Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering materials and metallurgy : Non-Metallic Materials
Polymer Structure
POLYMER STRUCTURE
Polymer
Polymer is a substance (natural or synthetic),
molecules of which consist of numerous small repeated chemical units (monomers) linked to each other in a
regular pattern. Polymers usually combine crystalline and amorphous structures
(semi-crystalline).
Degree of
polymerization
Degree of
polymerization is an average number of monomers (mers) in a polymer molecule.
Polymer molecules may combine up to million of monomers (mers) forming a
one-dimensional structure (chain), two-dimensional structure (planar molecules)
or threedimensional structure.
One-dimensional
structure is common for organic polymers.
Organic polymer
Organic polymer is a polymer compound built of
hydrocarbon base monomer units. Besides carbon and Hydrogen the following atoms
may be incorporated in polymer molecules: Oxygen, Nitrogen, chorine, fluorine,
silicon, phosphorous, and sulfur. Atoms of a polymer molecule are held by
covalent bonding.
Neighboring chains may form secondary bonds between
them (cross-links) which are less strong than covalent bonding between the
atoms within the molecules.
Cross-links provide elasticity to the polymer,
preventing sliding of the neighboring chains when the material is stretched.
Branched polymer
Branched polymer consists of molecules having side
chains (branches) attached to the main chain.
Copolymer
Copolymer is a polymer molecule of which contains
more than one kind of monomers. Nylon is a common copolymer. Its molecules
consist of two alternating monomers: diacid and diamine.
Graft copolymer
Graft copolymer is a kind of branch polymer, side
chains of which are made of monomers differing from the monomer of the main
chain.
Block copolymer
Block copolymer is a polymer molecules of which
built from alternating polymeric blocks of two or more different polymers.
Structure parameters
affecting polymer properties:
Increase
of the chain length.
Effect: increase of tensile
strength and Modulus of Elasticity (stiffness).
Increase
of number and length of side chains.
Effect: increase of tensile
strength and stiffness.
Introduction
of large monomers in molecules.
Effect: increase of stiffness.
Increase
of number and strength of cross-links.
Effect: increase of tensile
strength and stiffness.
Orientation
of the molecules as a result of deformation during manufacturing.
Effect: Anisotropy of the
material properties (properties along the deformation differ from those in
other directions). Every polymer is characterized by a temperature below of
which mobility of its molecules sharply decreases and the material becomes
brittle and glassy.
This
temperature is called Glass Transition
Temperature.
Monomer
molecular structures of different polymers are presented in the picture:
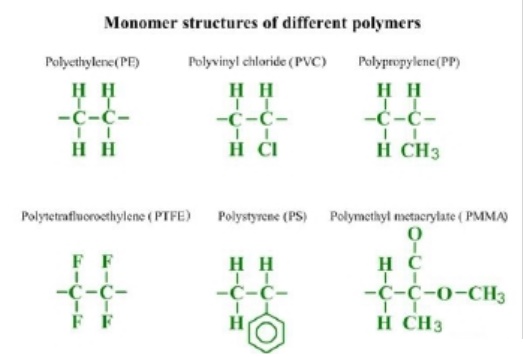
Elastomers
Elastomers are polymers possessing high elasticity
- may be reversibly stretched at high degree. Elastomers consists of long
lightly cross-linked molecules.
Common elastomers are:
Polyisoprene (natural rubber) Butyl
Nitrile
Neoprene
Ethylene-Propylene
Hypalon
Silicone
Elastomers may be strengthened by vulcanization process (heat treatment
in presence of chemical agents). Vulcanization results in increase of
cross-linking of the molecules. Vulcanized elastomers are elastic for small
deformations.
Vulcanization produces cross-links which make
impossible shaping material. Therefore most of elastomers are shaped before
cross-linking. However there are some elastomer materials which are not
cross-linked when heated. These astomers may be reversibly remolded by heating
many times (like Thermoplastics).
Such kind
of elastomers is called Thermoplastic
Elastomers.
Thermoplastic
elastomers are manufactured by copolymerization of two or more monomers forming
block polymers or graft polymers.
Common thermoplastic elastomers
are:
Polyurethanes
Polyester
Copolymers Styrene-Butadiene
Properties and applications of some
elastomers
Elastomer
Polyisoprene (natural rubber) Elastomer Butyl (Isobutene-Isoprene) Elastomer
Nitrile
Elastomer
Neoprene (Chloroprene)
Elastomer
Ethylene-Propylene (EPDM)
Elastomer Hypalon (CSM, Chlor-Sulfonated
Polyethylene) Elastomer Silicone
Thermoplastic
elastomer Polyurethane
Thermoplastic
elastomer Styrene-Butadiene Thermoplastic elastomer Polyester Copolymer
Related Topics