Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering Thermodynamics : Basic Concepts And Definitions
Statistical and Classical Thermodynamics
BASIC CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS
Thermodynamics is the
science of energy transfer which deals with the relations among heat, work and
properties of systems.
The name ‘thermodynamics’ is derived from the
Greek words therme, meaning ‘heat’ and dynamis meaning
power. Thus, thermodynamics is basically the study of heat and power.
Application Area of Thermodynamics
Energy transfer is
present in almost all the engineering activities. Hence, the principles of
thermodynamics are playing vital role in designing all the engineering
equipments such as internal combustion engines, rockets, jet engines, thermal
and nuclear power plants, refrigerators etc.
Statistical and Classical Thermodynamics
Statistical
Thermodynamics is microscopic approach in which, the matter is assumed to be
made of numerous individual molecules. Hence, it can be regarded as a branch of
statistical mechanics dealing with the average behaviour of a large number of
molecules.
Classical
thermodynamics is macroscopic approach. Here, the matter is considered to be a
continuum without any concern to its atomic structure.
Consider a gas in a
container. Pressure exerted at the wall of the container is the average force
per unit area due to the collision of the gas molecules on the wall surface. To
determine this pressure, we need not know the behaviour of individual molecules
of the gas. This approach is macroscropic approach. However, the results
obtained from macroscopic and statistical study of matter.
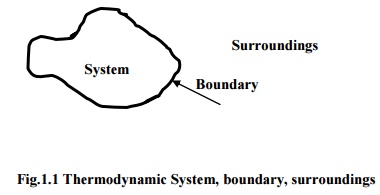
Thermodynamic Systems and Surroundings
A Thermodynamic system
is defined as a quantity of matter or a region in space whose behaviour is
being investigated.
Everything external to
the system is defined as surroundings. In its usual context the term ‘surroundings’ is restricted to the
regions in the immediate vicinity which has a detectable influence on the
system.
Boundary is the surface
which separates the system from its surroundings. It may be fixed or moving and
real or imaginary.
Related Topics