Chapter: 11th Statistics : Chapter 2 : Collection of Data and Sampling Methods
Sampling and Non-sampling errors
Sampling
and Non-sampling errors
Sampling error
The
purpose of sample is to study the population characteristics. The sample
size is not equal to population size except in the case
complete enumeration. Therefore, the statistical measurements like
mean of the sample and mean of the population differ.
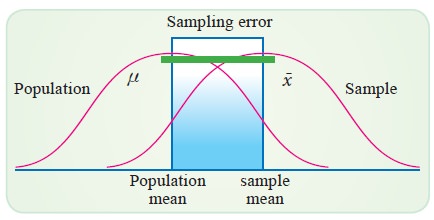
If
xr is the sample mean and μ is the population mean of the characteristic X
then the sampling error is -x
- μ. The sampling error may be
positive or negative or zero.
Non-Sampling Errors
The
non-sampling errors arise due to various causes right from the beginning stage
when the survey is planned and designed to the final stage where the data are
processed and analyzed. Non sampling errors are more serious than the sampling
errors because a sampling error can be minimized by taking a large sample. It
is difficult to minimize non sampling errors, even if a large sample is taken.
The main sources of non-sampling errors are now described.
(i) Non-response:
The
errors due to non-response may occur due to omission or lapse on the part of
the interviewer, or the refusal on the part of the respondents to questions or
because of the non-availability of the individuals during the period of survey.
(ii) Errors in measurement:
The
measuring device may be biased or inaccurate. The respondent may not know the
correct answer and may give imprecise answers. Common examples are questions on
age, income, and events that happened in the past. The interviewer may also
fail to record the responses correctly. Errors in measurement include errors in
coding, editing, and tabulation.
Coverage errors:
The
coverage errors are classified as ‘under coverage errors’ and ‘over coverage errors’. Under-coverage errors occur in the
following situations:
·
The
selected unit in the sampling frame is not interviewed by the investigator.
·
The
selected unit is incorrectly classified as ineligible for surveys
·
The
unit is omitted or skipped by the interviewer.
Similarly,
over-coverage occurs under the following situations:
·
The
sampling frame covers ineligible units.
·
The
frame may contain the same unit more than once.
The
errors cannot be ignored since the cumulative effect of these errors affect the
objectives of the survey.
Organising a sample survey
The
above said things provide a comprehensive idea about collection of data.
However, when one decides to collect data through sampling the following steps
are to be followed.
Stage I: Developing a sample plan
Definite
sequence of steps the interviewer ought to go in order to draw and ultimately
arrive at the final sample.
i.
Define
the relevant population.
ii.
Obtain
a population list, if possible: may only be some type of a sampling frame.
iii.
Fix
the sample size
iv.
Choose
the appropriate sampling.
v.
Draw
the sample.
vi.
Assess
the validity of the sample.
vii.
Resample
if necessary.
Stage II: Pilot survey or Pilot Study
It
is a guiding survey, usually on a small scale, carried out before the main
survey. The information received by pilot survey is utilized in improving the
efficiency of the large scale main survey. It helps in:
·
Estimating
the cost of the regular survey
·
Correcting
the questionnaire of the survey
·
Training
the field workers.
·
Removing
the faults of the field organization.
·
Deciding
about the other details of the survey.
Stage III. Dealing with Non- respondents
Procedures
will have to be devised to deal with those who do not give information.
Related Topics