Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 6 : Solid State
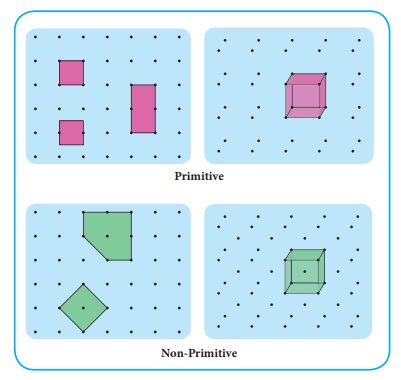
Primitive and non-primitive unit cell
Primitive
and non-primitive unit cell
There are two types of
unit cells: primitive and non- primitive. A unit cell that contains only one
lattice point is called a primitive unit cell, which is made up from the
lattice points at each of the corners.
In case of non-primitive
unit cells, there are additional lattice points, either on a face of the unit
cell or with in the unit cell.
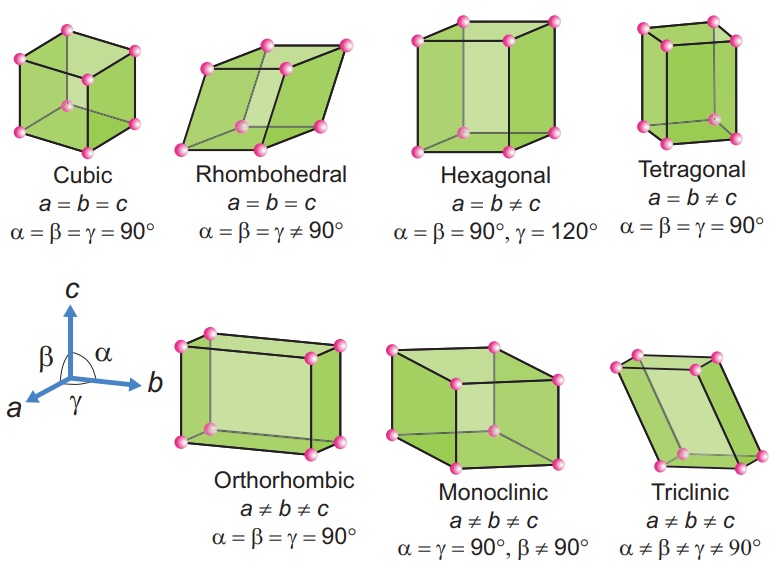
There are seven primitive crystal systems; cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, monoclinic, triclinic and rhombohedral. They differ in the arrangement of their crystallographic axes and angles. Corresponding to the above seven, Bravis defined 14 possible crystal systems as shown in the figure.
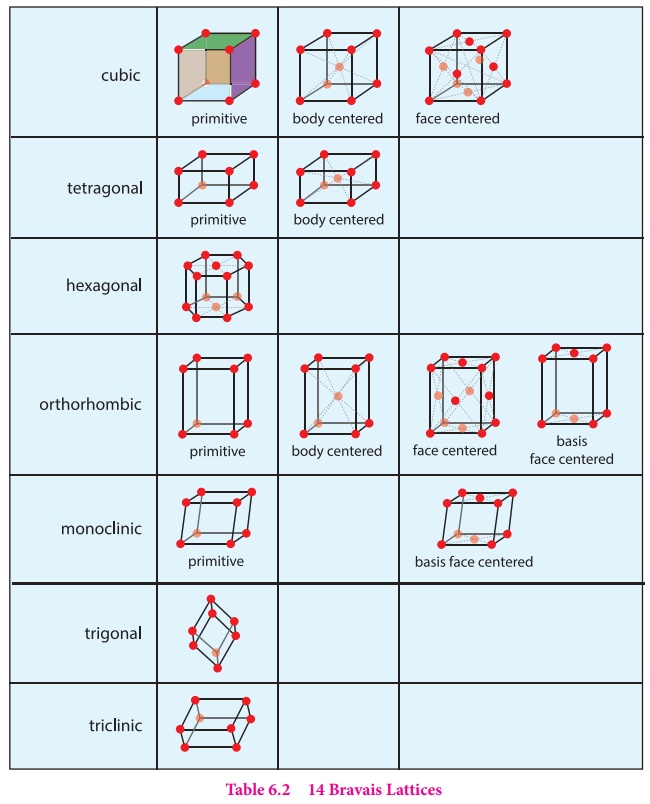
Number
of atoms in a cubic unit cell:
1. Primitive (or) simple cubic unit cell.(SC)
In the simple cubic unit
cell, each corner is occupied by an identical atoms or ions or molecules. And
they touch along the edges of the cube, do not touch diagonally. The
coordination number of each atom is 6.
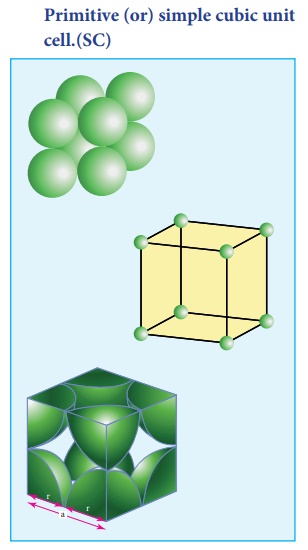
Each atom in the corner of the cubic unit cell is shared by 8 neighboring unit cells and therefore atoms `per unit cell is equal to Nc/8 , where Nc is the number of atoms at the corners.

