Chapter: Biochemistry: The Metabolism of Nitrogen
Purine Catabolism
Purine Catabolism
The
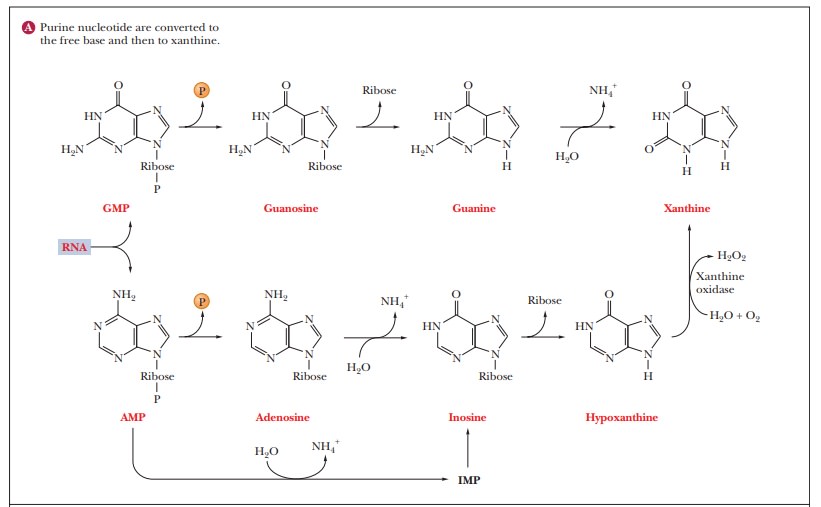
catabolism of purine nucleotides proceeds by hydrolysis to the nucleoside and
subsequently to the free base, which is further degraded. Deamination of
guanine produces xanthine, and deamination of adenine produces hypoxanthine,
the base corresponding to the nucleoside inosine, which is shown in Figure
23.23a. Hypoxanthine can be oxidized to xanthine, so this base is a common
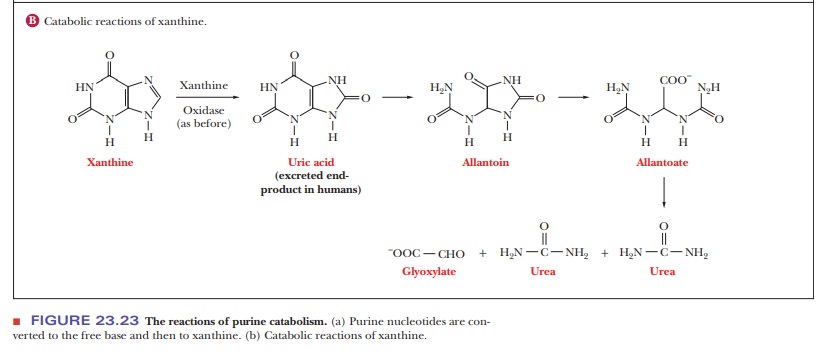
degradation product of both adenine and guanine. Xanthine is oxidized in turn
to uric acid. In birds, some
reptiles, insects, Dalmatian dogs, and primates (including humans), uric acid
is the end product of purine metabolism and is excreted. In all other
terrestrial animals, including all other mammals, allantoin is the product
excreted, whereas allantoate is the product in fish. Allantoate is further
degraded to glyoxylate and urea by microorganisms and some amphibians, as shown
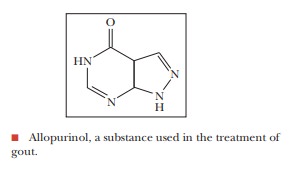
in Figure 23.23b. Gout is a disease
in humans that is caused by the overproduction of uric acid. Deposits of uric
acid (which is barely soluble in water) accumulate in the joints of the hands
and feet. Allopurinol is a compound used to treat gout; it inhibits the
degradation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and of xanthine to uric acid,
preventing the buildup of uric acid deposits.
Salvage reactions are important in the metabolism of purine
nucleotidesbecause of the amount of energy required for the synthesis of the
purine bases. A free purine base that has been cleaved from a nucleotide can
produce the corresponding nucleotide by reacting with the compound
phosphoribosylpyro-phosphate (PRPP), formed by a transfer of a pyrophosphate
group from ATP to ribose-5-phosphate (Figure 23.24).
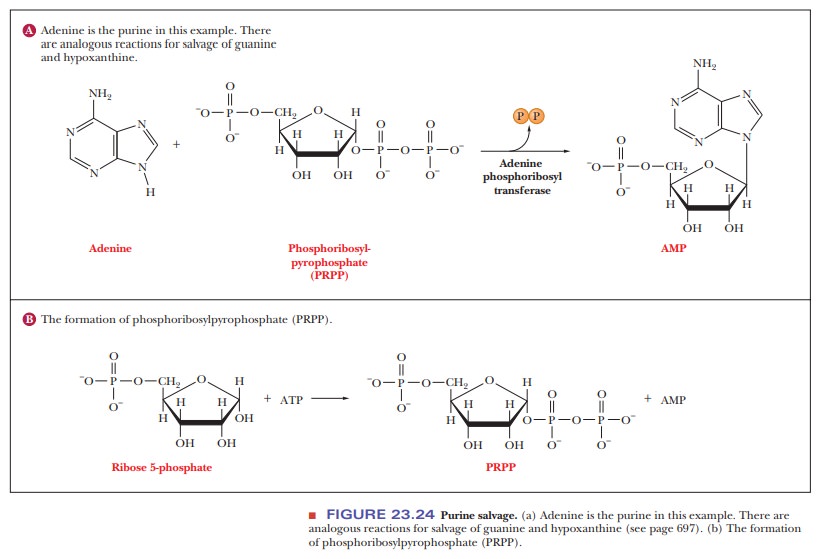
Two
different enzymes with different specificities with respect to the purine base
catalyze salvage reactions. The reaction
Adenine
+ PRPP - > AMP + PPi
is
catalyzed by adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. The corresponding reactions of
guanine and hypoxanthine
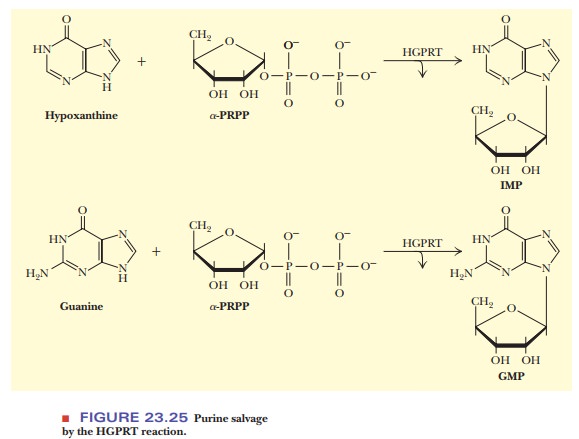
HGPRT
Hypoxanthine
+ PRPP - > IMP + PPi
HGPRT
Guanine
+ PRPP - > GMP + PPi
are
catalyzed by hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) (Figure
23.25). A deficiency in HGPRT can result in a serious disorder, Lesch–Nyhan syndrome.
Summary
Purines are degraded to uric acid in primates (including humans)
and further degraded in other organisms. Overproduction of uric acid causes
gout in humans.
Salvage reactions exist for reuse of some of purines.
Related Topics