Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 12 : Medical Microbiology
Reproductive Tract Infections
Reproductive Tract Infections
Reproductive tract infections are caused by organisms normally
present in the reproductive or genital tract or introduced from the outside
during sexual contact or medical procedures. It occur both in men and women.
Based on mode of infection reproductive tract infections are classified into
three types:
1. Sexually Transmitted Disease
It is caused
through means of
sexual contact. Examples: Chlamydia, Gonnorhea, Chancroid, and Acquired
Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
2. Endogenous Infections
These are caused by the overgrowth of organisms normally present
in the genital tract of healthy women. Example: Bacterial Vaginosis or Vulvo
Vaginal Candidiasis.
3. Iatrogenic Infections
These infections are associated with improperly performed
medical procedures such as unsafe abortion or poor delivery practices. The
endogenous organisms in the vagina or sexually transmitted organisms in the
cervix may be transferred during a transcervical procedure into the upper
reproductive tract and cause serious infections of the uterus, fallopian tubes,
and other pelvic organs.
In men reproductive tract infections transmitted by sexual
contact are much more common than by endogenous or iatrogenic reproductive
infections. In women reproductive infections spread through non sexual routes
are usually more common.
Mode of Transmission
Reproductive tract infections are caused by pathogenic bacteria,
parasite, virus. It is mainly caused by pathogens entering into the body
through the mucous mem-branes during unprotected vaginal, oral, anal
intercourse with an infected part-ner. In developing countries bacterial
infections like Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia, Syphilis, Bacterial Vaginosis,
Lympho-granuloma Venereum, Trichomoniasis, Chancroid, and viral infections
caused by Human Papilloma Virus, Hepatitis B Virus, Herpes Simplex Virus, Human
Im-munodeficiency Virus are very common.
Normal Flora of Reproductive Tract
Mycobacterium
smegmatis,
a harmless commensal found in the
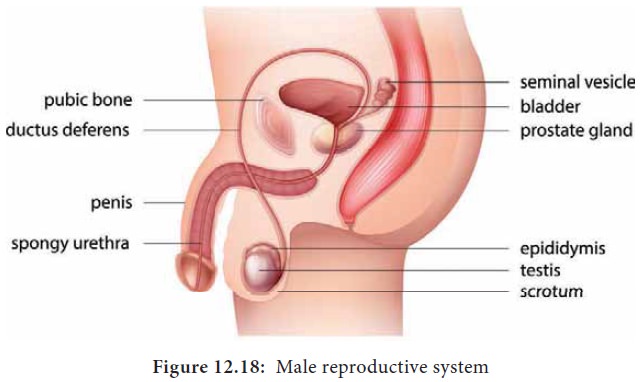
smegma of the genitalia of both men and women. (Figure 12.17 & 12.18). In
nomal men aerobic and anaerobic bacteria,
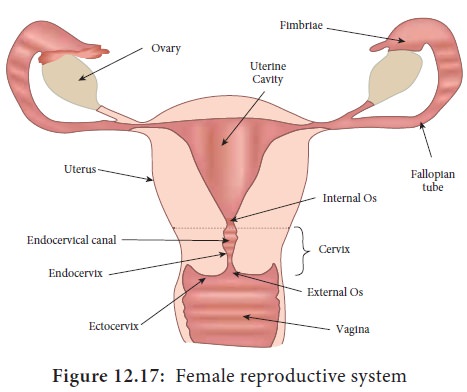
The adult female genital tract has a very complex microflora.
The character of the population changes with the variation of the menstrual
cycle. Mostly the predominant bacteria are acid tolerant Lactobacilli. Glycogen is accumulated in the vaginal wall due to ovarian hormonal activity. The breakdown
of glycogen by the lactic acid bacteria (Doderlien’s bacillus) leads to the
formation of acidic pH (4.4-4.5). This acidic nature prevents the vagina from
bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections. However before puberty and after
menopause there is no glycogen formation. The normal flora during this period
contain normal skin microorganisms. The vaginal pH is mild alkaline. The normal
vaginal flora often includes Listeria,
anaerobic Streptococci, Mycoplasma,
Gardnerella vaginalis, Neisseria, Spirochetes, Candida, Staphylococcus
epidermidis.
Pathogenesis
After the entry of pathogenic organisms, with sufficient
incubation time, symptoms are clearly manifested in the affected individual.
The most common symptoms include unusual vaginal discharge, penile discharge,
pelvic pain, itching, abnormal or heavy vaginal bleeding, rashes, warts,
lesions, burning or pain during urination. However most of the infections are
asymptomatic, which act as a effective control of reproductive tract
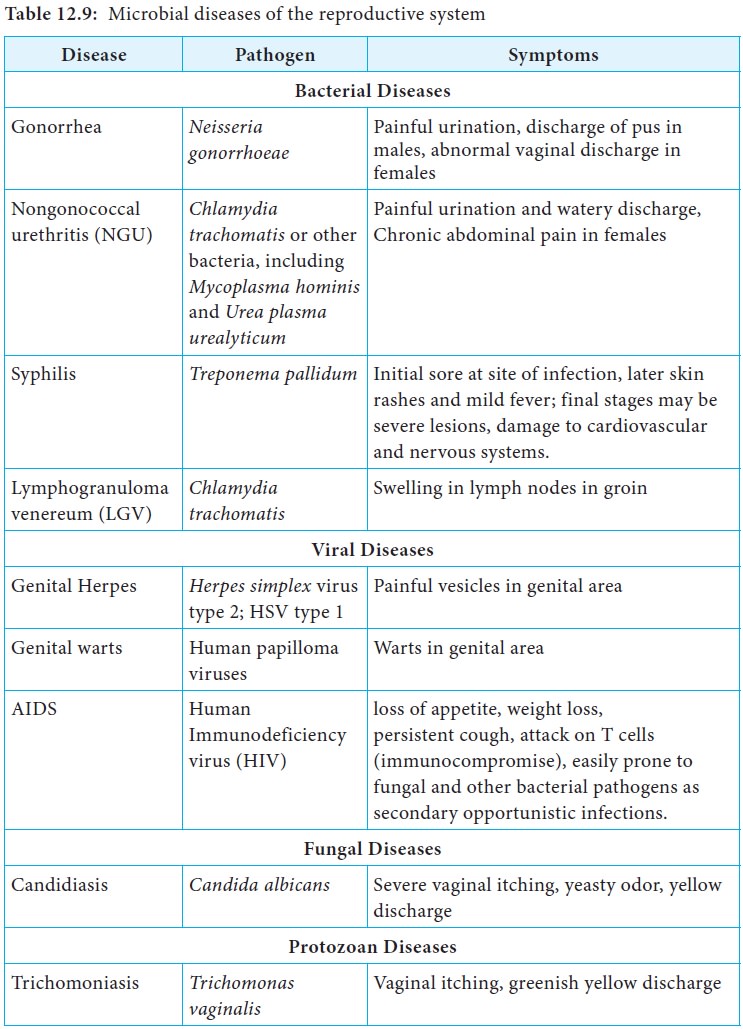
infections. Diseases of reproductive system are listed in Table 12.9.
Related Topics