2. Body centered cubic unit cell. (BCC)
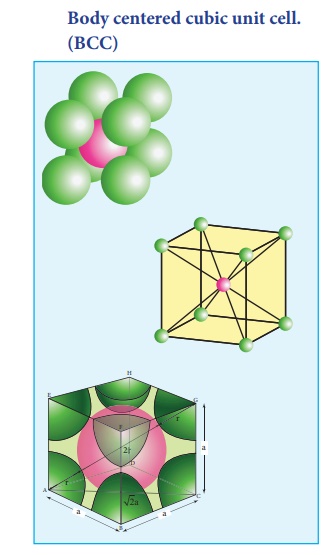
In a body centered cubic
unit cell, each corner is occupied by an identical particle and in addition to
that one atom occupies the body centre. Those atoms which occupy the corners do
not touch each other, however they all touch the one that occupies the body
centre. Hence, each atom is surrounded by eight nearest neighbours and
coordination number is 8. An atom present at the body centre belongs to only to
a particular unit cell i.e unshared by other unit cell.
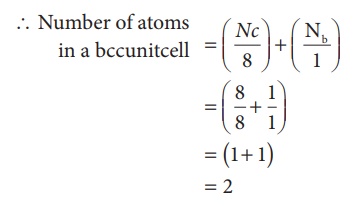
3. Face centered cubic unit cell.(FCC)
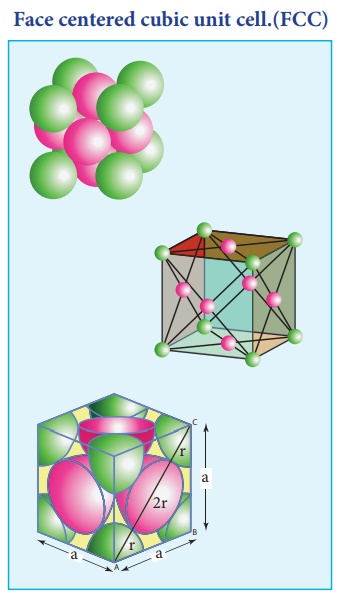
In a face centered cubic
unit cell, identical atoms lie at each corner as well as in the centre of each
face. Those atoms in the corners touch those in the faces but not each other.
The atoms in the face centre is being shared by two unit cells, each atom in
the face centers makes ( 1/2 ) contribution to the unit cell.
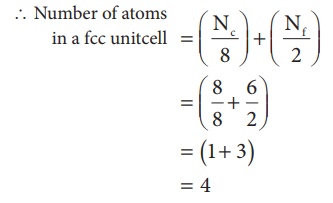
Drawing the crystal
lattice on paper is not an easy task. The constituents in a unit cell touch
each other and form a three dimensional network. This can be simplified by
drawing crystal structure with the help of small circles (spheres)
corresponding constituent particles and connecting neighbouring particles using
a straight line as shown in the figure.
4. Calculations involving unit cell dimensions:
X-Ray diffraction
analysis is the most powerful tool for the determination of crystal structure.
The inter planar distance between two successive planes of atoms can be
calculated using the following equation form the X-Ray diffraction data 2dsinθ = nλ
The above equation is
known as Bragg’s equation.
Where
λ is the wavelength of X-ray used for
diffraction.
θ is the angle of diffraction
By knowing the values of
θ, λ and n we can calculate
the value of d.
d = n λ /2sin θ
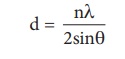
Using these values the
edge of the unit cell can be calculated.
5. Calculation of density:
Using the edge length of
a unit cell, we can calculate the density (
ρ ) of the crystal by
considering a cubic unit cell as follows.
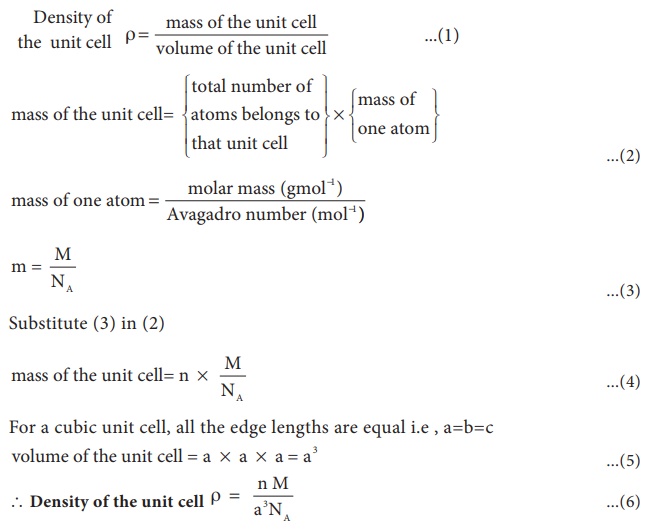
Equation (6) contains
four variables namely ρ
, n , M and a . If any three variables are known, the fourth one can be
calculated.
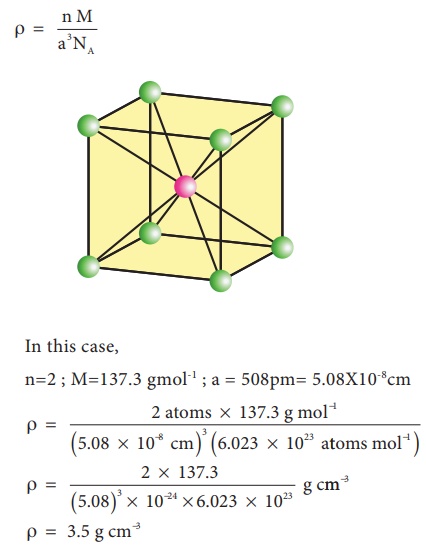
Example 2
Barium has a body
centered cubic unit cell with a length of 508pm along an edge. What is
the density of barium in g cm-3?
Solution:
In this case,
n=2 ; M=137.3 gmol-1 ; a = 508pm= 5.08X10-8cm
Related Topics