Zoology - Reproduction in Organisms: Summary | 12th Zoology : Chapter 1 : Reproduction in Organisms
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 1 : Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction in Organisms: Summary
Summary
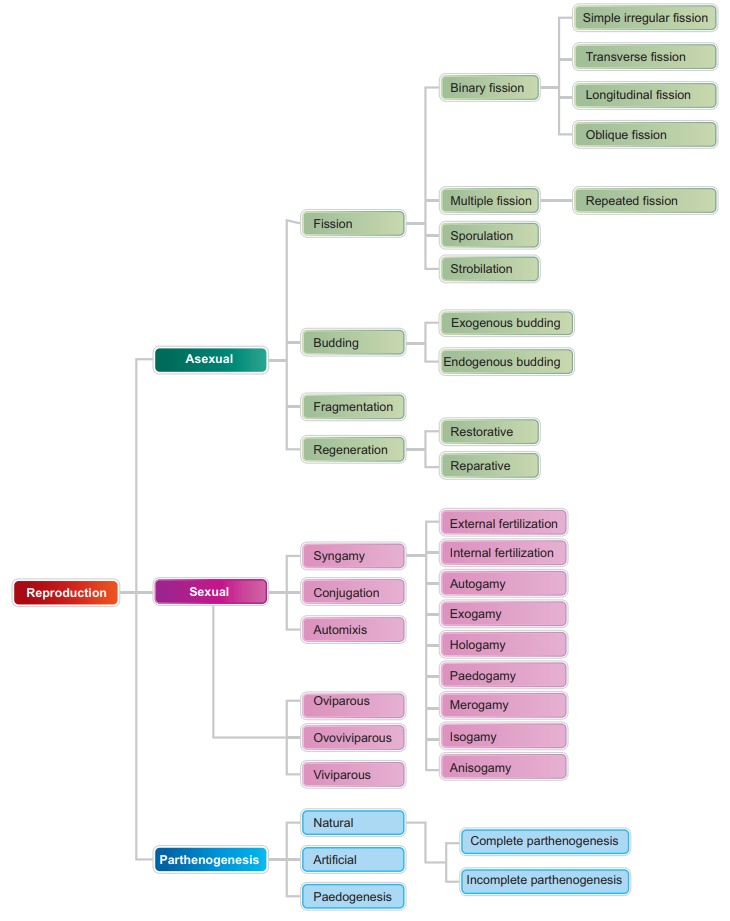
Reproduction is a
process by which the living beings propagate or duplicate their own kind.
Reproduction can be broadly classified into asexual reproduction and sexual
reproduction. In asexual reproduction fusion of gametes are not involved, but
in sexual reproduction the formation and fusion of gametes occur. Different
modes of asexual reproduction are fission, budding, fragmentation and
regeneration. Fission is further divided into binary fission, multiple fission,
sporulation and strobilation.
According to the plane
of fission different kinds of binary fission have been identified in different
organisms. They are simple irregular binary fission, transverse binary fission,
longitudinal binary fission and oblique binary fission. Multiple fission is the
division of the parent into many small daughter cells simultaneously. Budding
is another mode of asexual reproduction. The parent body produces one or more
buds; each bud grows into a young one and may separate from the parent to lead
a normal life. When many buds are formed on the outer surface of the parent, it
is known as exogenous budding. Hundreds of buds are formed inside the cytoplasm
and remain within the body of the parent, this process is called endogenous
budding. Fragmentation is another mode of asexual reproduction. In
fragmentation the body of the parent breaks into fragments (pieces) . Each
fragment has the potential to develop into a new individual. Regeneration is
the development of the whole body of an organism from a small fragment. It is
of two types namely restorative regeneration and reparative regeneration.
Various modes of sexual
reproduction is seen in animals. In syngamy the fusion of two haploid gametes
takes place to produce a zygote. The following kinds of syngamy is prevalent
among the living organism. They are autogamy, exogamy, hologamy, paedogamy,
merogamy, isogamy, anisogamy and conjugation. Parthenogenesis is the special
type of sexual reproduction seen in animals. It is of two main types namely
natural parthenogenesis and artificial parthenogenesis.
According to the
development of the embryo, animals may be oviparous, viviparous and
ovoviviparous.
Related Topics