History - Prehistory: From Australopithecus through Homo erectus to Homo sapiens | 9th Social Science : History : Evolution of Humans and Society - Prehistoric Period
Chapter: 9th Social Science : History : Evolution of Humans and Society - Prehistoric Period
Prehistory: From Australopithecus through Homo erectus to Homo sapiens
Prehistory: From Australopithecus through Homo erectus to Homo sapiens
The introduction of writing system is a hallmark of
the human civilisation. The period before the introduction of writing is called
prehistory.
Prehistoric societies are treated as pre-literate. But pre-literate should not
be taken to mean primitive. The prehistoric people developed language, made
beautiful paintings and artefacts, and they were highly skilful.
Who are we? What is the name of our species?
We are Homo sapiens sapiens
Human Evolution and Migration
The chimpanzee, gorillas and orangutans, along with
humans, are collectively called the Great Apes. Among them, the chimpanzee is
genetically the closest to humans.
The ancestors to humans were called Hominins, and
their origins have been traced to Africa. They evolved from those origins and
then began to move to other parts of the world in due course of time. The Hominins emerged around 7 to 5 million
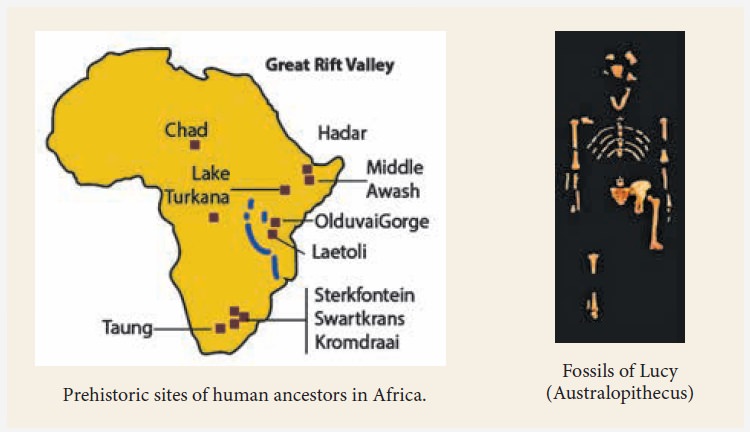
years ago. Skeletons of Australopithecus,
one of the early species of this
tribe, have been found in Africa.
The Great Rift Valley in Africa has many sites that
have evidence for the prehistoric period.
The Great Rift Valley is a valley-like formation
that runs for about 6,400 km from the northern part of Syria to Central
Mozambique in East Africa. This geographical feature is visible even from the
space, and many prehistoric sites are found in eastern Africa.
Human ancestors are divided into various species
according to their physical features.
Hominid refers to all the species of the modern and extinct
great apes, which also includes humans.
Hominins (a zoological tribe) refers to the close relatives of human ancestors and their sister species including Homo sapiens (the modern humans) and the extinct members of Homo neanderthalensis, Homo erectus, Homo habilis and various species of Australopithecines. Humans are the only living species of this ‘tribe’. They stand erect, walk with two legs and have large brains. They can use tools and a few of them can communicate. It excludes the gorillas.
Homo habilis
(handy
human) was the earliest known human
ancestors to make tools in Africa about 2.6 million years ago. Around 2 million
years ago, the species of Homo
erectus/ergaster emerged. This species made hand axes between 2 and 1
million years ago. They began to spread into various parts of Asia and Africa
in time.
Anatomically, modern humans, called Homo sapiens (wise man), first appeared
around 3,00,000 years ago in Africa. It is believed that these modern humans
eventually migrated and dispersed into various parts of the world from around
60,000 years ago.
Prehistoric Cultures
While the fossil bones are classified as various
species such as Homo habilis, Homo erectus and Neanderthalensis, based on
the lithic tools, cultures are assigned names such as Earliest Lithic
Assemblages, Oldowan Technology, Lower, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic and
Mesolithic cultures.
Earliest Lithic Assemblages of Human Ancestors
The earliest tools made by human ancestors are
found in Lomekwi in Kenya. They are dated to 3.3 million years. Oldowan tools
occur in the Olduvai Gorge in Africa. They are 2 to 2.6 million years old. The
human ancestors (Australopithecines)
used hammer stones and produced sharp-edged flakes. The tools were used for
cutting, slicing and processing food.

Lower Palaeolithic Culture
The Lower Palaeolithic Culture is marked by the
human ancestors belonging to the species Homo
habilis and Homo erectus. The human ancestors flaked
large stone blocks and designed
various tools including hand axes. These tools, which

are found in Africa, Asia, and Europe, are dated
the earliest to about 1.8 million years ago. They made various tools such as
hand axes and cleavers to meet their subsistence needs. These tools are also
known as bifaces. These tools have physical symmetry and convey the humans’
cognitive (perception) skills. This culture is called the Lower Palaeolithic
Culture. The hand axe tools are also known as Acheulian. This tool-making
tradition continued till 250,000 years to 60,000 years ago in India.
Acheulian – They were first hand axes recognized at a place
called St. Acheul in France. Hence they are called Acheulian tools.
Bifaces are tools that have flaking on both sides (bi = two, face
= side).
Subsistence necessities of prehistoric humans were mainly
food and water.
The human ancestors perhaps did not possess complex
language skills we have now. They might have voiced a few sounds or words and
possibly used sign language. They were intelligent enough to select stones as
raw material and used the hammer stones
to carefully flake the rocks and design tools for their needs. They hunted
animals, fed on the meat of the animals killed by predators and gathered plant
foods such as roots, nuts and fruits. In India, the Acheulian tools have been
found near Chennai and many other sites such as Isampur in Karnataka and
Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh.
Raw material is the naturally available stone block
or pebbles selected by humans for making tools. Since these stones produced
flakes with sharp edges, they were selected for making stone tools.
Core is the main block of stone from which small chips are
flaked by using a hammer stone.
Flake is a small chip removed from a large stone block called
the core.
Middle Palaeolithic Culture
After about 398000 years BCE, further changes took
place in the lithic technology in Africa. The Homo erectus species existed during this period. Anatomically
modern humans are said to have emerged around 3 lakh years ago.

