Textiles and Dress Designing - Process Flow in a Garment Industry | 12th Textiles and Dress Designing : Chapter 12 : Apparel Merchandising
Chapter: 12th Textiles and Dress Designing : Chapter 12 : Apparel Merchandising
Process Flow in a Garment Industry
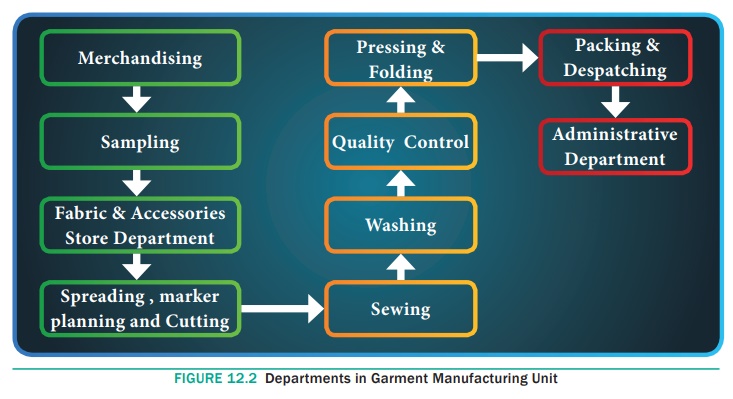
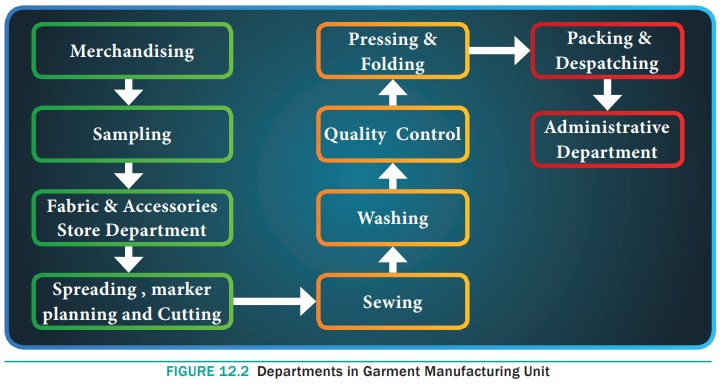
Process Flow in a Garment Industry
Garment manufacturing includes a number of processes from order
receiving to dispatching and shipment of the finished garments.
Merchandising Department
Merchandiser is a person who interacts with the buyer and seller,
and also puts efforts into proper relation between buying offices, buying agents,
agency and seller, exporter in terms of executing an order. A garment export
unit generally has many departments like stores, cutting, production, packing
and checking. Merchandising department is the star of the department among all
the working departments in the export concern, because merchandising is the
only department having maximum control over the departments and totally
responsible for profit and loss of the company. The job of a merchandiser is to
coordinate with the entire department in the office as well as the customers.
Merchandiser meets the buyers and collects the details of their requirements to
develop the relationship with the customer. After conformation of an order from
the buyer the planning process for execution of the order is done.
Sampling
Designing and sampling are the main process in garment industry
and it has a vital role in attracting buyers. The buyers generally places the
order after they are satisfied with the quality of the samples. The samples
decide the ability of an exporter. The buyer will access the exporter and his
organisation only by the samples. The purpose of sampling is not only to get
bulk orders and also give some additional benefits to the exporters. By doing
sampling the exporter can estimate the yarn consumption for developing the
fabric, a clear idea on costing and more over the manufacturing difficulties.
There are different phases of sampling; the first phase covers the development
of the initial concept or design idea through its approval by the customer. The
second phase covers the process following acceptance of the first prototype
sample and includes the functions of sourcing and ordering component, testing
the product and carry out trails and finalized sample specifications. The third
and final phase includes a range of activities that are carried out before
large scale or bulk production capacity outside the home producer or developers
wherever this is applicable.
Fabric and Accessories Store Department
After receiving purchase order from the buyer merchandiser plans
and issues purchase order for buying raw materials like fabric, buttons,
thread, and for dyeing, printing, embroidery and other accessories. These raw
materials’ are checked for colour, quality and then approved by the
merchandiser.
Spreading, Marker Planning and Cutting Department
Approved sample, pattern and measurement chart must be ready in
the department. The head of the department will be a pattern master. His skill
will be a very big asset to the company by way of saving the fabric and making
new designs for the export trade.
Machinery required: one cutting machine. One table of 18
m/1.5m length and breadth
Spreading
In the cutting department, spreading plays a vital role. In
spreading, the number of plies of fabric, that the production planning process
has dictated to the length of the marker plan, colours required are correctly
aligned as to length and width, and without tension. This saves time, cost of
cutting and cost of materials.
Marker Planning
The amount of fabric consumed per garment and the total profit of
the garment unit is decided by the marker planning and marker making. The
length and width of the marker is very important here. Based on this marker
only the spreading length will be decided. The fabric consumptions and fabric
wastages depends on this marker making. The industry has always paid great
attention to marker planning, because when the cutting room cuts cloth it
spends around half the company’s turnover. Any reduction in the amount of cloth
used per garment leads to increased profit.
Sewing
Power operated machines preferably batch system is used to get
uniform quality andbetter productivity. Production in charge will be
responsible for the sewing operation. He must know quality aspects in every
stage, guide tailors and supervisors to get the work done at satisfactory level
and to meet the targets. Additional to sewing machines, attachments, guides,
folders are required for special operations. Machines like Double needle, Feed
of arm, Button Hole and Buttoning machines are also required.
Washing Department
Either for effects or shrinkage garments are washed. Washes vary
depending upon the type of fabric used and the type of garment. Some of the
common washes are garment wash, stone wash, caustic wash, bleaching acid wash,
sand wash and enzyme wash.
Machinery required : Washing machine, Hydro Extractor, Tumbler
Drier, Store/ Chemicals
Quality Control
Quality is an important concept in all stages of garment
production. To get the quality product, check and controls must be ensured in
each stage of the production. This will also avoid all kinds of mistakes.
Prevention is better than cure and also do the things right at the
first time. These will really bring an awareness in the production line. By any
chance an alteration or a mistake in the garment is difficult to be rectified
properly. For upkeep of quality, good housekeeping and cleanliness should be of
top priority.
Pressing and Folding
Presentation of a packed garment makes all the difference in
sales. The real skill of the industry lies in this point. A well-tailored
garment can be finished badly or a badly stitched garment can be presented
properly. Garments can be folded as follows:
1.
Stand up pack
2.
Plat pack
3.
Deadmen fold
4.
Semi stand pack
Machinery Required
Steam pressing with vacuum table, Dummy blowers, Shift folding tables, Stain removing guns.
Packing and Despatching
In the garment export trade packing is an art and is a very
important stage. If the presentation and packing is good, it will really
attract customers and sales will be faster. Our ultimate aim must be to impress
the buyer with quality product. While packing, ratios, size, colour, tables are
to be observed and followed meticulously. As policy matters decision taking or
making has to be done as early as possible. Delay in minutes/ hours will create
problems and losses. Concentration, involvement and commitment will fetch real
good foreign exchange to the entrepreneur and to the country in the
international market.
Administrative Department
All the departments in a clothing industry require administrative
support for their operations to ensure orderly and systematic functioning. The
procedure covers preparing orders to supplies, checking goods, timing and
methods of stock taking, imports and exports, obtaining credits for returned
goods and materials, issuing credit for customer returns, negotiating and
issuing tenders for major projects and purchase of furniture and equipments.
Related Topics