Chapter: Business Science : Services Marketing : Service Marketing Opportunities
The Purchase Process for Services
THE PURCHASE PROCESS FOR SERVICES
CONSUMPTION VALUES:
It is a perceived value or utility an individual believes a specific choice will provide. Consumers purchase goods and services because they satisfy certain needs or wants in their lives. Businesses purchase goods and services for the same basic reactions: to satisfy the needs and wants of themselves or their clients.
FUNCTIONAL VALUE:
Perceived utility acquired when a particular choice provides utilitarian or functional benefits for the consumer.
SOCIAL VALUE:
Perceived utility acquired from making a purchase decision that is associated with a particular referent group. This group could be friends or it could be based on demographics such as age, sex, ethnic origin, or religion.
EMOTIONAL VALUE:
It is obtained when the choice stimulates feelings and emotions within the consumer. For many services, especially entertainment services, perceived emotional utility is an important motivating factor in the purchase decision.
EPISTEMIC VALUE:
It is acquired when a purchase decision is perceived to satisfy a desire for knowledge, provide novelty, or arouse curiosity.
CONDITIONAL VALUE:
It is the perceived utility provided when an alternative is chosen because of temporary situational factors that will enhance one of the other consumption values. Finances may be a temporary situational factor that would alter a purchase decision.
A PURCHASE MODEL FOR SERVICES:
The purchase model for services has three distinct phases. The first phase is called the pre-purchase phase, which is when purchase options are contemplated and decisions are actually made..
PRE-PURCHASE PHASE:
The pre-purchase phase occurs before the consumer decides to purchase the service and usually involves a decision-making process that is influenced by four different factors: internal factors, external factors, firm-produced factors, and perceived risk.
INTERNAL FACTORS:
Four internal factors impact-purchase phaseconsumer„s.Thesefactorsare de individual needs and wants of consumers, past experience, expectations, and level of involvement. In
every purchase decision, the most important factor is the particular needs and wants of the individual. Not only do these needs and wants vary from one person to another but they also vary for each individual consumer.
EXTERNAL FACTORS:
Three external factors influence the purchase decision during the pre-purchase phase: the competitive options available to the consumer, the social context of the purchase, and word-of-mouth communications. The selection of a service is influenced by the social context of the purchase. Example: The hotel one selects for a business trip will probably differ from that chosen for a vacation.
FIRM-PRODUCED FACTORS:
Promotions, pricing and the distribution system are firm-produced factors that impact the purchase decision. Promotions include advertising, personal selling, and sales promotions, such as coupons, premiums, sweepstakes and contests. All of these promotional efforts are designed to persuade consumers to purchase particular services from a specific service provider.
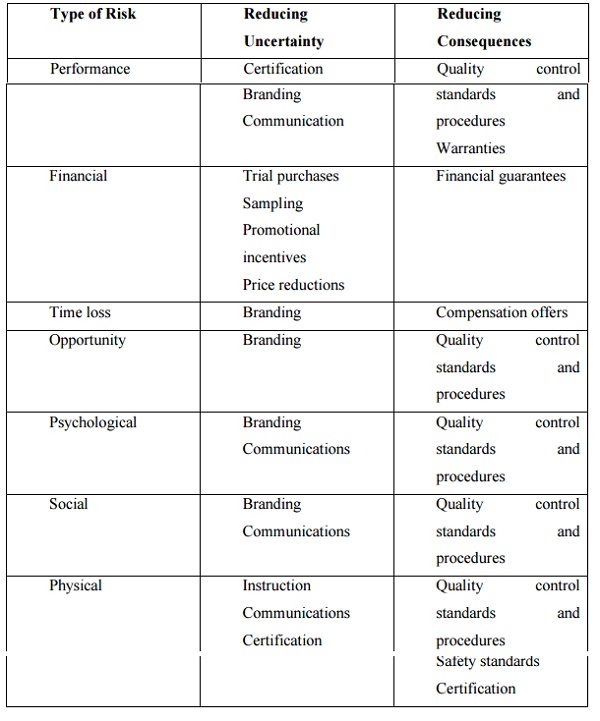
PERCEIVED RISK:
Risk is the exposure of the consumer to the chance of injury, loss or damage resulting from the purchase decision. Consumers seek means to reduce this risk through the use of the internal factors, the external factors, and the firm-produced factors discussed above. Risk has two components: uncertainty and
consequences.
PERFORMANCE RISK:
It is the chance that the service will not perform or provide the benefit for which it was purchased.
