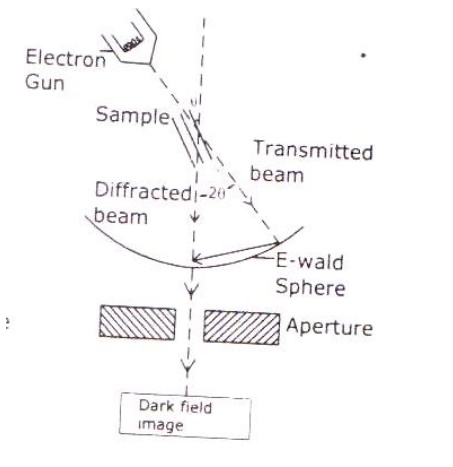
Based on the angle of incidence the beam is partially transmitted and partially diffracted. Both these beams are recombined at the E-wald sphere to form the image. The combined image is called the phase contrast image.
In order to increase the intensity and the contrast of the image, an amplitude contrast has to be obtained. This can be achieved only by using the transmitting beam and thus the diffracted beam can be eliminated.
Now in order to eliminate the diffracted beam, the resultant beam is passed through the magnetic objective lens and the aperture. The aperture is adjusted in such a way that the diffracted image is eliminated. Thus, the final image obtained due to transmitted beam alone is passed through the projector lens for further magnification.
The magnified image is recorded in fluorescent screen or CCD. This high contrast image is called Bright Field Image.
Also, it has to be noted that the bright field image obtained is purely due to the elastic scattering (no energy change) i.e., due to transmitted beam alone.
Related Topics