Chapter: Power Quality : Introduction to Power Quality
Terms and Definitions- Power Quality
Terms and Definitions:
1. Power Quality:
It is any deviation of the voltage or current waveform from its normal
sinusoidal wave shape.
2. Voltage quality:
Deviations
of the voltage from a sinusoidal waveform.
3. Current quality:
Deviations
of the current from a sinusoidal waveform.
4. Frequency Deviation:
An
increase or decrease in the power frequency.
5. Impulsive transient:
A sudden, non power frequency change in the steady state condition of
voltage or current that is unidirectional in polarity.
6. Oscillatory transients:
A sudden, non power frequency change in the steady state condition of
voltage or current that is bidirectional in polarity.
7. DC Offset:
The
presence of a DC voltage or current in an AC power system.
8. Noises:
An
unwanted electric signal in the power system.
9. Long duration Variation:
A variation of the RMS value of the voltage from nominal voltage for a
time greater than 1 min.
10. Short Duration Variation:
A variation of the RMS value of the voltage from nominal voltage for a
time less than 1 min.
11. Sag:
A
decrease in RMS value of voltage or current for durations of 0.5 cycles to 1 min.
12. Swell:
A Temporary increase in RMS value of voltage or current for durations of
0.5 cycles to 1 min.
13. Under voltage:
10% below
the nominal voltage for a period of time greater than 1 min.
14. Over voltage:
10% above
the nominal voltage for a period of time greater than 1 min.
15. Voltage fluctuation:
A
cyclical variation of the voltage that results in flicker of lightning.
16. Voltage imbalance:
Three
phase voltages differ in amplitude.
17. Harmonic:
It is a sinusoidal component of a periodic wave or quantity having a
frequency that is an integral multiple of the fundamental power frequency.
18. Distortion:
Any
deviation from the normal sine wave for an AC quantity.
19. Total Harmonic Distortion:
The ratio of the root mean square of the harmonic content to the RMS
value of the fundamental quantity.
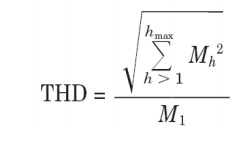
20. Interruption:
The complete loss of voltage on one or more phase conductors for a time
greater than 1 min.
Related Topics