Chapter: Medical Physiology: Muscle Blood Flow and Cardiac Output During Exercise; the Coronary Circulation and schemic Heart Disease
Stages of Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction
Stages of Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction
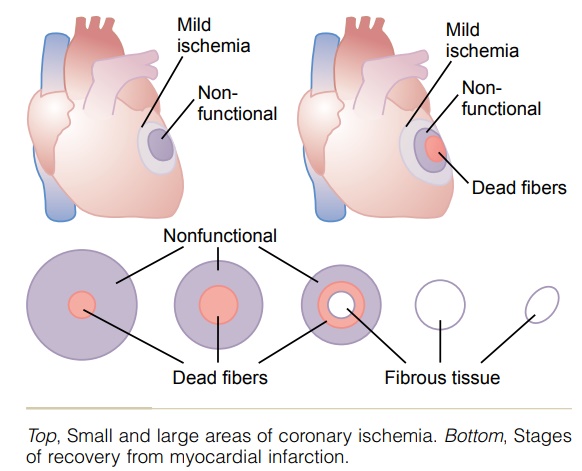
The upper left part of Figure 21–8 shows the effects of acute coronary occlusion in a patient with a small area
When the area of ischemia is small, little or no death of the muscle cells may occur, but part of the muscle often does become temporarily nonfunctional because of inadequate nutrition to support muscle contraction.
When the area of ischemia is large, some of the muscle fibers in the center of the area die rapidly, within 1 to 3 hours where there is total cessation of coronary blood supply. Immediately around the dead area is a nonfunctional area, with failure of contrac-tion and usually failure of impulse conduction. Then, extending circumferentially around the nonfunctional area is an area that is still contracting but weakly so because of mild ischemia.
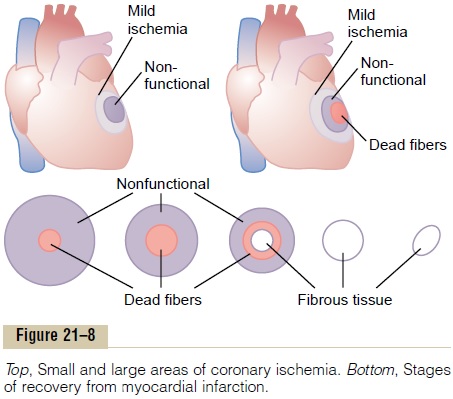
Replacement of Dead Muscle by Scar Tissue. In the lowerpart of Figure 21–8, the various stages of recovery after a large myocardial infarction are shown. Shortly after the occlusion, the muscle fibers in the center of the ischemic area die. Then, during the ensuing days, this area of dead fibers becomes bigger because many of the marginal fibers finally succumb to the prolonged ischemia. At the same time, because of enlargement of collateral arterial channels supplying the outer rim of the infarcted area, much of the nonfunctional muscle recovers. After a few days to three weeks, most of the nonfunctional muscle becomes functional again or dies—one or the other. In the meantime, fibrous tissue begins developing among the dead fibers because ischemia can stimulate growth of fibroblasts and promote development of greater than normal quanti-ties of fibrous tissue. Therefore, the dead muscle tissue is gradually replaced by fibrous tissue. Then, because it is a general property of fibrous tissue to undergo progressive contraction and dissolution, the fibrous scar may grow smaller over a period of several months to a year.
Finally, the normal areas of the heart gradually hypertrophy to compensate at least partially for the lost dead cardiac musculature. By these means, the heart recovers either partially or almost completely within a few months.
Value of Rest in Treating Myocardial Infarction. The degreeof cardiac cellular death is determined by the degreeof ischemia and the workload on the heart muscle.When the workload is greatly increased, such as during exercise, in severe emotional strain, or as a result of fatigue, the heart needs increased oxygen and other nutrients for sustaining its life. Furthermore, anasto-motic blood vessels that supply blood to ischemic areas of the heart must also still supply the areas of the heart that they normally supply. When the heart becomes excessively active, the vessels of the normal musculature become greatly dilated. This allows most of the blood flowing into the coronary vessels to flow through the normal muscle tissue, thus leaving little blood to flow through the small anastomotic channels into the ischemic area, so that the ischemic condition worsens. This condition is called the “coronary steal” syndrome. Consequently, one of the most important factors in the treatment of a patient with myocardial infarction is observance of absolute body rest during the recovery process.
Related Topics