Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Urinary System
The breast
The breast
The
breasts, otherwise known as the mammary glands are the accessory organs of
reproduction. They are two in number. Shape: the breast is hemispherical in
shape in nulliparae and pendulous in multiparae.
Situation:
the breasts are situated on either sides of the sternum. They lie on the
superficial fascia of the anterior chest wall, over the pectorialis major
muscles. Each breast extends from the 2nd above to the 6th
rib below and are stabilized by the suspensory ligament.
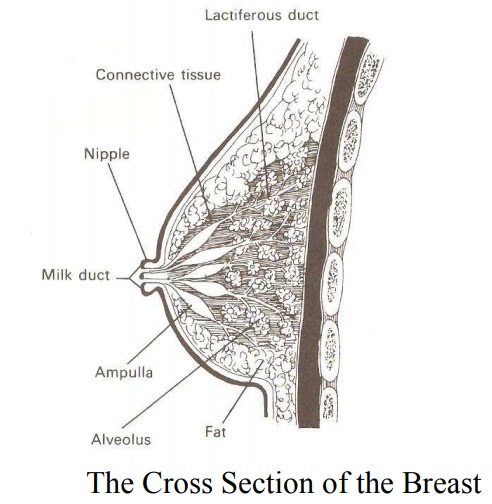
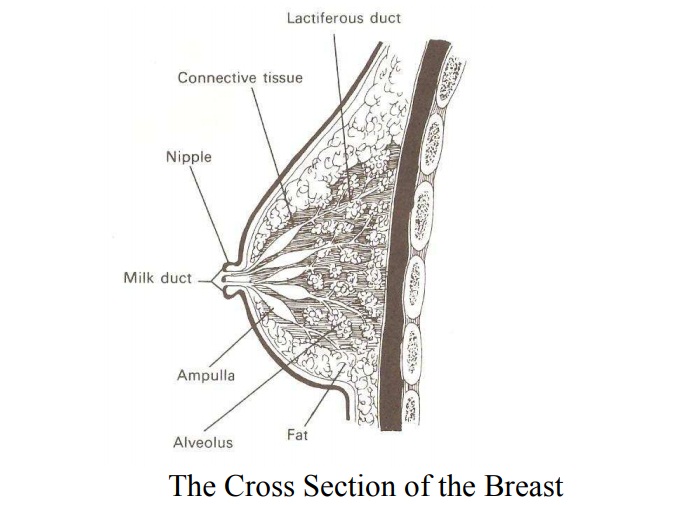
Gross structure: the size of the breast varies
with individuals,stage of development and age. At birth the breast is
rudimentary, at puberty the breast develops and develop even further during
pregnancy. At the centre of breast is a pigmented circular area,
about
2.5cm wide known as the areola. It surrounds the nipple. During pregnancy it is
darker in colour known as the primary areola and enlarges further known as
secondary areola. At the center of the areola is the nipple. The nipple is made
up of erectile muscle. The surface of the nipple is perforated by small
orifices known as the milk ducts. Within the areola are about 20 sebaceous
glands. It secretes sebum which lubricates the nipple during pregnancy and
breast feeding. During pregnancy it is known as Montgomery’s tubercles. The
breast has axillary tail which extends to the axilla.
Microscopic Structure: the
breat is made up of mainly secretaryglands known as glandular tissue and some
fatty tissue and it is covered by the skin. The glandular tissue is divided
into about 20 lobes which are separated by fibrous tissue. Each lobe is an
independent working unit and is made up of the following parts:
1.
Alveoli – it is made of acini cells which are the m
ilk secreting cells surrounded by myo-epithelial cells.
2.
Lactiferous tubules – these are small ducts which c
onnects the alveoli.
3.
Lactiferous ducts – a center duct into which the tu
bules run.
4.
Ampulla – the widened part of the duct where milk i
s stored reservoir.
5.
Milk Ducts – these open into nipples.
Blood Supply:
the breast are richly supplied with blood
·
Internal and External mammry arteries: (which
branches of subclavia and thoracic and axillary arteries) and branches from
upper intercostals arteries
·
Venous Drainage: mammary and axillary vein – arrang
ed in circular fashion around the nipple.
·
Lymphatic Drainage: axillary glands and portal
fissure of the liver. Gland in the anterior mediasternum.
·
Nerve Supply: nervous supply is poor because
function is controlled by hormones.
i.
Thoracic nerves supply the skin
ii.
Sympathetic nerves supply the areola and nipple.
Function of the breasts
i.
To manufacture milk
ii.
To supply milk for the infant
iii.
Beautifies womens’ sex organ
Related Topics