Chapter: Electrical machines : Synchronous Motors
Torque and Power Relations
Torque and Power Relations
Motor Torque
Gross torque, T =9.55 Pm/Ns N-M where Pm = Gross motor output in watts = Eb Ia cos(d - ф)
Ns = Synchronous speed in r.p.m.
Shaft torque, Tsh = 9.55 Pshout/Ns N-M
It may be seen that torque is directly proportional to the mechanical power because rotor speed (i.e., Ns) is fixed.
Mechanical Power Developed
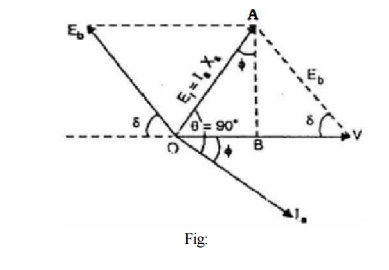
Neglecting the armature resistance Fig: 2.25 shows the phasor diagram of an under-excited synchronous motor driving a mechanical load. Since armature resistance Ra is assumed zero. tanq= Xs/Ra = ¥ and hence q =90°.
Input power/phase = V Ia cos ф
Since Ra is assumed zero, stator Cu loss (I Ra)2 will be zero. Hence input power is equal to the mechanical power Pm developed by the motor.
Mechanical power developed/ phase, Pm = V Ia cos ф, referring to the phasor diagram in Fig: .

Related Topics