Chapter: Anatomy of Flowering Plants: An Introduction to Structure and Development : Stem
Secondary Phloem
Secondary Phloem
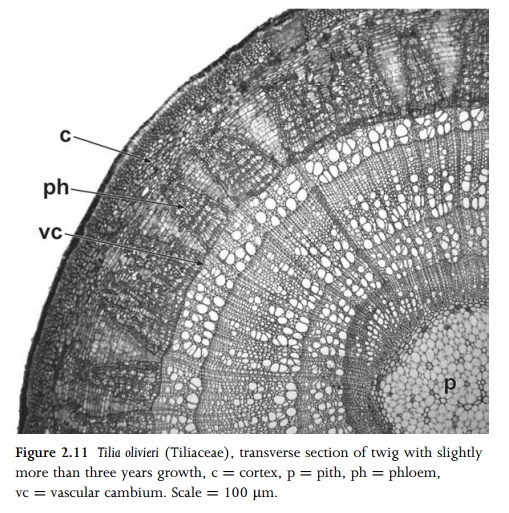
Secondary phloem is also a product of the vascular cambium in woody species. As in secondary xylem, secondary phloem consists of both axial and radial systems, formed from the fusiform and ray initials respectively. Phloem rays are radially continuous with xylem rays, and may be similarly uniseriate or multiseriate, though in transverse section they often appear dilated towards the cortex as a result of cell divisions to accommodate increase in stem thickness (Fig. 2.11). At their outer periphery, the parenchymatous ray cells are often difficult to distinguish from cortical cells. Older ray cells sometimes become lignified to form sclereids. The axial system of the phloem consists of sieve elements and companion cells, as in primary phloem. It also typically includes fibres, sclereids and axial parenchyma cells. In some species fibres are formed in groups at regular intervals, resulting in characteristic tangential bands of fibres alternating with groups of sieve elements and parenchyma cells.
Related Topics