Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Individual and Family Considerations Related to Illness
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
In medical-surgical settings, especially in emergency depart-ments, burn units, and rehabilitation centers, nurses care for ex-tremely anxious patients who have experienced devastating events that are typically considered to be outside the realm of normal human experience. Many of these patients suffer from posttrau-matic stress disorder (PTSD).
PTSD has been described as a condition that generates
waves of anxiety, anger, aggression, de-pression, and suspicion that threaten
the person’s sense of self and interfere with daily functioning. Specific
examples of events that place a person at risk for PTSD are rape, family
violence, torture, terrorism, fire, earthquake, and military combat. Patients
who have suffered a traumatic event are often frequent users of the health care
system by virtue of their extensive injuries, the vari-ous treatment modalities
that they require, and the overall emo-tional and physical difficulties
experienced.
The physiologic
responses noted in people who have been se-verely traumatized include increased
activity of the sympathetic nervous system, increased plasma catecholamine
levels, and in-creased urinary epinephrine and norepinephrine levels. It has
been postulated (Gelles, 1997; Gelles & Loseke, 1993) that peo-ple with
PTSD lose the ability to control their response to stim-uli. The resulting
excessive arousal can increase overall body metabolism and trigger emotional
reactivity. In this situation, the nurse would observe that the patient has
difficulty sleeping, has an exaggerated startle response, and is excessively
vigilant.
Older people are more
susceptible to the physical effects of trauma and the effects of PTSD because
of the increased neural inactivation associated with aging. It has also been
speculated that when people have a preexisting tendency to become ex-tremely
anxious, their vulnerability to PTSD increases (Nursing Research Profile 7-2).
Symptoms of PTSD can
occur hours to years after the trauma is experienced. Acute PTSD is defined as
the experience of symp-toms for less than a 3-month period. Chronic PTSD is
defined as the experience of symptoms lasting longer than 3 months. In the case
of delayed PTSD, up to 6 months may elapse between the trauma and the
manifestation of symptoms (American Psychi-atric Association, 2000). For more
information see Chart 7-9.
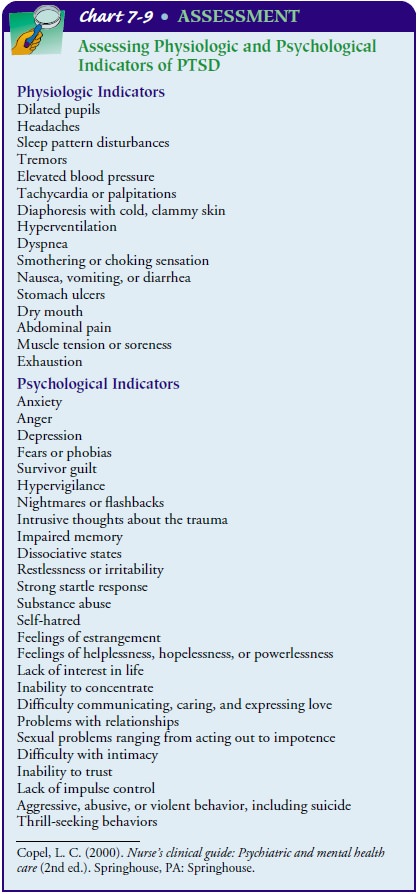
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
It is often thought that
the incidence of PTSD is very low in the overall population; when high-risk
groups are studied, however, the results indicate that more than 50% of study
participants have PTSD (McCann & Pearlman, 1990). Therefore, it is
important that nurses consider which of their patients are at risk for PTSD and
be knowledgeable about the common symptoms associated with it.
The sensitivity and
caring of the nurse creates the inter-personal relationship necessary to work
with patients who have PTSD. These patients are physically compromised and are
strug-gling emotionally with situations that are outside the realm of normal
human experience–situations that violate the commonly held perceptions of human
social justice. Treatment of patients with PTSD includes several essential
components: establishing a trusting relationship, addressing and working
through the trauma experience, and providing education about the coping skills
needed for recovery and self-care. The patient’s progress can be influenced by
the ability to cope with the various aspects of both the physical and the
emotional distress.
Related Topics