Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Perioperative & Critical Care Medicine: Acid-Base Management
Respiratory Alkalosis
RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
Respiratory alkalosis is defined as a primary
decreasein Paco2. The mechanism is usually an inappropriate increase
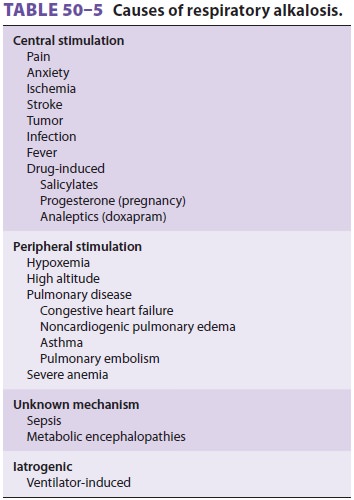
in alveolar ventilation relative to CO2 pro-duction. Table 50–5 lists the most common
causes of respiratory alkalosis. Plasma [HCO 3−] usually
decreases 2 mEq/L for each 10 mm Hg acute decrease
in Paco2 below 40 mm Hg. The distinction between acute and chronic
respiratory alkalosisis not always made, because the compensatory response to
chronic respiratory alkalosis is quite variable: plasma [HCO3−] decreases 2–5
mEq/L for each 10 mm Hg decrease in Paco2 below 40 mm Hg.
Treatment of Respiratory Alkalosis
Correction of the underlying process is the only treatment for
respiratory alkalosis. For severe alka-lemia (arterial pH >7.60), intravenous hydrochloric
acid, arginine chloride, or ammonium chloride may be indicated .
Related Topics