Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Train Resistance and Tractive Power
Train Resistance Due to Wind
Various forces offer resistance
to the movement of a train on the track. These resistances may be a result of
the movement of the various parts of the locomotives as well as the friction
between them, the irregularities in the track profile, or the atmospheric
resistance to a train moving at great speed. The tractive power of a locomotive
should be adequate enough to overcome these resistances and haul the train at a
specified speed.
Resistance Due to Wind
When a vehicle moves with speed, a certain resistance
develops, as the vehicle has to move forward against the wind. Wind resistance
consists of side resistance, head resistance, and tail resistance, but its
exact magnitude depends upon the size and shape of the vehicle, its speed, and
wind direction as well as velocity. Wind resistance depends upon the exposed
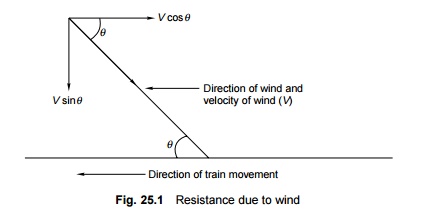
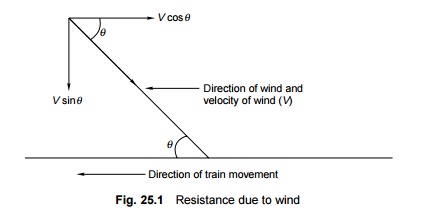
area of the vehicle and the velocity and direction of the wind. In Fig. 25.1, V
is the velocity of wind at an angle q . The
horizontal component of wind, V cosq ,
opposes the movement of the train. Wind normally exerts maximum pressure when
it acts at an angle of 60 o to the direction of the movement of the train.
Wind
resistance can be obtained by the following formula:
R3
= 0.000017AV2 (25.3)
where A is the exposed area of vehicle (m2)
and V is the velocity of wind (km/h).
Studies also support the fact
that the important factors that affect wind resistance are the exposed area of
the vehicle and the relative velocity of the wind vis-à-vis that of the
vehicle. In fact, wind resistance depends upon the square root of the velocity
of the wind. The following formula has been empirically established on the
basis of studies.
|
R3 =
0.0000006WV2 |
(25.4) |
where R3 is the wind resistance in tonnes, V
is the velocity of the train in km/h, and W is the weight of the train
in tonnes.
Related Topics