Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Primary structure of monocot stem - Maize stem
Primary structure of monocot stem - Maize stem
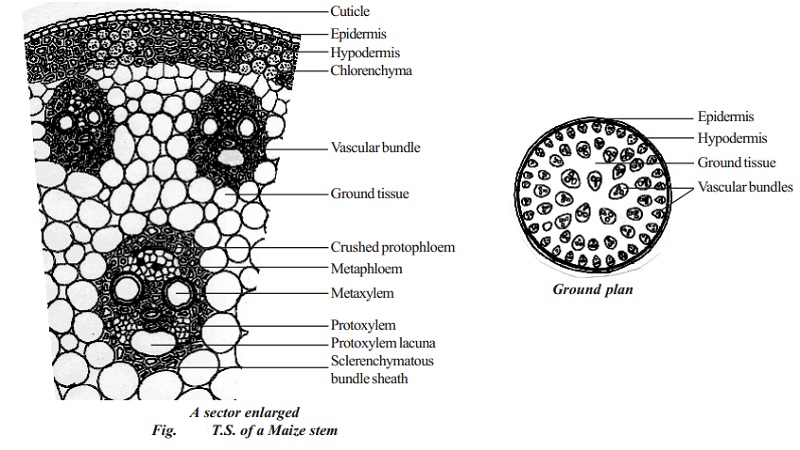
The outline of the maize stem in transverse section is more or less circular. Internal structure of monocotyledonous stem reveals epidermis, hypodermis, ground tissue and vascular bundles.
Epidermis
It is the outermost layer of the stem. It is made up of single layer of tightly packed parenchymatous cells. Their outer walls are covered with thick cuticle. The continuity of this layer may be broken here and there by the presence of a few stomata. There are no epidermal outgrowths.
Hypodermis
A few layer of sclerenchymatous cells lying below the epidermis constitute the hypodermis.. This layer gives mechanical strength to the plant. It is interrupted here and there by chlorenchyma cells.
Ground tissue
There is no distinction into cortex, endodermis, pericycle and pith. The entire mass of parenchymatous cells lying inner to the hypodermis forms the ground tissue. The cell wall is made up of cellulose. The cells contain reserve food material like starch. The cells of the ground tissue next to the hypodermis are smaller in size, polygonal in shape and compactly arranged. Towards the centre, the cells are loosely arranged, rounded in shape and bigger in size. The vascular bundles lie embedded in this tissue. The ground tissue stores food and performs gaseous exchange..
Vascular bundles
Vascular bundles are scattered in the parenchymatous ground tissue. Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a sheath of sclerenchymatous fibres called bundle sheath. The vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral, endarch and closed. Vascular bundles are numerous, small and closely arranged in the peripheral portion. Towards the centre, the bundles are comparatively large in size and loosely arranged. Vascular bundles are skull shaped.
Phloem
The phloem in the monocot stem consists of sieve tubes and companion cells. Phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres are absent. It can be distinguished into an outer crushed protophloem and an inner metaphloem.
Xylem
Xylem vessels are arranged in the form of the letter 'Y'. The two metaxylem vessels are located at the upper two arms and one or two protoxylem vessels at the base. In a mature bundle, the lowest protoxylem disintegrates and forms a cavity known as protoxylem lacuna.
Related Topics