Chapter: civil : Applied Hydraulic Engineering: Uniform Flow
Steady Uniform flow: The Chezy and Manning Equation
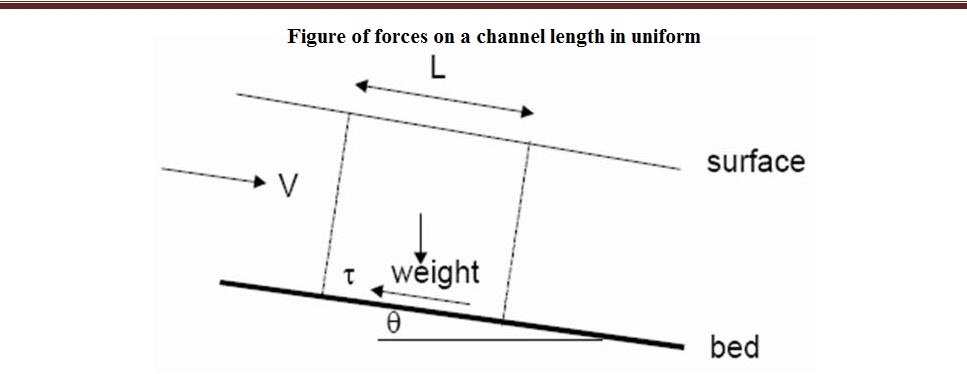
Steady Uniform flow
When
uniform flow occurs gravitational forces exactly balance the frictional
resistance forces which apply as a shear force along the boundary (channel bed
and walls).
Considering
the above diagram, the gravity force resolved in the direction of flow is Gravity
orce = rgAL sinq
and the
boundary shear force resolved in the direction of flow is
shar force
= toPL
In uniform flow these balance
toPL = rgALsinq
Considering
a channel of small slope, (as channel slopes for unifor and gradually varied
flow seldom exceed about 1 in 50) then
So
sinq ~ tanq = So
to = rgA
So / P = rgRSo
1.The Chezy equation
If an
estimate of ? o can be made then we can make use of
Equation.
If we assume the state of rough turbulent flow
then we can also make the assumption the shear force is proportional to the
flow velocity squared i.e.
to a V2
to =
KV2
Substituting this into equation
gives
V
= Rt(pg/K . RSo)
Or
grouping the constants together as one equal to C
V=C. Rt(RSo)
This is
the Chezy equation and the C the 'Chezy C'
Because the K is not constant the
C is not constant but depends on Reynolds number and boundary roughness (see
discussion in previous section).
The
relationship between C and is easily seen be substituting equation 1.9 into the
Darcy- Wiesbach equation written for open channels and is
C = Rt(2g/f)
2 The Manning equation
A very
many studies have been made of the evaluation of C for different natural and
manmade channels. These have resulted in today most practising engineers use
some form of this relationship to give C:
C = R1/4/n
This is known as Manning's
formula, and the n as Manning's n
. Substituting equation 1.9 in to 1.10 gives velocity of uniform flow:
Or in
terms of discharge
V=R2/3So1/2
/ n
Q = 1/n .
A5/3 / P2/3 . So1/2
Note:
Several other names have been
associated with the derivation of this formula - or ones
similar and consequently in some countries the same equation is named after one
of these people. Some of these names are; Strickler, Gauckler, Kutter,
Gauguillet and Hagen.
The
Manning's n
is also numerically identical to the Kutter n .
The Manning equation has the
great benefits that it is simple, accurate and now due to it long extensive
practical use, there exists a wealth of publicly available values of n
for a very wide range of channels.
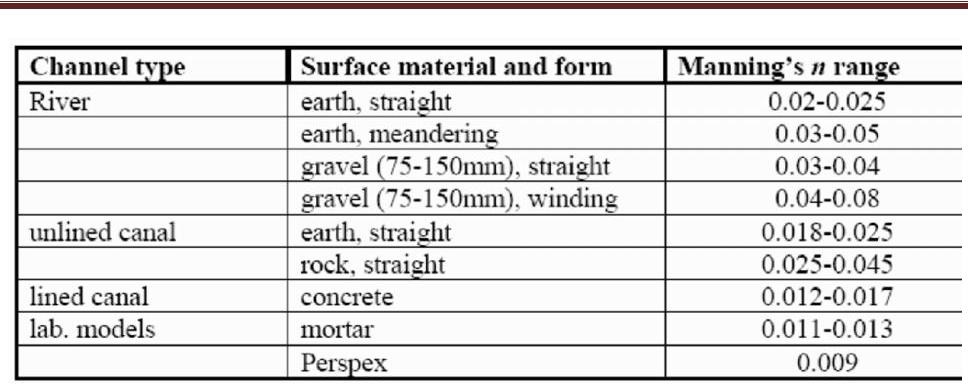
Below is
a table of a few typical values of Manning's n
Conveyance
Channel
conveyance, K , is a measure of the carrying capacity of a channel. The K
is really an agglomeration of several terms in the Chezy or Manning's equation:
Q=KSo1/2
K=ACR1/2
Use of
conveyance may be made when calculating discharge and stage in compound
channels and also calculating the energy and momentum coefficients in this
situation.
Related Topics