Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Tools and Techniques in Biotechnology
RNA Isolation and mRNA Purification - Techniques of Biotechnology and Innovations
RNA ISOLATION AND mRNA PURIFICATION
Preparation of tips, tubes and glasswares for RNA isolation
All the materials such as micropestle, tubes, tips, glass bottles, forceps, culture tubes, tips boxes and tube boxes used for RNA isolation are treated with diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) water to make them free from RNase. One mL of DEPC was mixed with 999 mL of autoclaved Nanopure water (0.1% of DEPC water) and incubates the bottles on rotor shaker at room temperature overnight for uniform dispersion of DEPC in water. The water was decanted and materials were dried in the hot air oven. These RNase free materials were autoclaved at 121oC, 15 lbs for 15 min and dried.
Cell lysis and phase separation
The Trichoderma mycelia were crushed with liquid nitrogen in RNase free 2 mL micro centrifuge tube. The frozen materials were immediately subjected for cell lysis by use of TRIzol reagent (1 mL/100 mg of sample). After addition of TRIzol reagent the tubes were inverted for couple of times and incubated for 20 min at room temperature. Then 200 µl of chloroform was added to sample, mixed well and incubated for 5 min at room temperature. The sample was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4oC. Within the tube TRIzol reagent separated the DNA, RNA and protein into three separate layers. The bottom layer considered of protein, middle layer consisted of DNA and top aqueous layer will contain RNA. Carefully upper layer was transferred to fresh pre chilled 1.5 mL RNase free tube without getting contamination from other layers.
RNA precipitation
The tubes were placed back in to ice as soon as aqueous layer was transferred. An equal amount (600 µl) of chilled Isoproponol was added to each tube and mixed gently by inverting them for couple of times. The samples were incubated at -80oC for 2 h. Later it wascentrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 30 min at 4oC. A very small gel like white pellet will be visible at the bottom side of the tube.
RNA wash
One mL of 75% alcohol was added to each tube and gently mixed and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min at 4oC. The liquid was decanted and allowed the tubes for complete drying of alcohol on tissue paper.
RNA solubilisation
The RNA pellet was air dried for 5-10 min and care was taken not to completely dry the pellet. Add 30-40 µl of nuclease free water to tube and the pellet was dissolved by repeated pipetting with a micropipette at 55oC for 10-15 minutes. Later the RNA sample was stored at -80oC until next use.
Restriction digestion
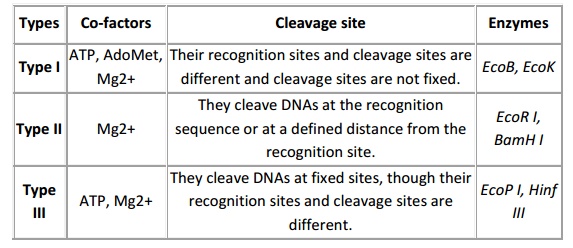
Restriction enzymes are nucleases which are able to cleave the DNA at specific sites. These are predominantly employed by microbes to restrict the multiplication of foreign DNA/ virus particles. Among the three different types of restriction endonucleases, the restriction endonuclease (RE) type II is predominantly using for most of the cloning experiments because of their site specific cleavage at recognition site and they require only Mg2+ as cofactor for their activity. The 1 U of enzyme is able to restrict the 1 µg of DNA in 60 min. Hence, depending on concentration of DNA the enzyme concentration to be use is various. Most of the RE works better at 37oC. However, there are few exceptions and some shows star activity at a prolong incubation or at excess enzyme concentration such as BamHI. Therefore, the enzyme concentration and incubation timing are most important in restriction digestion. The restriction digestion performed in microfuge tube containing DNA, RE, buffer and water. The buffer system is specific to RE and some RE requires the 1 X concentration of BSA as a cofactor. The restriction is performing with two different enzymes than it can be performed by
either double digest restriction or sequential digestion it is based on buffer system compatibility. The standard restriction performed for 60-90 min and depending up on enzyme property in activation will be performed like heat inactivation (65oC for 15 min) or addition of 1/10th volume of 0.5 M EDTA but for some enzymes inactivation is not required. Based on the specificity and co-factor required Restriction enzymes are classified into three major classes, described below.
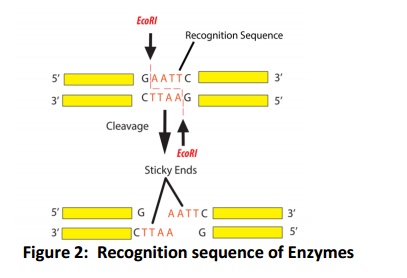
Among these restriction enzymes, type II enzymes are generally used in genetic engineering experiments and widely available in the market. Up on restriction type II class enzymes, few produce the blunt end and few produces the sticky/cohesive ends (Fig. 2). Therefore, the first thing in restriction digestion is need to decide, which enzyme has to use and their compatible buffer for their action. Single molecule of DNA can be digest with one or more than one restriction enzymes (generally two) if the compatible buffer available that is called double digest, if the compatible buffer is not available than serial digestion can be used. The detailed protocol of the restriction digestion is described below.
1. Select restriction enzymes to digest the target plasmid
To decide the type of restriction to use, first we need to know the sequence of the DNA molecule. Based on that, type of restriction enzymes can be decided.
2. Determine an appropriate reaction buffer
Each enzyme works best at optimum pH, this pH and the co-factor required for the enzyme action is provides by buffer. Usually, it will be supplied by restriction enzyme suppliers.
3. Template concentration
1 µg of DNA can be cleaved by one unit (U) of an enzyme in 1 h. Therefore, accordingly amount of enzyme required for amount of template has to decide. The amount of DNA that needs to be cut depends on the application. Diagnostic digests typically involve ~500ng of DNA, while molecular cloning often requires 1-3μg of DNA. The total reaction volume usually varies from 10-50μL depending on application and is largely determined by the volume of DNA to be cut. The template should be free of restriction inhibition compounds such as salt, DMSO and phenols.
4. Sterile water
Water need to be pure and free of nucleases, in general the molecular biology grade water can be used. The amount of water has to add varies and depend on volume of other compounds addition and final reaction mixture.
Mix the above mixture gently and incubate for 1 - 2 hr at desired temperature (varies from enzymes to enzymes, usually 37ºC). After the reaction, some of the enzymes need inactivation either by chemical or heat (65ºC for 15-20min).
Need to take care:
· While keeping the reaction, do not add the enzyme directly on the buffer, it may cause irreversible damage to enzyme. Hence, first add water than buffer and BSA (if it is recommended). The enzyme needs to add last.
· Restriction enzymes must be placed in an ice bucket immediately after removal from the -20°C freezer because heat can cause the enzymes to denature and lose their function.
· The amount of restriction enzyme want to use for a given digestion will depend on the amount of DNA want to cut.
· If your enzyme did not cut, check to make sure that it isn't methylation sensitive.
· Sometimes enzymes cut sequences which are similar, but not identical, to their recognition sites. This is due to "Star Activity" and can happen for a variety of reasons like excess enzyme usage, excess time of incubation and high glycerol concentration.
· If the reaction is kept for more number of sample than it is better to prepare the master mix (all the component except template).
Related Topics