Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Equipment & Monitors : Breathing Systems
The Circle System
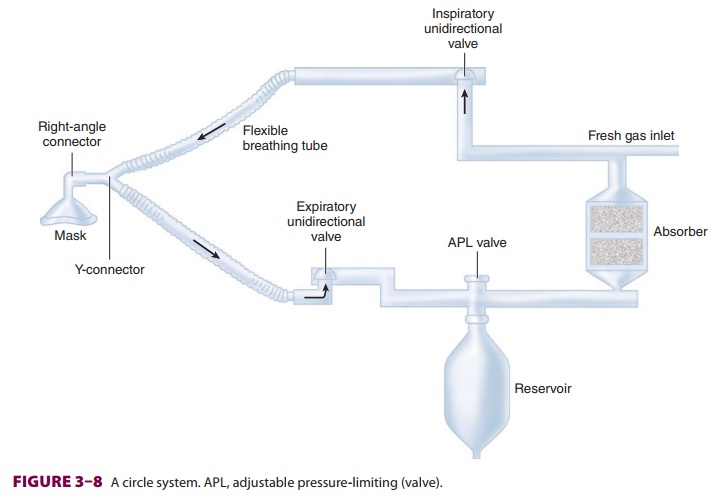
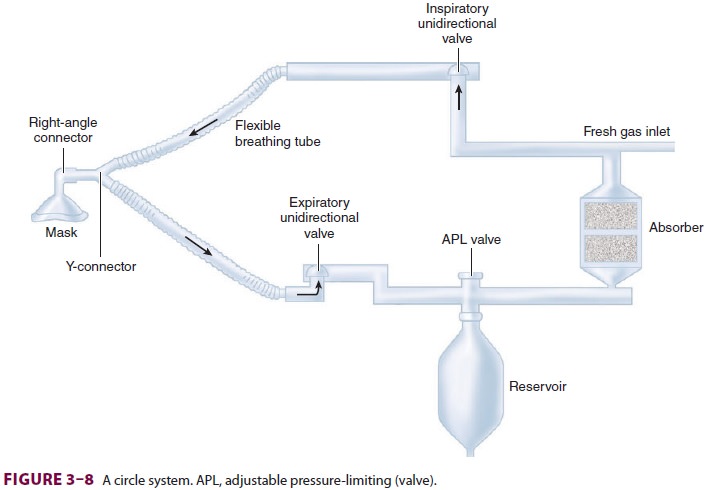
THE CIRCLE SYSTEM
Although Mapleson circuits overcome some
of the disadvantages of the insufflation and draw-over sys-tems, the high fresh
gas flows required to prevent rebreathing of CO2
result in waste of anesthetic agent, pollution of the operating room
environment, and loss of patient heat and humidity (Table 3–3). Inan attempt to
avoid these problems, the circle system
adds more components to the breathing system.
The components of a circle system
include: (1) a CO2 absorber containing CO2 absorbent; (2) a fresh gas inlet; (3) an
inspiratory unidirectional valve and inspiratory breathing tube; (4) a
Y-connector; (5) an expiratory unidirectional valve and expiratory breathing
tube; (6) an APL valve; and (7) a reservoir (Figure 3–8).
Related Topics