Lithic Technology: ‘Lith’ means stone. The methods and
techniques involved in the production of stone tools are called lithic
technology.
The hand axes turned out to be much attractive in
design and many smaller tools were also produced. The core was prepared and
then tools were made. Points and scrapers were used. Short blades were also
produced. The lithic tool-making tradition of the Levalloisian belonged to this
period. The tools made during this time are found in Europe and Central and
western Asia.
Levalloisian tools are the
implements made after preparing the core. It was named after the town of
Levallois in France.
The Middle Palaeolithic Culture appeared between
3,85,000 and 1,98,000 years BCE ago in Europe and parts of western and South
Asia. The tools that were made during this period were in use till about 28,000
BCE.
The people of this period were called Neanderthals.
They buried the dead people systematically. Perhaps they were the first human
ancestors to mourn death properly and bury the dead.
Upper Palaeolithic Culture
The cultural phase that succeeded the Middle
Palaeolithic is called the Upper Palaeolithic phase. This period was marked by
innovation in tool technology. Long blades and burins were produced during this
time. People used different varieties of silica-rich raw materials in this
phase. Numerous paintings and art objects were made. The diversity of artefacts
suggests the improvement in cognitive skills and the development of languages.
Microliths appeared in this phase.
Burin is a stone-made chisel with a sharp cutting edge.
The modern humans, who first appeared as a result
of human evolution in the sub-Saharan Africa 300,000 years ago, began to move
to various parts of Asia around 60,000 years ago. They probably replaced the
earlier populations. In Europe, humans known as Cro-Magnons lived in this
period.
Horns and ivory were used for making tools and art
works. Bone needles, fishhooks, harpoons and spears were also employed
creatively. The humans of this time wore clothes and cooked food. The dead were
placed in the burials with folded hands placed over their chest. Pendants and
richly carved tools were also seen in use. Evidences from paintings, clay model
sculptures and carvings are available. Images on stone and bone called Venus
Statues were produced in Europe and in some parts of Asia.
The Upper Palaeolithic Culture appeared about
60,000 years ago. It continued till about the beginning of the Holocene about
12,000 years ago, when the Ice Age ended. Some of the rock paintings of India
are also dated to this period.

Ice Age – the period before 8,000 BCE when many parts of
the world remained covered by ice sheets and snow.
Mesolithic Culture
Mesolithic period is known as the Middle Stone Age,
as it is placed between the Palaeolithic and Neolithic periods. People mainly
used microlithic (small stone) tools during this period. These people were
hunter-gatherers. With the global warming occurring after the Ice Age, they
became highly mobile and occupied various eco-zones.
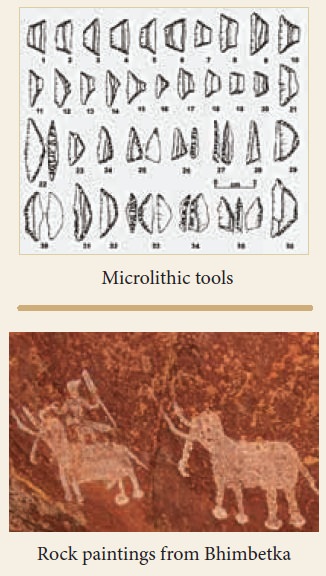
People of Mesolithic period widely employed
microlithic technology. They made tiny artefacts that were less than 5 cm in
size. They produced points, scrapers and arrowheads. They also used geometric
tools such as lunates, triangles and trapezes. These tools were hafted onto
wooden or bone handles and used.
Microliths are stone artefacts of small size.
The dating of the Mesolithic Culture varies across
different parts of the world. It was pre-agricultural in certain areas. In
northwest Europe, the people of this culture appeared between 8,000 and 3,000
years ago. In India, Mesolithic
Culture emerged around 10,000 BCE and in Tamil Nadu
it continued up to 1000 BCE, till the beginning of the Iron Age. Some of the
rock paintings of India date to the Mesolithic Period.
Neolithic Culture and the Beginning of Agriculture
The period called Neolithic marks the beginning of
agriculture and animal domestication. It is an important phase in history.
Early evidence of the Neolithic period is found in the fertile crescent region
of Egypt and Mesopotamia, the Indus region, the Gangetic valley and in China.
By about 10,000 BCE to 5000 BCE, agriculture had come to be practised in these
regions.
Fertile Crescent Region refers to the area covering Egypt,
Israel- Palestine, and Iraq, which is in the shape of crescent moon.
Neolithic Age is called the ‘new age’, because of
the new grinding and polishing techniques used for the tools. The Neolithic
people also used the flaked stone tools. Until the Mesolithic period, people
mainly hunted and gathered food for their subsistence. By hunting and gathering
people obtained very limited food as a result of which only a small number of
people could exist in a particular region.
The introduction of domestication of animals and
cultivating plants at home led to production and supply of large quantities of
grains and animal food. The fertile soil deposited by the river on its banks helped
the growth of agriculture. People preferred to live on river banks as it was
better for adaptation. As a result of domestication and cultivating plants,
there was an excess food production. The surplus food production was a main
factor for the development of early civilisations. Permanent residences were
built and large villages emerged as a result. Hence, the development of this
period is called Neolithic Revolution.

Related Topics