Chapter: Essential Microbiology: Procaryote Diversity
Pseudomonads
The Pseudomonads
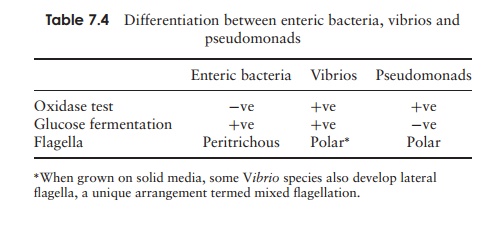
Members of this group of proteobacteria, the most im-portant genus of which is Pseudomonas, are straight or curved rods with polar flagella. They are chemo-heterotrophs that generally utilise the Entner–Doudoroff pathway rather than glycolysis for the oxidation of hexoses. They are differentiated from the enteric bacteria (Table 7.4) by being oxidase-positive and incapable of fermentation. A characteristic of many pseudomonads is the ability to utilise an extremely wide range of organic compounds (maybe over 100!) for car-bon and energy, something that makes them very im-portant in the recycling of carbon in the environment. Several species are significant pathogens of animals and plants; Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an effective coloniser of wounds and burns in humans, while P. syringae causes chlorosis (yellowing of leaves) in a range of plants. Because of their ability to grow at low temperatures, a number of pseudomonads are important in the spoilage of food.
Although most species carry out aerobic respiration with oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor, a few are capable of substituting nitrate.
Related Topics