Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With HIV Infection and AIDS
Prevention of HIV Infection
Prevention
of HIV Infection
Until an effective vaccine is developed,
preventing HIV by elim-inating or reducing risk behaviors is essential. Primary
prevention efforts through effective educational programs are vital for
con-trol and prevention. HIV is not transmitted by casual contact.
PREVENTIVE EDUCATION
Effective educational programs have been
initiated to educate the public regarding safer sexual practices to decrease
the risk of trans-mitting HIV-1 infection to sexual partners (Chart 52-2).
Latex condoms should be used during vaginal or anal intercourse. Non-latex
condoms are available for people with latex allergy. A con-dom should be used
for oral contact with the penis, and dental dams (a piece of latex used by
dentists to isolate a tooth for treat-ment) should be used for oral contact
with the vagina or rectum. As a result of a clinical trial that found that
female sex workers who used a nonoxynol-9 (N-9) gel intravaginally in addition
to condoms were 50% more likely to be infected with HIV than those who did not
use N-9 gel, the CDC issued the recommen-dation that intravaginal application
of N-9 should no longer be recommended as an effective means of HIV prevention
(AIDS Institute, 9/21/00).
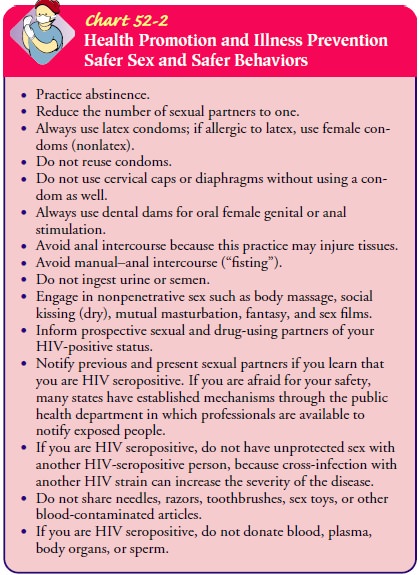
Other topics important in preventive
education include the importance of avoiding sexual practices that might cut or
tear the lining of the rectum, penis, or vagina and avoiding sexual contact
with multiple partners or people who are known to be HIV positive or injection
drug users. In addition, people who are HIV positive or use injection drugs
should be instructed not to donate blood or share drug equipment with others.
Increas-ingly, needle exchange programs are available to enable injec-tion drug
users to obtain sterile drug equipment at no cost. Extensive research has
demonstrated that needle exchange pro-grams do not promote increased drug use;
on the contrary, they have been found to decrease the incidence of blood-borne
in-fections in persons who use injection drugs (Trzcianowska &Mortensen,
2001). In the absence of needle exchange programs, injection drug users should
be instructed on methods to clean their syringes and to avoid sharing cotton
and other drug use equipment.
RELATED REPRODUCTIVE EDUCATION
Because HIV infection in women usually occurs during the child-bearing years, family planning issues need to be addressed. At-tempts to achieve pregnancy by couples in which one partner has HIV and the other does not expose the unaffected partner to the virus.
Efforts at artificial insemination
using processed semen from an HIV-infected partner are underway. Studies are
needed because HIV has been found in the spermatozoa of patients with AIDS,
with possible HIV replication in the male germ cell. Women con-sidering
pregnancy need to have adequate information about the risks of transmitting HIV
infection to themselves, their partner, and their future children and about the
benefits of antiretroviral agents in reducing perinatal HIV transmission. Other
than ab-stinence, the condom has been the only method that has proved to
decrease the risk of sexual transmission of HIV infection.
Certain contraceptive methods may pose
additional health risks for women. Estrogen in oral contraceptives may increase
a women’s risk for HIV infection. In addition, women infected with HIV who use
estrogen oral contraceptives have shown increased shedding of HIV in vaginal
and cervical secretions. The intra-uterine contraceptive device (IUD) may also
increase the risk for HIV transmission because the device’s string may serve as
a means to transmit HIV infection. It also can cause penile abrasions. The
female condom is as effective in preventing pregnancy as other bar-rier
methods, such as the diaphragm and the male condom. Unlike the diaphragm, the
female condom is also effective in preventing the transmission of HIV infection
and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). The female condom has the distinction
of being the first barrier method that can be controlled by women.
Related Topics