Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Hepatic, biliary and pancreatic systems
Signs: Ascites
Ascites
Definition
Ascites is the accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
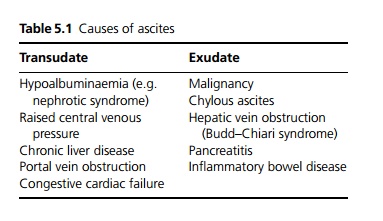
Ascites may be a transudate or an exudate dependent on the protein content (see Table 5.1).
Clinical features
Ascites presents as abdominal distension with shifting dullness and a fluid thrill on examination. Discomfort is common but severe pain is more likely to result from the underlying cause.
Investigations
The diagnosis can be confirmed by ultrasonography. A diagnostic aspiration of the fluid should be obtained. A transudate is suggested by a protein of≥11 g/L below the serum albumin level.
Clear fluid is seen in liver disease and hypoalbuminaemia. Bloodstained fluid suggests malignancy. Milky fluid suggests chylous ascites.
Very high protein counts are found in tuberculous ascites, pancreatic ascites and Budd–Chiari syndrome.
Ascitic fluid amylase is raised in pancreatic ascites.
Fluid is sent for microscopy, Gram stain and culture (in blood culture bottles). More than 250 white blood cells per millilitre indicates infection (subacute bacterial peritonitis).
Fluid should also be sent for cytology.
Management
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. The progress of ascites can be monitored using repeated weight and girth measurements. Sodium intake should be restricted but protein and calorie intake should be maintained. Water restriction is only necessary if the serum sodium concentration drops below 128 mmol/L. The combination of spironolactone and furosemide is effective in the majority of patients. Patients who not respond to this treatment may require
· therapeutic paracentesis, the removal of fluid over a number of hours. If more than 1 L of fluid is removed then intravenous albumin or plasma expander is required to prevent hypovolaemia.
· refractory ascites may be treated by TIPPS
Related Topics