FINANCIAL RISK:
It is the amount of monetary loss incurred by the consumer if the service fails. Purchasing services involves a higher degree of financial risk than purchasing goods because fewer service firms have money back guarantees or warranties of any kind.
TIME LOSS RISK:
It refers to the amount of time lost by the consumer as a result of the failure of the service. A consumer who takes his or her automobile into a repair shop for servicing because it is running poorly will experience time loss if the vehicle is left there for six hours and the service performed does not correct the problem.
OPPORTUNITY RISK:
Risk involved when consumers must choose one service over another.
PSYCHOLOGICAL RISK:
Chance that the purchase of a service will no
SOCIAL RISK:
Probability that a service will not meet with approval from others who are significant to the consumer making the purchase.
PHYSICAL RISK:
Chance that a service will actually cause physical harm to the customer.
RISK REDUCTION STRATEGIES USED BY CONSUMERS:
How do consumers and businesses reduce the risk of a purchase? First, they examine their own personal experiences. Consumers tend to continue to patronize the same firm if they have not received bad service from that firm in the past. This is especially true if one has patronized a particular firm regularly. Going to a new service firm has a much higher element of the unknown, thus is a higher risk. As a result, there tends to be higher loyalty toward service firms than toward sellers of tangible goods.
STRATEGIES TO REDUCE PERCEIVED PURCHASE RISK:
THE SERVICE ENCOUNTER:
The second stage of the purchase process model is the service encounter, which is the actual interaction point between the customer and the service provider.
ROLE THEORY:
In the purchasing of services, consumers and service providers play certain roles in the transaction process, a concept referred to as role theory. Role Theory is similar to what occurs in Hollywood with the production of a movie. Individuals are hired to play a certain role. For example, Julia Roberts was hired to play a secretary in her Oscar award winning performance in Erin Brockovich.
1.call for an appointment
2. Go to dental office
3.Check in with the receptionist
4. Fill out papers
5. Wait in the waiting room
6. Taken to dental Chair by an assistant
11. X-rays and prep by an assistant
12. wait for dentist.
13. Dentist explains procedure
14. Dental procedure is performed.
15. Dentist explains dental care ane any instructions concerning procedure just performed
16. Cleaned by dental assistant
SCRIPT THEORY:
Scripts are a learned sequence of behaviors obtained through experience or through communication with others. Julia Robert‟s role in the movie script provided the details of how she was to perform the role and the way she should dress. The script provided both the actions and words to be used. In the service industry, the script provides the detailed
actions that are expected of service personnel and customers.
An example of a script that a patient may have for a dentist appears below:
It becomes a routinized behavior sequence in which the customer is not even cognizant of what is going on. He has done it so many times that little or no thought is required.
BENEFITS:
Understanding the script expected of customers allows firms to flowchart their operation. From this flowchart, operational flaws can be detected. In addition, scripts provide information for standardization of operations and enhancement of productivity.
CONSEQUENCES:
Altering scripts can also be frustrating to service personnel. Management must be sure all service personnel understand the new script and the benefits it provides. If the employee does not understand and recognize the benefits of the script change, it is doubtful it will be successful and accomplish the desired results.
THE SERVICE ENVIRONMENT:
The third component that affects the service encounter is the environment is which the service is performed. Tangible elements of the facility, of this environment.
SERVICE PERSONNEL:
In service encounters where service personnel and customers have face-to-face interaction, the most critical element of the experience becomes the conduct of the service personnel. Customers expect the service personnel to perform specific roles and follow certain scripts. Management must hire individuals qualified for the service jobs. Once hired, training should include scripts, role expectations, and guidelines for customer interaction. Incentives and compensation systems should encourage employees to provide high-quality service.
SUPPORT SERVICES:
Support services include all of the activities and materials service personnel need to perform their work properly. A primary responsibility of support services is to provide the equipment and supplies needed to perform the service. Example, for a dentist, the support services are the dental hygienist, chair-side assistant, and the receptionist.
POST PURCHASE PHASE:
The third stage of the purchase process is the post purchase phase. During the post purchase phase, customers make an evaluation of the service quality they received and their overall level of satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
Evaluation of Service Quality:
Compare what you perceive you received to what you expected to receive. If your expectations were met or exceeded, you will believe you received high quality service. If your expectations were not met, you will feel the quality of service was poor.
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION:
Service quality is a global evaluation of all past service experiences. Research has found that customers‟ perceived evaluations of service quali “Therefore, service quality evaluation is an a
ATTRIBUTION THEORY:
The process of deciding the cause of a service failure is called attribution theory. Idea in which a customer uses a process to analyze the level and cause of dissatisfaction with a service.
Related Topics