Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Infectious Diseases
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually
Transmitted Diseases
A sexually transmitted disease (STD) is a disease
acquired through sexual contact with an infected person. Table 70-4 identifies
dis-eases that can be classified as STDs.
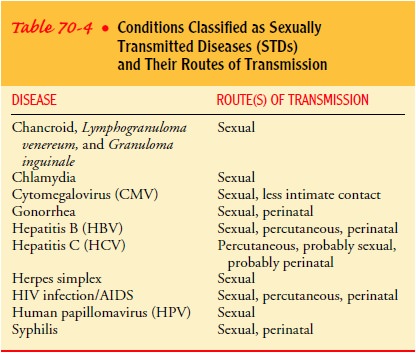
Other organisms can be transmitted during sexual contact,
although they are generally not considered to be STDs. For example, G. lamblia, usually associated with
contaminated water, can also be transmitted through sexual exposure.
STDs are the most common infectious diseases in the
United States and are epidemic in most parts of the world (Chart 70-3). Portals
of entry of STD microorganisms and sites of infection in-clude the skin and
mucosal linings of the urethra, cervix, vagina, rectum, and oropharynx.

In June 2001, U.S. Surgeon General Satcher published a doc-ument entitled, The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to PromoteSexual Health and Responsible Sexual Behavior. This documentdiscusses the public health impact of sexually transmitted diseases and other problems associated with lack of sexual responsibility.
The Surgeon General reports that approximately 12 million
Americans become infected with an STD each year. He encour-ages educators and
health care providers to study methods of in-fluencing irresponsible behavior
and to provide education and services appropriate to the communities they serve
(Satcher, 2001).
Prevention
Education about
prevention of STDs includes information about risk factors and behaviors that
can lead to infection. Included in this education is information about the
relative value of condoms in reducing risk for infection.
The use of a condom to provide a protective barrier from
transmission of STD-related organisms has been broadly pro-moted, especially
since the recognition of HIV/AIDS. At first re-ferred to as a method to ensure safe sex, the use of condoms has been
shown to reduce but not eliminate the risk of transmission of HIV and other
venereal diseases. The term safer sex
more ap-propriately connotes the public health message to be used when
promoting the use of condoms.
Significance
STDs provide a unique
set of challenges for nurses, physicians, and public health officials. Because
of perceived stigma and pos-sible threat to emotional relationships, those with
symptoms of STDs are often reluctant to seek health care in a timely fashion.
Similar to many other infectious diseases, STDs may progress without symptoms.
A delay in diagnosis and treatment is poten-tially harmful because the risk of
complications for the infected individual and the risk of transmission to
others increase over time.
Infection with one STD
suggests the possibility of infection with other organisms as well. After one
STD is identified, diag-nostic evaluation for others should be performed. The
possibility of HIV infection should be pursued when any STD is diagnosed.
Related Topics