Chapter: Anatomy of Flowering Plants: An Introduction to Structure and Development : Stem
Primary Vascular System
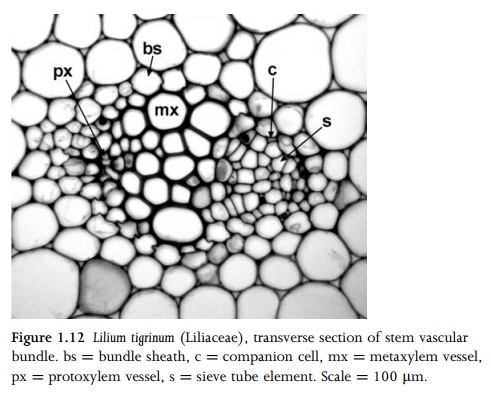
Primary Vascular System
The
primary vascular system is mostly derived from the pro-cambium near the shoot
apex. Primary vascular bundles possess both xylem and phloem, arranged either
adjacent to each other (in collateral vascular bundles: Fig. 1.12), or with
strands of phloem on both sides of the xylem (bicollateral vascular bundles),
or with xylem surrounding the phloem (amphivasal vascular bundles). In woody
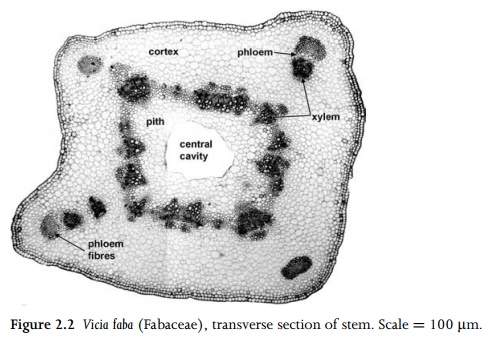
angiosperms, internodal stem vasculature is typically arranged either in a
continuous cylinder, or in a cylinder of separate or fused collateral bundles,
with the phloem external to the xylem (Fig. 2.2). In some stems the bundles may
be bicollateral; for example in species of Cucurbita internal phloem is present
in addition to the external phloem. The vascular cambium, which produces
secondary vascular tissue in woody species, is initially situated between the
xylem and phloem within vascular bundles, but eventually extends between the
vascular bundles to form a complete vascular cylinder. Some stems also possess
cortical or medullary (pith) bundles, which can be associated with leaf
vasculature.
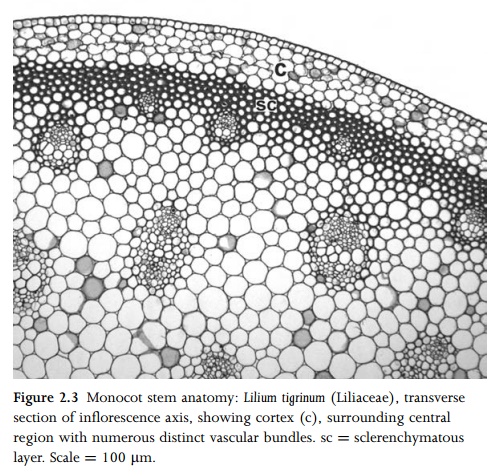
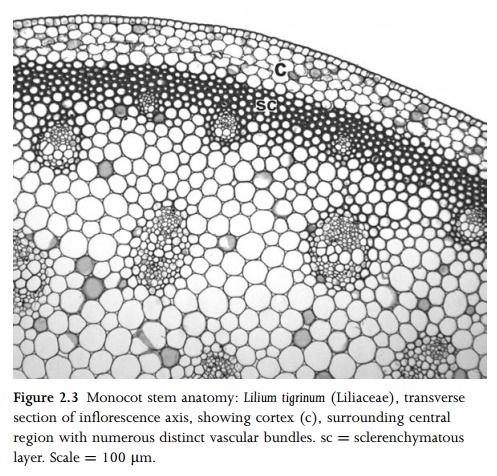
In monocots, which lack a vascular cambium, the stem vascu-lar bundles are typically scattered throughout the central ground tissue (Fig. 2.3), or sometimes arranged in two or more distinct rings. Vascular bundles may be collateral, bicollateral or amphi-vasal. Cortex and pith are frequently indistinct from each other, though the cortex may be defined by an endodermoid layer, or a distinct ring of vascular bundles, or in some stems, particularly inflorescence axes, by a cylinder of sclerenchyma that encloses the majority of vascular bundles. The monocot vascular system is often extremely complex. Each major bundle, when traced on an upward course from any point in the stem, branches or forms bridges with other bundles at several points before passing into a leaf. One of its major branches then continues a similar upward course towards the apex. Some palms possess literally thousands of vascular bundles in a single transverse section of the stem, though in most other monocots the number is much smaller.
Related Topics