Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
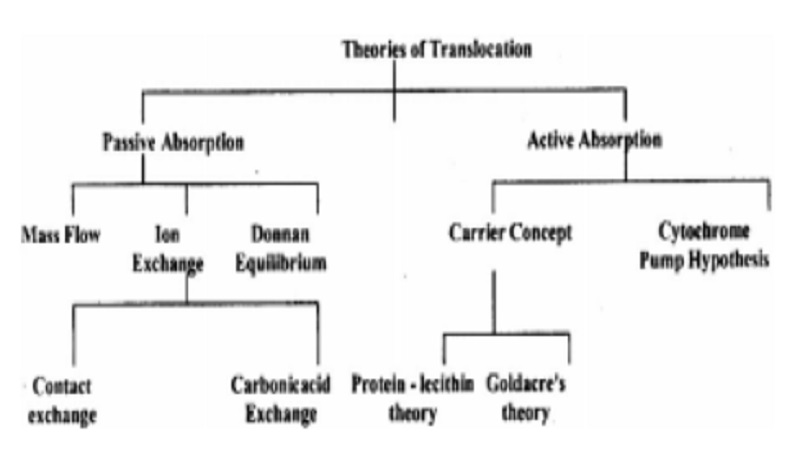
Theories of Translocation for Plant : Passive absorption and Active Absorption
Theories of Translocation for Plant
Plants absorb minerals from the soil and translocate them to other parts of the body. Minerals are absorbed in the form of soil solution contained in the pore spaces between the soil particles and the root hair. The soil solution contains the mineral salts in the dissolved state. Several theories have been put forth to explain the mechanism of translocation of mineral salts. These theories can be placed under two headings (i) Passive absorption and (ii) Active Absorption which can be further subdivided as follows.
i. Passive Absorption
When the movement of mineral ions into the roots occurs by diffusion without any expenditure of energy in the form of ATP it is called Passive Absorption. This form of absorption is not affected by temperature and metabolic inhibitors. Rapid uptake of ions is observed when a plant tissue is transferred from a medium of low concentration to a medium high concentration. Various theories have been put forward to explain mineral salt uptake by passive absorption.
(a) Ion exchange theory
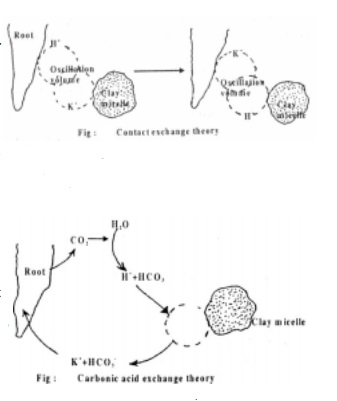
Mineral elements are absorbed in the form of ions. The anions and cations within the plant cells are exchanged with the anions and cations of equivalent charge from the external medium in which the cells are kept. This mechanism can be explained by two theories.
(i) Contact exchange theory
(ii) Carbonic acid exchange theory : According to this theory the soil solution plays an important role in exchange of ions by providing a medium. CO2 released during respiration combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) which dissociates as H+ (Hydrogen ions) and HCO3 (bicarbonate ions). A cation adsorbed on clay micelle may be exchanged with the H+ of soil solution and this cation diffuses into the root in exchange for H+ion.
(b) Donnan Equilibrium
This was proposed by F.G.Donnan in which the fixed or indiffusible ions play an important role. These ions are present on the inner side of the cell and cannot diffuse out. When a cell having fixed anions is immersed in sals solution, anions equal in number and charge to the fixed ions move into the cell. To balance the negative charges of the fixed ions additional cations also move into the cell and the cell sap cation concentration becomes higher than the external medium. This is called Donnan Equilibrium.
In the same way if there are fixed cations, additional anions will accumulate from the external medium.
II. Active Absorption
The absorption of ions against the concentration gradient with the expenditure of metabolic energy is called active absorption. In plants, the vacuolar sap shows accumulation of anions and cations against the concentration gradient which cannot be explained by the theories of passive absorption. The mechanism of active absorption of salts can be explained by several theories.
(a) Carrier Concept
The cell shows the presence of Carriers or transporters which are highly specific for a particular ion. The carrier picks up an ion from external medium to form a carrier-ion complex, undergoes rotation at 180 o , moves across the membrane and releases the ions on the inner side of membrane and returns to pick up another ion. The carrier may be an enzyme or a protein. Metabolic energy is expended in this process. This concept is supported by Isotopic exchange using radioactive isotopes, saturation effect andspecificity of carriers. The carrier concept is explained by two theories:
specificity of carriers. The carrier concept is explained by two theories:
(i) Protein-Lecithin as carrier
(ii) Goldacre's theory
Protein - Lecithin as carrier
Bennet - Clark proposed that the carrier can be a protein associated with a phosphatide e.g. Lecithin which carries both anions and cations and forms a lecithin-ion complex. this moves to the inner side of membrane, releases the ion by hydrolysis forming phosphatidic acid and choline due to the action of the enzyme lecithinase. Lecithin is regenerated with the help of enzymes Choline esterase and choline acetylase. This requires expenditure of metabolic energy.
(b) Cytochrome Pump Theory or Electron Transport Theory
This theory was proposed by H.Lundegardh (1954) who suggested that anions could be transported across the membranes by cytochrome system utilising energy released by direct oxidation of respiratory intermediates.
The important postulates are:
i) Only anions can be actively transported.
ii) Cytochromes act as carriers in absorbing anions.
iii) Oxygen gradient helps in oxidation at outer surface and reduction at the inner surface.
iv) Transport of cations can be along the electrical gradient created by ion accumulation.
v) Selectivity in ion absorption cannot be explained and
vi) this is absent in plants respiring anaerobically.
Therefore this theory explains respiration due to anion absorption which was called anion respiration or salt respiration.
Related Topics