in Human, Mutation | Heredity - Sex Determination | 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Sex Determination
Sex
Determination
The formation of zygote into
male or female sex during development is called sex determination. Sex is
determined by the chromosomes of an individual.
1. Sex Determination in Human
Recall that human beings
have 23 pairs of chromosomes out of which 22 pairs are autosomes and one pair
(23rd pair) is the sex chromosome. The female gametes or the eggs formed are
similar in their chromosome type (22+XX) . Therefore, human females are homogametic.
The male gametes or
sperms produced are of two types. They are produced in equal proportions. The
sperm bearing (22+X) chromosomes and the sperm bearing (22+Y)
chromosomes. The human males are called heterogametic.
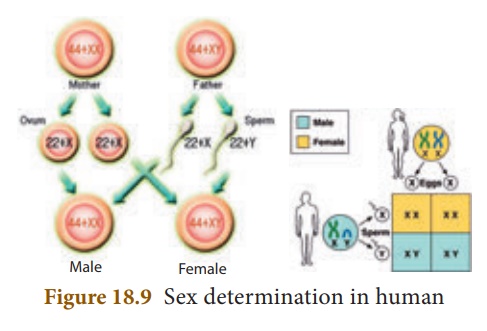
It is a chance of
probability as to which category of sperm fuses with the egg. If the egg (X) is
fused by the X-bearing sperm an individual (female) is produced. If the
egg (X) is fused by the Y-bearing sperm an XY individual (male) is
produced. The sperm, produced by the father, determines the sex of the
child. The mother is not responsible in determining the sex of the child.
Now let’s see how the
chromosomes take part in this formation. Fertilization of the egg (22+X) with a
sperm (22+X) will produce a female child (44+XX). while fertilization of the
egg (22+X) with a sperm (22+Y) will give rise to a male child (44+XY).
2. Mutation
The term mutation was
introduced by Hugo De Vries in 1901 when he observed phenotypic
changes in the evening primrose plant, Oenothera lamarckiana. Mutation
is an inheritable sudden change in the genetic material (DNA) of an organism. Mutations
are classified into two main types, namely chromosomal mutation and gene
mutation.
1. Chromosomal mutation
The sudden change
in the structure or number of chromosomes is called chromosomal
mutation. This may result in
(i) Changes in the
structure of chromosomes: Structural changes in the chromosomes
usually occurs due to errors in cell division. Changes in the number and
arrangement of genes takes place as a result of deletion, duplication,
inversion and translocation in chromosomes.
(ii) Changes
in the number of chromosomes: They involve
addition or deletion in the number of chromosomes present in a cell.
This is called ploidy. There are two types of ploidy
(a) Euploidy (b)
Aneuploidy.
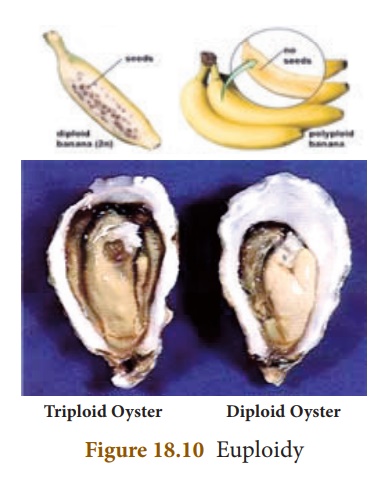
Euploidy: It is the condition in
which the individual bears more than the usual number of diploid
(2n) chromosomes. If an individual has three haploid sets of chromosomes, the
condition is called triploidy (3n). Triploid plants and animals are
typically sterile.If it has four haploid sets of chromosomes, the condition is
called tetraploidy (4n). Tetraploid plants are advantageous as they
often result in increased fruit and flower size.
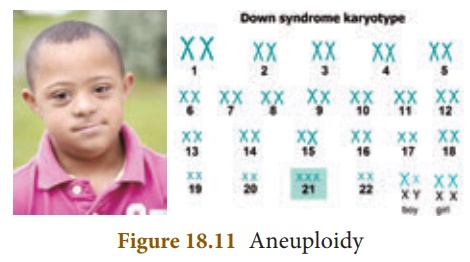
Aneuploidy: It is the loss or
gain of one or more chromosomes in a set. It is of three
types. Monosomy (2n-1), Trisomy (2n+1)and Nullisomy (2n-2).
In man, Down’s syndrome is one of the commonly known aneuploid
condition.
Down’s syndrome
This condition was first
identified by a doctor named Langdon Down in1866.
It is a genetic
condition in which there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 (Trisomy 21).
It is associated with mental retardation, delayed development, behavioural
problems, weak muscle tone, vision and hearing disability are some of the
conditions seen in these children.
2. Gene or point mutation
Gene mutation is the changes
occurring in nucleotide sequence of a gene. It involves substitution,
deletion, insertion or inversion of a single or more than one nitrogenous base.
Gene alteration results in abnormal protein formation in an organism.
Related Topics