Chapter: Biology: Structural Organization and Acquaintance of Animals
Toad: Excretory system
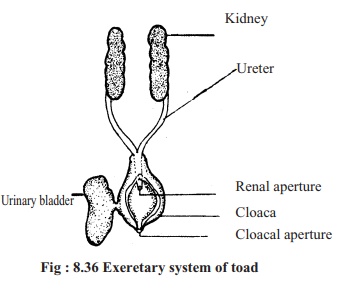
Excretory system : During metabolism in the body of toad various types ofnitrogenous excretory products are produced. These substances are of no use to the body, but may cause harm if remain inside the body for a long time. So it is essential to remove these nitrogenous waste products from the body. The process through which nitrogen enriched excretory products, produced due metabolism is eliminated from the body is called excretion. Kidney is the main organ of excretion.
Excretory system and Excretion process
The excretory system of toad is formed by the following organs.
A. Kidney
B. Ureter or Urinogenital duct
C. Urinary bladder
D. Cloaca
E. Cloacal aperture.
Kidney: The two kidneys of toad are located in the abdominal region on theboth sides of the backbone. The kidneys are elongated, deep red coloured with the anterior and posterior ends slightly pointed. The outer part of the kidney convex and wavy and the inner side smooth. Each kidney remains covered by a thin is membrane called peritoneum.
Functions:
1. To assist in the removal of nitrogenous waste products and other unwanted materials.
2. To control the balance of water in the body.
Structure of Kiney
The kidney can be divided into two parts :
i. Renal wall
ii. Renal cavity.
i. Renal wall: It is the outer part of the kidney. This wall is divided into twoparts.
· Outer part or cortex, and
· Inner part or medulla.
The renal wall encircles a cavity in the middle portion of the kidney.
ii. Renal cavity: The renal cavity is surrounded by the renal wall. This, cavity remains connected with the Ureter.
Microscopic structure of kidney:
Each kidney of toad is formed by the combination of numerous fine coiled renal tubules. In each kidney there are about two thousand such coiled microscopic tubules. These tubules are called nephrons. Each nephron is divided into two portions.
a) Malpighian body or organ
b) Renal tubules.
a. Malpigbhian organ: It is the anterior rounded part of the nephron. Thisorgan is again formed of two parts, such as: Bowman's capsule and Glomerulus.
1. Bowman's capsule and Glormerulus
At the free end of each renal tubulethere is a closed cup-like part called theBowman's capsule. The wall of this cupis formed of an epithelial cell layer.branch of the renal artery enters thecavity of the Bowsman's capsule. Thisbranch of the artery is known as afferent artery. Inside the cavity of Bowmans capsule the afferent artery form a cluster of blood capillaries.
This cluster is called glomerulus. Joining together these blood capillaries form an efferent artery. Glornmerulus and Bowman's capsule together are called Malpighian body or Malpighian Organ. This part of the kidney is situated in the cortex or wall of the kidney.
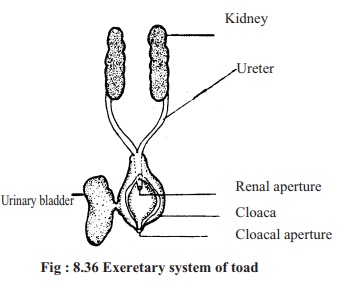
b. Renal tubules: The duct like tubule behind the Bowman's capsule is calledthe renal tubule. This tubule being turned into coil opens into the collecting duct. The collecting duct ultimately opens into the ureter. The tubule is surrounded by the branches of efferent artery.
Ureter: From the outer end of each kidney a whitish elastic duct originates andgoes towards the posterior part of the body. This duct is known as ureter. The ureters of the two sides meet and form a common renal duct and opens into the cloaca through a common renal aperture.
Urinary bladder: The thin, incompletely divided sac situated on the ventralside of the cloaca is called urinary bladder. Urine is stored here temporarily. The urinary bladder opens into the cloaca through an aperture.
Cloaca: The cloaca is situated behind the rectum. It is a narrow chamber. Theurinary bladder opens into the cloaca through the renal aperture. Through it urine passes towards the cloacal aperture.
Cloacal aperture: The cloacal aperture is situated at the posterior end of thebody. Through this aperture stool, urine, sperms and ova are discharged outside.
Excretion process
Amino acid is produced due to digestion of protein. This amino acid is used to perform various Biological functions. Excess and unused amino acid under the influence of enzyme named de-aminase takes part in de-amination process. In this de-amination process amine reacts with water to produce ammonia, thus ammonia is separated from the amino acid. Ammonia is a harmful substance for the body of the toad.
Along with blood, ammonia reaches the liver. There under the influence of an enzyme, urginase, ammonia by reacting with carbon dioxide produces urea and water.
In kidney

You have learnt earlier that the afferent branches of the renal arteries dividing into numerous fine blood capillaries form the glomerulus. Through these afferent branches blood enters the glomerulus and passes through the capillaries. Due to high blood pressure, urea, glucose, and othersoluble substances of blood enter the renal tubules crossing by the delicate walls of glomerulus and Bowman's capsule. Refined blood leaves the Bowman's capsule through different arteries. By the cells of the walls of renal ducts water, glucose, sodium chloride and other substances are absorbed from the solution inside these ducts. Residues are discharged with urea from thebody by uretor.
Related Topics